Use the diagram to match the letter (A-C) to the correct term(1
... 4. ______ Complementary base pair. 5. ______ Hydrogen bond. 6. ______ Individual nitrogen base. 7. ______ Sugar-phosphate backbone. 8. In DNA, which of the following determines the traits of an organism? a. Amount of adenine b. Number of sugars c. Sequence of nitrogen bases d. Strength of hydrogen b ...
... 4. ______ Complementary base pair. 5. ______ Hydrogen bond. 6. ______ Individual nitrogen base. 7. ______ Sugar-phosphate backbone. 8. In DNA, which of the following determines the traits of an organism? a. Amount of adenine b. Number of sugars c. Sequence of nitrogen bases d. Strength of hydrogen b ...
Genetic Engineering - Duplin County Schools
... • Continued breeding of individuals with similar characteristics • Useful in retaining a certain set of characteristics • Can produce some serious genetic defects ...
... • Continued breeding of individuals with similar characteristics • Useful in retaining a certain set of characteristics • Can produce some serious genetic defects ...
a10c Biotechnology
... 2. What is a restriction enzyme, and what does it catalyze? How do restriction enzymes differ in what they cleave? What do they "look for"? Name an example of a restriction enzyme. 3. Describe the steps of cloning (transferring a gene to bacteria for purposes of "growing" DNA or protein). What enzym ...
... 2. What is a restriction enzyme, and what does it catalyze? How do restriction enzymes differ in what they cleave? What do they "look for"? Name an example of a restriction enzyme. 3. Describe the steps of cloning (transferring a gene to bacteria for purposes of "growing" DNA or protein). What enzym ...
Figure 2 Representation of the steps required for DNA sequence
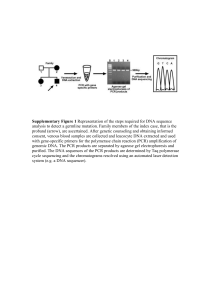
... Supplementary Figure 1 Representation of the steps required for DNA sequence analysis to detect a germline mutation. Family members of the index case, that is the proband (arrow), are ascertained. After genetic counseling and obtaining informed consent, venous blood samples are collected and leucocy ...
... Supplementary Figure 1 Representation of the steps required for DNA sequence analysis to detect a germline mutation. Family members of the index case, that is the proband (arrow), are ascertained. After genetic counseling and obtaining informed consent, venous blood samples are collected and leucocy ...
Game 2
... and all of the offspring are oval. If 2 oval watermelons are crossed, what is the percent of watermelons that will be round? ...
... and all of the offspring are oval. If 2 oval watermelons are crossed, what is the percent of watermelons that will be round? ...
1406 final exam guide.doc
... The chromosomal basis of sex varies with the organism (human, grasshopper, chicken and bees) ex. XY, XO, ZW Sex linked genes are more likely to be inherited by males or females What is Duchenne muscular dystrophy What is a linked gene What is Nondisjunction, at what stage of meiosis does this occurs ...
... The chromosomal basis of sex varies with the organism (human, grasshopper, chicken and bees) ex. XY, XO, ZW Sex linked genes are more likely to be inherited by males or females What is Duchenne muscular dystrophy What is a linked gene What is Nondisjunction, at what stage of meiosis does this occurs ...
DNA the Molecule of molecules - Foothill Technology High
... b. In human cells, it takes only a few hours to copy the 6 billion bases. 2. Accurate Only about 1 in a billion base pairs is incorrectly paired. ...
... b. In human cells, it takes only a few hours to copy the 6 billion bases. 2. Accurate Only about 1 in a billion base pairs is incorrectly paired. ...
DNA and Chromosomes
... What is the relationship between DNA, chromosomes, and any organism? Drag and drop the descriptive phrase to the correct column, thereby helping us to describe the relationships between these important components of inheritance. ...
... What is the relationship between DNA, chromosomes, and any organism? Drag and drop the descriptive phrase to the correct column, thereby helping us to describe the relationships between these important components of inheritance. ...
Genetic Engineering Short Notes
... 1. Genetic engineering- remaking genes for practical purposes 2. Recombinant DNA- DNA made from two or more different organisms 3. Restriction enzyme- enzymes that recognize short specific DNA sequences and that cut the DNA there 4. Plasmid- small, circular DNA molecules that can replicate independa ...
... 1. Genetic engineering- remaking genes for practical purposes 2. Recombinant DNA- DNA made from two or more different organisms 3. Restriction enzyme- enzymes that recognize short specific DNA sequences and that cut the DNA there 4. Plasmid- small, circular DNA molecules that can replicate independa ...
the element makes na RNA copy of itself which is reversed
... • Breakage and joining also directed by enzymes. • Homologous recombination occurs during synapsis in meiosis I, general recombination in bacteria, and viral genetic exchange. • Molecular mechanism proposed by Holliday and Whitehouse (1964). • Depends on complementary base pairing. ...
... • Breakage and joining also directed by enzymes. • Homologous recombination occurs during synapsis in meiosis I, general recombination in bacteria, and viral genetic exchange. • Molecular mechanism proposed by Holliday and Whitehouse (1964). • Depends on complementary base pairing. ...
Cre-Lox recombination

In the field of genetics, Cre-Lox recombination is known as a site-specific recombinase technology, and is widely used to carry out deletions, insertions, translocations and inversions at specific sites in the DNA of cells. It allows the DNA modification to be targeted to a specific cell type or be triggered by a specific external stimulus. It is implemented both in eukaryotic and prokaryotic systems.The system consists of a single enzyme, Cre recombinase, that recombines a pair of short target sequences called the Lox sequences. This system can be implemented without inserting any extra supporting proteins or sequences. The Cre enzyme and the original Lox site called the LoxP sequence are derived from bacteriophage P1.Placing Lox sequences appropriately allows genes to be activated, repressed, or exchanged for other genes. At a DNA level many types of manipulations can be carried out. The activity of the Cre enzyme can be controlled so that it is expressed in a particular cell type or triggered by an external stimulus like a chemical signal or a heat shock. These targeted DNA changes are useful in cell lineage tracing and when mutants are lethal if expressed globally.The Cre-Lox system is very similar in action and in usage to the FLP-FRT recombination system.