1 - life.illinois.edu
... c. genes encoding proteins allowing for conjugation between different bacteria. d. genes encoding proteins from humans. 32. A cDNA clone would contain only the __________ of a protein-coding gene. a. exons b. introns c. promoter d. spacer 33. Short tandem repeats (microsatellites) in our genome are ...
... c. genes encoding proteins allowing for conjugation between different bacteria. d. genes encoding proteins from humans. 32. A cDNA clone would contain only the __________ of a protein-coding gene. a. exons b. introns c. promoter d. spacer 33. Short tandem repeats (microsatellites) in our genome are ...
DNA mismatch-specific targeting and hypersensitivity of mismatch
... application of bulky rhodium intercalators to inhibit cellular proliferation differentially in MMR-deficient cells compared with cells that are MMR-proficient. Preferential inhibition by the rhodium complexes associated with MMR deficiency is seen both in a human colon cancer cell line and in normal ...
... application of bulky rhodium intercalators to inhibit cellular proliferation differentially in MMR-deficient cells compared with cells that are MMR-proficient. Preferential inhibition by the rhodium complexes associated with MMR deficiency is seen both in a human colon cancer cell line and in normal ...
Name___________________________ Date_________________ Period_____
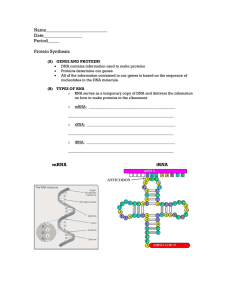
... Protein Synthesis (A) GENES AND PROTEINS DNA contains information used to make proteins ...
... Protein Synthesis (A) GENES AND PROTEINS DNA contains information used to make proteins ...
Human Genome
... plasmid with two different restriction endonucleases, even though he was using the enzymes in good condition and the plasmid had sites for both. ...
... plasmid with two different restriction endonucleases, even though he was using the enzymes in good condition and the plasmid had sites for both. ...
Bacteria cells reproduce differently from other single celled
... There are ___________essential amino acids? ...
... There are ___________essential amino acids? ...
Notes
... • How large quantities of recombinant DNA is made: • Requires a carrier, or vector, such as viruses and plasmids (small, circular, double-stranded DNA molecules that occur naturally in bacteria and yeast cells) • Plasmid and DNA fragment can be joined to make recombinant DNA • Vector transfers the ...
... • How large quantities of recombinant DNA is made: • Requires a carrier, or vector, such as viruses and plasmids (small, circular, double-stranded DNA molecules that occur naturally in bacteria and yeast cells) • Plasmid and DNA fragment can be joined to make recombinant DNA • Vector transfers the ...
Chapter 16 - drtracey.net
... clones with DNA fragment of interest identified from clone library preliminary screening - eliminate any clones without a vector and clones with vectors that do not contain DNA employ vector with gene for antibiotic resistance and lac Z’ gene expose to growth medium ...
... clones with DNA fragment of interest identified from clone library preliminary screening - eliminate any clones without a vector and clones with vectors that do not contain DNA employ vector with gene for antibiotic resistance and lac Z’ gene expose to growth medium ...
Lecture #9 Date - Biology Junction
... Biotechnology: manipulation of organisms or their components to perform practical tasks or provide useful products ...
... Biotechnology: manipulation of organisms or their components to perform practical tasks or provide useful products ...
Biochemistry and the Genomic Revolution
... • Based upon changing electronic charge distribution around atoms • Asymmetry of charge of one atom induces complementary asymmetry in neighboring atoms ...
... • Based upon changing electronic charge distribution around atoms • Asymmetry of charge of one atom induces complementary asymmetry in neighboring atoms ...
Chapter 9 answers
... contain all instructions, but most cells don’t need but a certain selection of the instructions. For instance a cell near your ear does not need to make the molecules that help your stomach with digestion. It would be terribly wasteful in terms of space, energy, and materials. That is why most genes ...
... contain all instructions, but most cells don’t need but a certain selection of the instructions. For instance a cell near your ear does not need to make the molecules that help your stomach with digestion. It would be terribly wasteful in terms of space, energy, and materials. That is why most genes ...
Cell wall
... Chloroplasts: green organelles that make food, found only in green plant cells Convert energy of light into chemical energy ...
... Chloroplasts: green organelles that make food, found only in green plant cells Convert energy of light into chemical energy ...
Handout on the Central Dogma
... and has its associated amino acid attached to the opposite end. A given codon (virtually) always associates with the same amino acid -- across all species. Generally a cell must have at least 30 of these tRNA molecules to make its proteins; each one must have the genes to build itself as part of the ...
... and has its associated amino acid attached to the opposite end. A given codon (virtually) always associates with the same amino acid -- across all species. Generally a cell must have at least 30 of these tRNA molecules to make its proteins; each one must have the genes to build itself as part of the ...
Team Publications
... Missense variants in the BRCA2 gene are routinely detected during clinical screening for pathogenic mutations in patients with a family history of breast and ovarian cancer. These subtle changes frequently remain of unknown clinical significance because of the lack of genetic information that may hel ...
... Missense variants in the BRCA2 gene are routinely detected during clinical screening for pathogenic mutations in patients with a family history of breast and ovarian cancer. These subtle changes frequently remain of unknown clinical significance because of the lack of genetic information that may hel ...
PGM Quizzes
... Name any two of the 3 sequence features that expression plasmids and basic cloning plasmids have in common. Ori, DrugR gene, cloning site What is the most important difference between an expression plasmid and a basic cloning plasmid? Expression plasmid is used to express a protein from an expressio ...
... Name any two of the 3 sequence features that expression plasmids and basic cloning plasmids have in common. Ori, DrugR gene, cloning site What is the most important difference between an expression plasmid and a basic cloning plasmid? Expression plasmid is used to express a protein from an expressio ...
Repressor - (www.ramsey.k12.nj.us).
... By inserting the nucleus of a fertilized egg into a bacterial cell. b. By fertilizing an egg with sperm from a different species. c. By injecting the desired set of genes into the fertilized egg. d. By injecting the desired set of genes into the unfertilized egg. e. By replacing the nucleus of the u ...
... By inserting the nucleus of a fertilized egg into a bacterial cell. b. By fertilizing an egg with sperm from a different species. c. By injecting the desired set of genes into the fertilized egg. d. By injecting the desired set of genes into the unfertilized egg. e. By replacing the nucleus of the u ...
FinalExamStudyGuideSemester1
... 2) There are 20 amino acids but 1,000’s of different proteins. How is this possible? 3) Enzymes are catalysts. What does that mean? 4) What are conditions that can affect enzyme function? 5) How do enzymes and substrates work together in a lock & key fashion? 6) When you heat an egg it changes color ...
... 2) There are 20 amino acids but 1,000’s of different proteins. How is this possible? 3) Enzymes are catalysts. What does that mean? 4) What are conditions that can affect enzyme function? 5) How do enzymes and substrates work together in a lock & key fashion? 6) When you heat an egg it changes color ...
Key
... c. equally long d. non-existent e. 20-times longer 8. To date, the type of enzyme used in the PCR reaction is: a. DNA polymerase I b. Klenow fragment c. a heat-stable DNA polymerase d. DNA ligase e. topoisomerase 9. Which of the following methods is used for assigning loci to specific chromosomes bu ...
... c. equally long d. non-existent e. 20-times longer 8. To date, the type of enzyme used in the PCR reaction is: a. DNA polymerase I b. Klenow fragment c. a heat-stable DNA polymerase d. DNA ligase e. topoisomerase 9. Which of the following methods is used for assigning loci to specific chromosomes bu ...
Cells - Salisbury University
... 2. A complementary strand is formed along each strand of the original molecule. 3. The result is two identical DNA molecules, each with one strand from the original molecule D. very fast, very accurate (ca. 1 mutation per 100 million nucleotides copied) E. involves many enzymes and other proteins F. ...
... 2. A complementary strand is formed along each strand of the original molecule. 3. The result is two identical DNA molecules, each with one strand from the original molecule D. very fast, very accurate (ca. 1 mutation per 100 million nucleotides copied) E. involves many enzymes and other proteins F. ...
pgat biotechnology-2016
... 25. The roots of a plant are converted into drug-producing structures in a process called A. microcosm establishment B. mibridization ...
... 25. The roots of a plant are converted into drug-producing structures in a process called A. microcosm establishment B. mibridization ...
Old exam 2 from 2002
... observation of their pollen mother cells showed no chromosome pairing (no bivalents, only univalents). A section from one of the hybrids that grew vigorously was propagated vegetatively, producing a plant with 36 chromosomes in its somatic cells. This plant was fertile, and produced large, showy flo ...
... observation of their pollen mother cells showed no chromosome pairing (no bivalents, only univalents). A section from one of the hybrids that grew vigorously was propagated vegetatively, producing a plant with 36 chromosomes in its somatic cells. This plant was fertile, and produced large, showy flo ...
Genetic engineering and biotechnology
... • ‘scissors’ made from enzymes • Restriction enzymes called endonucleases find and recognize a specific sequence of base pairs along the DNA molecule • Sets of four or six pairs • Gene is cut out and released • Can then be removed from the donor organism • DNA ligase pastes the genes to the sticky e ...
... • ‘scissors’ made from enzymes • Restriction enzymes called endonucleases find and recognize a specific sequence of base pairs along the DNA molecule • Sets of four or six pairs • Gene is cut out and released • Can then be removed from the donor organism • DNA ligase pastes the genes to the sticky e ...
Cloning Using Plasmid Vectors
... restriction enzymes may not digest at ends of DNA molecules) NEB, Stratagene, Fermentas all have online resources to consult ...
... restriction enzymes may not digest at ends of DNA molecules) NEB, Stratagene, Fermentas all have online resources to consult ...
Cre-Lox recombination

In the field of genetics, Cre-Lox recombination is known as a site-specific recombinase technology, and is widely used to carry out deletions, insertions, translocations and inversions at specific sites in the DNA of cells. It allows the DNA modification to be targeted to a specific cell type or be triggered by a specific external stimulus. It is implemented both in eukaryotic and prokaryotic systems.The system consists of a single enzyme, Cre recombinase, that recombines a pair of short target sequences called the Lox sequences. This system can be implemented without inserting any extra supporting proteins or sequences. The Cre enzyme and the original Lox site called the LoxP sequence are derived from bacteriophage P1.Placing Lox sequences appropriately allows genes to be activated, repressed, or exchanged for other genes. At a DNA level many types of manipulations can be carried out. The activity of the Cre enzyme can be controlled so that it is expressed in a particular cell type or triggered by an external stimulus like a chemical signal or a heat shock. These targeted DNA changes are useful in cell lineage tracing and when mutants are lethal if expressed globally.The Cre-Lox system is very similar in action and in usage to the FLP-FRT recombination system.