2015 Test 3 study guide Bio 105
... • What is a clone? How is it done? Why is it done? • What are stem cells? Chapter 6 • 6.1 DNA intro • Structure of nucleotides • Base pair rules • DNA is double helix and each strand is complementary • DNA strands held together by hydrogen bonds • 6.2 DNA replication • Method of duplication is semi- ...
... • What is a clone? How is it done? Why is it done? • What are stem cells? Chapter 6 • 6.1 DNA intro • Structure of nucleotides • Base pair rules • DNA is double helix and each strand is complementary • DNA strands held together by hydrogen bonds • 6.2 DNA replication • Method of duplication is semi- ...
Molecules of Life
... reasons why some people may not have believed the scientists who made the discovery reasons why we are now more certain about the structure of DNA how DNA is linked to the role of ribosomes in the cell ...
... reasons why some people may not have believed the scientists who made the discovery reasons why we are now more certain about the structure of DNA how DNA is linked to the role of ribosomes in the cell ...
Chapter 13 Review answers
... pathogen, stimulate antibody production but will not make you sick Gene Therapy – treat genetic disorders by transferring normal gene into cells that lack them; replacement gene is expressed in person’s cell 98%, therefore 2% codes for proteins Process of altering the genetic material of cells or or ...
... pathogen, stimulate antibody production but will not make you sick Gene Therapy – treat genetic disorders by transferring normal gene into cells that lack them; replacement gene is expressed in person’s cell 98%, therefore 2% codes for proteins Process of altering the genetic material of cells or or ...
交通大學特色研究計畫邀請 - 國立交通大學生物資訊研究所
... Both prokaryotic and eukaryotic chromosomes are organized into many independent topological domains. These topological domains may be formed through constraining each DNA end from rotating by interacting with nuclear proteins, i.e., DNA-binding proteins. However, so far, evidence to support this hyp ...
... Both prokaryotic and eukaryotic chromosomes are organized into many independent topological domains. These topological domains may be formed through constraining each DNA end from rotating by interacting with nuclear proteins, i.e., DNA-binding proteins. However, so far, evidence to support this hyp ...
Hershey & Chase
... protein labeled T2, most of the radioactivity was in the supernatant with viruses. In tubes with E. coli infected with DNA-labeled T2, most of the radioactivity was in the pellet with the bacterial cells. When the bacteria containing DNA-labeled phages were returned to culture medium, the bacteria ...
... protein labeled T2, most of the radioactivity was in the supernatant with viruses. In tubes with E. coli infected with DNA-labeled T2, most of the radioactivity was in the pellet with the bacterial cells. When the bacteria containing DNA-labeled phages were returned to culture medium, the bacteria ...
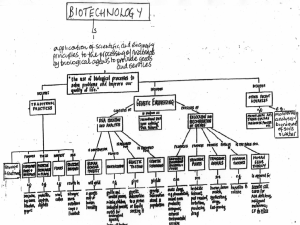
Biotech applic
... destroyed by a virus which causes black marks on the tubers. 3. higher tolerance to herbicides. Example: RoundupTM -tolerant corn, soybeans, and sugar beets, have been created by moving gene for herbicide resistance from a different plant. RoundupTM, a powerful herbicide, can then be used to kill al ...
... destroyed by a virus which causes black marks on the tubers. 3. higher tolerance to herbicides. Example: RoundupTM -tolerant corn, soybeans, and sugar beets, have been created by moving gene for herbicide resistance from a different plant. RoundupTM, a powerful herbicide, can then be used to kill al ...
Mutation identification by whole genome sequencing
... 1) they terminate DNA polymerization because they lack a 3’ –OH 2) each ddNPT (i.e. ddATP, ddCTP, etc.) has its own charateristic fluorphore b. protocol 1) combine DNA plus a short primer sequence that provides a 3’ -OH 2) add Polymerase, dNTPs, a small amount of ddNTPs 3) allow primers to anneal, p ...
... 1) they terminate DNA polymerization because they lack a 3’ –OH 2) each ddNPT (i.e. ddATP, ddCTP, etc.) has its own charateristic fluorphore b. protocol 1) combine DNA plus a short primer sequence that provides a 3’ -OH 2) add Polymerase, dNTPs, a small amount of ddNTPs 3) allow primers to anneal, p ...
I. DNA A. WHAT IS IT?
... • DNA + histones = chromatin • histones + chromatin = nucleosome • nucleosome allow lots of DNA to fit into a tiny space!! • Like a tape measure! ...
... • DNA + histones = chromatin • histones + chromatin = nucleosome • nucleosome allow lots of DNA to fit into a tiny space!! • Like a tape measure! ...
Document
... These are diagrams of specific DNA molecules that show the sites where the restriction enzymes cleave the DNA. To construct a restriction map, purified samples of DNA are treated with restriction enzymes, either alone or in combination, and then the reaction products are separated by agarose gel ele ...
... These are diagrams of specific DNA molecules that show the sites where the restriction enzymes cleave the DNA. To construct a restriction map, purified samples of DNA are treated with restriction enzymes, either alone or in combination, and then the reaction products are separated by agarose gel ele ...
Unit1-Probesweb
... Microarrays can be used to study the expression of genes and compare patterns between healthy and unhealthy cells. It is the mRNA from cells which is used to form labelled probes (after it has been copied into single stranded DNA). ...
... Microarrays can be used to study the expression of genes and compare patterns between healthy and unhealthy cells. It is the mRNA from cells which is used to form labelled probes (after it has been copied into single stranded DNA). ...
Powerpoint - rlsmart.net
... sections of chromosomes (or the whole thing) -Ex: Down’s syndrome, Turner’s syndrome ...
... sections of chromosomes (or the whole thing) -Ex: Down’s syndrome, Turner’s syndrome ...
What is Genetic Engineering?
... enzymes. Each different type of restriction enzyme "seeks out" and cuts DNA at a spot marked by a different sequence of base pairs. One restriction enzyme may cut the DNA at every "AATC", for example, while another cuts all "ATG" sequences. The DNA is cut in such a way that one helix is a bit longer ...
... enzymes. Each different type of restriction enzyme "seeks out" and cuts DNA at a spot marked by a different sequence of base pairs. One restriction enzyme may cut the DNA at every "AATC", for example, while another cuts all "ATG" sequences. The DNA is cut in such a way that one helix is a bit longer ...
Biotechnology Pre/PostTest Key (w/citations)
... A. They can produce their own pesticides B. They can grow larger than unmodified crops C. They cannot cause an allergic reaction D. They can contain extra nutrients Florida EOC Coach Jumpstart _____12) Consider the following statements about genetic engineering: I.A. B. II. C. D. ...
... A. They can produce their own pesticides B. They can grow larger than unmodified crops C. They cannot cause an allergic reaction D. They can contain extra nutrients Florida EOC Coach Jumpstart _____12) Consider the following statements about genetic engineering: I.A. B. II. C. D. ...
Virus -Consists or a nucleic acid surrounded by a protein coat
... replicated along with the host cell’s genome -The viral DNA is known as a prophage -Under certain conditions the prophage will enter into the lytic cycle ...
... replicated along with the host cell’s genome -The viral DNA is known as a prophage -Under certain conditions the prophage will enter into the lytic cycle ...
DNA: The Hereditary Material
... He used pus cells to investigate the chemical composition of DNA. He discovered that the nuclei of cells contain large quantities of a substance that does not act as a protein. He called this substance nuclein. ...
... He used pus cells to investigate the chemical composition of DNA. He discovered that the nuclei of cells contain large quantities of a substance that does not act as a protein. He called this substance nuclein. ...
Seminar Abstract - Las Positas College
... affecting DNA and in turn the proteins encoded by DNA. These new biomolecules confer new or enhanced capabilities, which can give rise to new species. Mechanisms of DNA variation include: deletions, insertions, duplications, and horizontal gene transfer; which can affect the number and arrangement o ...
... affecting DNA and in turn the proteins encoded by DNA. These new biomolecules confer new or enhanced capabilities, which can give rise to new species. Mechanisms of DNA variation include: deletions, insertions, duplications, and horizontal gene transfer; which can affect the number and arrangement o ...
HLA typing of renal patients and investigation of disease
... Amplification of DNA takes place in a thermal cycler. The process involves a series of up to thirty cycles consisting of three steps. 1) The double stranded DNA is heated to 95ºC breaking the hydrogen bonds between them and separating the two strands. 2) As the temperature is reduced, the primers an ...
... Amplification of DNA takes place in a thermal cycler. The process involves a series of up to thirty cycles consisting of three steps. 1) The double stranded DNA is heated to 95ºC breaking the hydrogen bonds between them and separating the two strands. 2) As the temperature is reduced, the primers an ...
Genes to Proteins Nucleic Acid Structure
... • Recombinant DNA serves as a cloning vector – Incorporate into cells – Select cells that have been transformed ...
... • Recombinant DNA serves as a cloning vector – Incorporate into cells – Select cells that have been transformed ...
Cre-Lox recombination

In the field of genetics, Cre-Lox recombination is known as a site-specific recombinase technology, and is widely used to carry out deletions, insertions, translocations and inversions at specific sites in the DNA of cells. It allows the DNA modification to be targeted to a specific cell type or be triggered by a specific external stimulus. It is implemented both in eukaryotic and prokaryotic systems.The system consists of a single enzyme, Cre recombinase, that recombines a pair of short target sequences called the Lox sequences. This system can be implemented without inserting any extra supporting proteins or sequences. The Cre enzyme and the original Lox site called the LoxP sequence are derived from bacteriophage P1.Placing Lox sequences appropriately allows genes to be activated, repressed, or exchanged for other genes. At a DNA level many types of manipulations can be carried out. The activity of the Cre enzyme can be controlled so that it is expressed in a particular cell type or triggered by an external stimulus like a chemical signal or a heat shock. These targeted DNA changes are useful in cell lineage tracing and when mutants are lethal if expressed globally.The Cre-Lox system is very similar in action and in usage to the FLP-FRT recombination system.