Cellular Control
... Culturing host cells Not all cells take up the genes Need to able to select bacteria that have taken up the gene. Use plasmids that carry genes that are resistant to antibiotics When grown with media containing antibiotics only those with the gene will then grow ...
... Culturing host cells Not all cells take up the genes Need to able to select bacteria that have taken up the gene. Use plasmids that carry genes that are resistant to antibiotics When grown with media containing antibiotics only those with the gene will then grow ...
Genetics and Heredity
... and yellow paints blend to make green. What would happen if this was the case? ...
... and yellow paints blend to make green. What would happen if this was the case? ...
1) Lecture notes: effects of bile salts on cholesterol metabolism
... in detail, for the March and April lectures continue discuss of these proteins throughout the semester. If there in an increase in the mRNA for a protein, you know the synthesis of that protein has been increased. ...
... in detail, for the March and April lectures continue discuss of these proteins throughout the semester. If there in an increase in the mRNA for a protein, you know the synthesis of that protein has been increased. ...
Test Review Sheet: Biology Final – 09 Know the steps of the
... 7. What are the building blocks of carbs, proteins, and nucleic acids? 8. What makes carbon such a special element? 9. What is an organism? 10. What are the differences between plant and animal cells? 11. What is changed during a controlled experiment? 12. What are the three laws of Gregor Mendel? 1 ...
... 7. What are the building blocks of carbs, proteins, and nucleic acids? 8. What makes carbon such a special element? 9. What is an organism? 10. What are the differences between plant and animal cells? 11. What is changed during a controlled experiment? 12. What are the three laws of Gregor Mendel? 1 ...
DNA replication.
... that move along each of the two single strands pairing up new nucleotide units and then zipping the strands closed. This produces two new pieces of DNA, each containing one strand from the old DNA and one newly made strand. This process isn't perfect and sometimes the proteins make mistakes and put ...
... that move along each of the two single strands pairing up new nucleotide units and then zipping the strands closed. This produces two new pieces of DNA, each containing one strand from the old DNA and one newly made strand. This process isn't perfect and sometimes the proteins make mistakes and put ...
DNA - KK College of Nursing
... • DNA is a double stranded structure like a twisted ladder. It is embedded in the nucleus of eukaryotic cell but in prokaryotic it is lying in cytoplasm because of the absence of nucleus. • Discovered by Oswald Avery in 1944 with a team of scientists. ...
... • DNA is a double stranded structure like a twisted ladder. It is embedded in the nucleus of eukaryotic cell but in prokaryotic it is lying in cytoplasm because of the absence of nucleus. • Discovered by Oswald Avery in 1944 with a team of scientists. ...
PowerPoint 簡報
... • Instead of constant current, alternate long pulses of current in forward direction with shorter pulses in either opposite or sideways direction • Technique is called pulsed-field gel electrophoresis (PFGE) ...
... • Instead of constant current, alternate long pulses of current in forward direction with shorter pulses in either opposite or sideways direction • Technique is called pulsed-field gel electrophoresis (PFGE) ...
Presentation
... Amniocentesis - a small amount of amniotic fluid (containing fetal tissues and cells) is extracted from the amniotic sac surrounding the developing fetus - the DNA is examined for genetic abnormalities Chorionic Villi Sampling (CVS) - the removal of a small piece of the placenta (chorionic villi) d ...
... Amniocentesis - a small amount of amniotic fluid (containing fetal tissues and cells) is extracted from the amniotic sac surrounding the developing fetus - the DNA is examined for genetic abnormalities Chorionic Villi Sampling (CVS) - the removal of a small piece of the placenta (chorionic villi) d ...
Answers to Mastering Concepts Questions
... Both enzymes produce complementary copies of a DNA sequence of interest. In DNA sequencing, the enzyme’s progress is intentionally interrupted with terminator nucleotides. In PCR, the DNA polymerase is heat-tolerant so that it does not become denatured when the temperature in the reaction tube is pe ...
... Both enzymes produce complementary copies of a DNA sequence of interest. In DNA sequencing, the enzyme’s progress is intentionally interrupted with terminator nucleotides. In PCR, the DNA polymerase is heat-tolerant so that it does not become denatured when the temperature in the reaction tube is pe ...
Microbial GeneticsIII MB - E
... 17. The relationship between a virus and host where no new viral particles are produces and the viral genome is replicated along with host chromosome (1) lysogeny (2) lysis (3) transformation 18. Interrupted mating experiments are used to determine what information? (1) DNA nucleotide sequences (2) ...
... 17. The relationship between a virus and host where no new viral particles are produces and the viral genome is replicated along with host chromosome (1) lysogeny (2) lysis (3) transformation 18. Interrupted mating experiments are used to determine what information? (1) DNA nucleotide sequences (2) ...
Slide 1
... When the gene is activated the DNA sequence is translated via messenger RNA into a string of amino acids. Proteins like the Tyrosine Kinase enzymes are made of these amino acid strings. The c-kit gene is located on the long arm of Chromosome 4 – called the q arm. ...
... When the gene is activated the DNA sequence is translated via messenger RNA into a string of amino acids. Proteins like the Tyrosine Kinase enzymes are made of these amino acid strings. The c-kit gene is located on the long arm of Chromosome 4 – called the q arm. ...
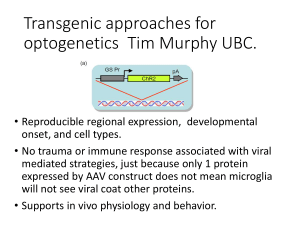
Transgenic approaches for optogenetics Tim Murphy UBC.
... Cre recombinase is a tyrosine recombinase enzyme derived from the P1 Bacteriophage. The enzyme uses a topoisomerase I like mechanism to carry out site specific recombination events. The enzyme (38kDa) is a member of the integrase family of site specific recombinase and it is known to catalyse the si ...
... Cre recombinase is a tyrosine recombinase enzyme derived from the P1 Bacteriophage. The enzyme uses a topoisomerase I like mechanism to carry out site specific recombination events. The enzyme (38kDa) is a member of the integrase family of site specific recombinase and it is known to catalyse the si ...
Translate your creativity
... 50 µL 5. lncubate the tube at 37° C for 2-4 hours. Please note that overnight incubation increases the amount of the produced protein. ...
... 50 µL 5. lncubate the tube at 37° C for 2-4 hours. Please note that overnight incubation increases the amount of the produced protein. ...
171392_ProteinSyn
... Why should you know about it? Because I say so!!! Just kidding. Really this process is one of the secrets of life so pay close attention. Today, ideas that are written in RED you should write down in your notes. Of course you can write down more if you want to So you can write the title of your no ...
... Why should you know about it? Because I say so!!! Just kidding. Really this process is one of the secrets of life so pay close attention. Today, ideas that are written in RED you should write down in your notes. Of course you can write down more if you want to So you can write the title of your no ...
doc Practice Midterm 2006
... These questions are intended to test your understanding of concepts that have been covered in the course. These questions can usually be answered in 25 words or less, certainly no more than 50. While a precise word count of your answers will not be conducted, excessively long answers and inclusion o ...
... These questions are intended to test your understanding of concepts that have been covered in the course. These questions can usually be answered in 25 words or less, certainly no more than 50. While a precise word count of your answers will not be conducted, excessively long answers and inclusion o ...
Genetics 310 Practice exam III-1
... 1. What are the two types of molecules found in eukaryotic chromosomes? 2. True or False? ____ Man has more DNA per genome than all other organisms. ____ The number of chromosomes is a direct reflection of the amount of DNA/genome in a species. ____ All of the DNA in a eukaryote is unique sequence D ...
... 1. What are the two types of molecules found in eukaryotic chromosomes? 2. True or False? ____ Man has more DNA per genome than all other organisms. ____ The number of chromosomes is a direct reflection of the amount of DNA/genome in a species. ____ All of the DNA in a eukaryote is unique sequence D ...
Isolating Hereditary Material
... To determine the roles that the T2 bacteriophage's DNA and protein play in infection, Hershey and Chase decided to use radioisotopes to trace the fate of the phage's protein and DNA by taking advantage of their chemical differences. Proteins contain sulfur, but DNA does not. Conversely, DNA contains ...
... To determine the roles that the T2 bacteriophage's DNA and protein play in infection, Hershey and Chase decided to use radioisotopes to trace the fate of the phage's protein and DNA by taking advantage of their chemical differences. Proteins contain sulfur, but DNA does not. Conversely, DNA contains ...
Creating an animated tutorial for the online classroom
... the mRNA strand using U instead of T for a pair with A. Then after you get the template strand, the other DNA strand will be the complementary base pair sequence of that. I think?” - MT “I think that’s what I did. Is what I came up with wrong? Hope not cause I thought I was starting to understand it ...
... the mRNA strand using U instead of T for a pair with A. Then after you get the template strand, the other DNA strand will be the complementary base pair sequence of that. I think?” - MT “I think that’s what I did. Is what I came up with wrong? Hope not cause I thought I was starting to understand it ...
Review 16-27 - Madeira City Schools
... Mismatch Repair ◦ A DNA polymerase does this as soon as nucleotide is added ◦ other proteins do this as well (they continually monitor) ...
... Mismatch Repair ◦ A DNA polymerase does this as soon as nucleotide is added ◦ other proteins do this as well (they continually monitor) ...
Science 103: Outline 17
... (iv) Ribosome moves one codon to the right. (v) A tRNA (plus amino acid) with the anticodon corresponding to the third codon binds and the first tRNA (empty) leaves. (v) The ribosomes move down the mRNA until they reach a stop codon. The ribosomes detach from the mRNA and the protein is released. 4. ...
... (iv) Ribosome moves one codon to the right. (v) A tRNA (plus amino acid) with the anticodon corresponding to the third codon binds and the first tRNA (empty) leaves. (v) The ribosomes move down the mRNA until they reach a stop codon. The ribosomes detach from the mRNA and the protein is released. 4. ...
nucleic acid
... other to form a double helix. The two DNA stands are organized in an antiparallel arrangement: the two strands run in opposite directions, one strand is oriented 5’→3’ and the other is oriented 3’ →5’. (2) The bases on the inside and the sugar-phosphate backbones in the outside. (3) The diameter of ...
... other to form a double helix. The two DNA stands are organized in an antiparallel arrangement: the two strands run in opposite directions, one strand is oriented 5’→3’ and the other is oriented 3’ →5’. (2) The bases on the inside and the sugar-phosphate backbones in the outside. (3) The diameter of ...
Cre-Lox recombination

In the field of genetics, Cre-Lox recombination is known as a site-specific recombinase technology, and is widely used to carry out deletions, insertions, translocations and inversions at specific sites in the DNA of cells. It allows the DNA modification to be targeted to a specific cell type or be triggered by a specific external stimulus. It is implemented both in eukaryotic and prokaryotic systems.The system consists of a single enzyme, Cre recombinase, that recombines a pair of short target sequences called the Lox sequences. This system can be implemented without inserting any extra supporting proteins or sequences. The Cre enzyme and the original Lox site called the LoxP sequence are derived from bacteriophage P1.Placing Lox sequences appropriately allows genes to be activated, repressed, or exchanged for other genes. At a DNA level many types of manipulations can be carried out. The activity of the Cre enzyme can be controlled so that it is expressed in a particular cell type or triggered by an external stimulus like a chemical signal or a heat shock. These targeted DNA changes are useful in cell lineage tracing and when mutants are lethal if expressed globally.The Cre-Lox system is very similar in action and in usage to the FLP-FRT recombination system.