Human Genome Project
... Human genome has far more repeat DNA than any other sequenced organism (over half). • Parasitic elements–45% of this repeat DNA is from selfish, parasitic DNA: – Transposable elements. – May play role in evolution. ...
... Human genome has far more repeat DNA than any other sequenced organism (over half). • Parasitic elements–45% of this repeat DNA is from selfish, parasitic DNA: – Transposable elements. – May play role in evolution. ...
coding and non-coding functions of the genome
... “More than 80% of DNA is transcribed to non-coding RNA,” explained Tony Kouzarides, professor of cancer biology at the University of Cambridge. “And nearly half of that DNA is retrovirus inserted into the genome at some point of evolution,” added Simon J. Elsäser of Karolinska Institutet in Stockhol ...
... “More than 80% of DNA is transcribed to non-coding RNA,” explained Tony Kouzarides, professor of cancer biology at the University of Cambridge. “And nearly half of that DNA is retrovirus inserted into the genome at some point of evolution,” added Simon J. Elsäser of Karolinska Institutet in Stockhol ...
Biological Diversity Topic 5
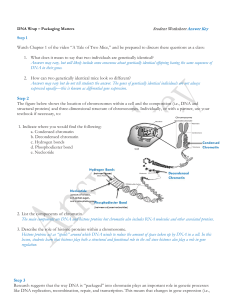
... • Recall that when organisms divide through binary fission, the two new organisms created are identical. • In order for them to be identical, they have to have the same DNA. • In order for this to happen, the parent must double its DNA before it divides. • In multicellular organisms, that production ...
... • Recall that when organisms divide through binary fission, the two new organisms created are identical. • In order for them to be identical, they have to have the same DNA. • In order for this to happen, the parent must double its DNA before it divides. • In multicellular organisms, that production ...
RNA (Transcription)
... Exactly how RNA polymerase recognizes the end of a gene is very complicated but we will discuss as it reaching a Stop signal. ...
... Exactly how RNA polymerase recognizes the end of a gene is very complicated but we will discuss as it reaching a Stop signal. ...
LECT14 DNA
... Are the forces of interaction the same for all bases? No. Stacking interactions between G and C give rise to greater stacking energy than A to T ...
... Are the forces of interaction the same for all bases? No. Stacking interactions between G and C give rise to greater stacking energy than A to T ...
December - Drake Neighborhood Association
... • The Thresholds Festival 2006 has come to the DNA requesting a donation of $750 for this year’s event; the DNA would get ad space in the event program. There was discussion about appropriate levels of funding the DNA should offer to sponsor local events; we will discuss further at the 2006 plannin ...
... • The Thresholds Festival 2006 has come to the DNA requesting a donation of $750 for this year’s event; the DNA would get ad space in the event program. There was discussion about appropriate levels of funding the DNA should offer to sponsor local events; we will discuss further at the 2006 plannin ...
Proto-Cells - TextAddOns.com
... Think Critically (cont’d) It is known that protocells are readily broken up by agitation and dissolved with changes in PH, heat and temperature. Are protocells likely to occur outside of a laboratory? ...
... Think Critically (cont’d) It is known that protocells are readily broken up by agitation and dissolved with changes in PH, heat and temperature. Are protocells likely to occur outside of a laboratory? ...
Dear Sir - PhagesDB
... operon on the negative strand. In “The Secret Lives of Bacteriophages”, the following is noted about gene 33 in G1 phages: A rather striking feature of repressor/integrase gene organization is that the crossover site for integrase-mediated, sitespecific recombination within the phage attachment site ...
... operon on the negative strand. In “The Secret Lives of Bacteriophages”, the following is noted about gene 33 in G1 phages: A rather striking feature of repressor/integrase gene organization is that the crossover site for integrase-mediated, sitespecific recombination within the phage attachment site ...
Platform Partition in Translational Medicine Data
... L266V tau mutation is associated with frontotemporal dementia and Picklike 3R and 4R tauopathy. Acta Neuropathol (Berl). 2003;106(4):323-36 http://myhealth-guide.org/glioblastoma-multiforme-pathology-andpictures/613 ...
... L266V tau mutation is associated with frontotemporal dementia and Picklike 3R and 4R tauopathy. Acta Neuropathol (Berl). 2003;106(4):323-36 http://myhealth-guide.org/glioblastoma-multiforme-pathology-andpictures/613 ...
Study Guide: Unit 1 Test 1. How would a DNA analyst`s job differ
... d. They help to determine height, age, and sex of human remains 2. A forensic anthropologist would least likely be doing which of the following tasks? a. Examining human remains after a natural disaster b. Recovering DNA from a bloodstain c. Estimating the height and ethnicity of an unidentified bod ...
... d. They help to determine height, age, and sex of human remains 2. A forensic anthropologist would least likely be doing which of the following tasks? a. Examining human remains after a natural disaster b. Recovering DNA from a bloodstain c. Estimating the height and ethnicity of an unidentified bod ...
I - Nutley Public Schools
... v. Watson and Crick built DNA model of ________________ vi. Their historic paper describing structure pointed out "possible copying mechanism for the genetic material." ...
... v. Watson and Crick built DNA model of ________________ vi. Their historic paper describing structure pointed out "possible copying mechanism for the genetic material." ...
Applications Lecture 4 - Rose
... individual proteins. (the production of these proteins is known as gene expression) b. Gene expression takes place in two stages i. Transcription—DNA is turned into RNA via the enzyme RNA polymerase. ii. Translation—RNA is turned into Protein in the rough Endoplasmic Reticulum found in the cytoplasm ...
... individual proteins. (the production of these proteins is known as gene expression) b. Gene expression takes place in two stages i. Transcription—DNA is turned into RNA via the enzyme RNA polymerase. ii. Translation—RNA is turned into Protein in the rough Endoplasmic Reticulum found in the cytoplasm ...
DNA helix mRNA strand transcription gene A > A G > G C > C T > U
... different in the children (i.e. the frequency of recombination between those two genes). This will help us estimate p and therefore d. If we are able to determine the distance between all pairs of genes in our example genome, then we can use these distances to determine the exact sequence of the gen ...
... different in the children (i.e. the frequency of recombination between those two genes). This will help us estimate p and therefore d. If we are able to determine the distance between all pairs of genes in our example genome, then we can use these distances to determine the exact sequence of the gen ...
BINF6201/8201 Basics of Molecular Biology
... Ø In eukaryotic cells, DNA molecules are highly compacted by wrapping around the histone protein core, forming nucleosomes. Ø The histone core is made up of 2 copies of each of the four histone proteins (H2A, H2B, H3 and H4). Ø Nucleosomes are further coiled to form super coils. Ø The N-terminal ta ...
... Ø In eukaryotic cells, DNA molecules are highly compacted by wrapping around the histone protein core, forming nucleosomes. Ø The histone core is made up of 2 copies of each of the four histone proteins (H2A, H2B, H3 and H4). Ø Nucleosomes are further coiled to form super coils. Ø The N-terminal ta ...
File
... The direct human manipulation of an organism’s genome using modern DNA technology is called genetic modification. It involves the introduction of foreign DNA into another organism, in many cases from bacteria. Why would we want to genetically modify an organism? 1) Improve crops 1) ex: inserti ...
... The direct human manipulation of an organism’s genome using modern DNA technology is called genetic modification. It involves the introduction of foreign DNA into another organism, in many cases from bacteria. Why would we want to genetically modify an organism? 1) Improve crops 1) ex: inserti ...
Chapter 14 - Genomes and genomics
... • DNA Sequencing and the rise of genomics • Annotation of genome sequence – Comparative genomics – Functional genomics ...
... • DNA Sequencing and the rise of genomics • Annotation of genome sequence – Comparative genomics – Functional genomics ...
Leukaemia Section t(8;19)(p12;q13) Atlas of Genetics and Cytogenetics in Oncology and Haematology
... of the juxtamembrane domain and the tyrosine kinaseencoding regions of the FGFR1 gene. ...
... of the juxtamembrane domain and the tyrosine kinaseencoding regions of the FGFR1 gene. ...
`Quickie` Quikchange mutagenesis (Stratagene)
... a) The most frequent problem, not surprisingly, is ‘no colonies’. Almost always, if you get colonies (even just a couple), you’re going to get your mutant. To facilitate screening for mutants, you may incorporate a ‘silent’ (one that doesn’t change the coding) restriction site (or aim to lose a site ...
... a) The most frequent problem, not surprisingly, is ‘no colonies’. Almost always, if you get colonies (even just a couple), you’re going to get your mutant. To facilitate screening for mutants, you may incorporate a ‘silent’ (one that doesn’t change the coding) restriction site (or aim to lose a site ...
document
... Answers may vary, but will likely include some consensus about genetically identical offspring having the same sequences of DNA in their genes. 2. How can two genetically identical mice look so different? Answers may vary but do not tell students the answer. The genes of genetically identical indivi ...
... Answers may vary, but will likely include some consensus about genetically identical offspring having the same sequences of DNA in their genes. 2. How can two genetically identical mice look so different? Answers may vary but do not tell students the answer. The genes of genetically identical indivi ...
Chapter 8 Gene Transfer in Bacteria Conjugation Hfr Cells
... translated – New phage particles assembled, cell lyses. ...
... translated – New phage particles assembled, cell lyses. ...
Fianl Exam Review
... a. The difference in DNA between animals, plants, bacteria… is the order of the nitrogen bases. b. The difference in DNA between animals, plants, bacteria… is the number of the nitrogen bases. c. Neither A nor B d. Both A and B 63. One codon on mRNA has how many nitrogen bases? a. 1 b. 3 c. random d ...
... a. The difference in DNA between animals, plants, bacteria… is the order of the nitrogen bases. b. The difference in DNA between animals, plants, bacteria… is the number of the nitrogen bases. c. Neither A nor B d. Both A and B 63. One codon on mRNA has how many nitrogen bases? a. 1 b. 3 c. random d ...
DNA Profiles
... possible using DNA chips (microarrays), which can hold thousands of genes DNA microarray • A series of short nucleotide sequences placed on a solid support (such as glass) that have several different uses ...
... possible using DNA chips (microarrays), which can hold thousands of genes DNA microarray • A series of short nucleotide sequences placed on a solid support (such as glass) that have several different uses ...
Cre-Lox recombination

In the field of genetics, Cre-Lox recombination is known as a site-specific recombinase technology, and is widely used to carry out deletions, insertions, translocations and inversions at specific sites in the DNA of cells. It allows the DNA modification to be targeted to a specific cell type or be triggered by a specific external stimulus. It is implemented both in eukaryotic and prokaryotic systems.The system consists of a single enzyme, Cre recombinase, that recombines a pair of short target sequences called the Lox sequences. This system can be implemented without inserting any extra supporting proteins or sequences. The Cre enzyme and the original Lox site called the LoxP sequence are derived from bacteriophage P1.Placing Lox sequences appropriately allows genes to be activated, repressed, or exchanged for other genes. At a DNA level many types of manipulations can be carried out. The activity of the Cre enzyme can be controlled so that it is expressed in a particular cell type or triggered by an external stimulus like a chemical signal or a heat shock. These targeted DNA changes are useful in cell lineage tracing and when mutants are lethal if expressed globally.The Cre-Lox system is very similar in action and in usage to the FLP-FRT recombination system.