Document
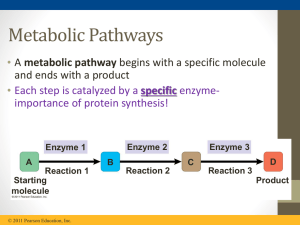
... • Catabolic pathways release energy by breaking down complex molecules into simpler compounds (Cellular respiration, the breakdown of glucose in the presence of oxygen) • Anabolic pathways consume energy to build complex molecules from simpler ones (synthesis of protein from amino acids) ...
... • Catabolic pathways release energy by breaking down complex molecules into simpler compounds (Cellular respiration, the breakdown of glucose in the presence of oxygen) • Anabolic pathways consume energy to build complex molecules from simpler ones (synthesis of protein from amino acids) ...
Visualization of ATP levels inside single living cells with
... (bottom, pseudocolored) of a HeLa cell expressing AT1.03. Inhibitors of glycolysis (10 mM 2-deoxyglucose [2DG]) and OXPHOS (1 mM potassium cyanide [KCN]) were added at time ⫽ 0 (min). Elapsed time (in minutes) after addition of the inhibitors is shown to the top left of the cells. Images were obtain ...
... (bottom, pseudocolored) of a HeLa cell expressing AT1.03. Inhibitors of glycolysis (10 mM 2-deoxyglucose [2DG]) and OXPHOS (1 mM potassium cyanide [KCN]) were added at time ⫽ 0 (min). Elapsed time (in minutes) after addition of the inhibitors is shown to the top left of the cells. Images were obtain ...
Energy Substrate Modulates Mitochondrial
... relative to normal tissues generally reveals a strong diminution in mitochondrial content and in oxidative phosphorylation capacity. However, little is known about what triggers these modifications and whether or not they are physiologically reversible. We hypothesized that energy substrate availabi ...
... relative to normal tissues generally reveals a strong diminution in mitochondrial content and in oxidative phosphorylation capacity. However, little is known about what triggers these modifications and whether or not they are physiologically reversible. We hypothesized that energy substrate availabi ...
Science Course Outline Template
... components of a cell are synthesized from simpler units. ‘Catabolism’ covers the processes whereby complex compounds are degraded to release energy and to provide the smaller units for the cell's synthetic processes. All living organisms break down food materials and synthesize cell components by or ...
... components of a cell are synthesized from simpler units. ‘Catabolism’ covers the processes whereby complex compounds are degraded to release energy and to provide the smaller units for the cell's synthetic processes. All living organisms break down food materials and synthesize cell components by or ...
Third Generation Biofuels via Direct Cellulose Fermentation
... gasification, and steam reformation of natural gas or through the action of biological systems. Production of H2 using fermentative biological processes is potentially the most attractive of these strategies as it is not as energy intensive as other means and could potentially utilize refuse or agri ...
... gasification, and steam reformation of natural gas or through the action of biological systems. Production of H2 using fermentative biological processes is potentially the most attractive of these strategies as it is not as energy intensive as other means and could potentially utilize refuse or agri ...
AP Biology - TeacherWeb
... blocks enzyme that breaks down alcohol severe hangover & vomiting 5-10 minutes after drinking ...
... blocks enzyme that breaks down alcohol severe hangover & vomiting 5-10 minutes after drinking ...
Metabolism, Energy Balance, and Body Composition © 2009 Cengage - Wadsworth
... Generate ATP when the cell is low in energy © 2009 Cengage - Wadsworth ...
... Generate ATP when the cell is low in energy © 2009 Cengage - Wadsworth ...
Eubacterium limosum on glucose/methanol mixtures
... concentrations of the substrate mixture have a profound influence on the metabolic activity of the constituent microbial population. To date, two modes of substrate utilization are regularly encountered dependent largely upon the substrate concentration. When substrate is in excess, sequential utili ...
... concentrations of the substrate mixture have a profound influence on the metabolic activity of the constituent microbial population. To date, two modes of substrate utilization are regularly encountered dependent largely upon the substrate concentration. When substrate is in excess, sequential utili ...
The Presence and Function of Cytochromes in
... anaerobic bacteria which, like the propionic acid bacteria, form propionate via the succinate pathway (Paynter & Elsden, 1970; Hobson & Summers, 1967; Johns, 1951). V. alcalescens and certain strains of S. ruminantium form nitrite from nitrate, whereas A . lipolytica does not reduce nitrate (Hungate ...
... anaerobic bacteria which, like the propionic acid bacteria, form propionate via the succinate pathway (Paynter & Elsden, 1970; Hobson & Summers, 1967; Johns, 1951). V. alcalescens and certain strains of S. ruminantium form nitrite from nitrate, whereas A . lipolytica does not reduce nitrate (Hungate ...
Circadia-Product-Knowledge-Retail
... Application of pyruvate-succinic acid complex activates the Kreb’s Cycle, increases flow of electrons to the Electron Transport System generating more energy through ATP synthesis. This product is not removed. It remains on the skin and is followed by the Fraction V. ...
... Application of pyruvate-succinic acid complex activates the Kreb’s Cycle, increases flow of electrons to the Electron Transport System generating more energy through ATP synthesis. This product is not removed. It remains on the skin and is followed by the Fraction V. ...
photosynthesis in higher plants
... Some simple experiments show that chlorophyll (green pigment of the leaf), light and CO2 are required for photosynthesis to occur. Look for starch formation in two leaves - a variegated leaf or a leaf that was partially covered with black paper and one that was exposed to light. On testing these lea ...
... Some simple experiments show that chlorophyll (green pigment of the leaf), light and CO2 are required for photosynthesis to occur. Look for starch formation in two leaves - a variegated leaf or a leaf that was partially covered with black paper and one that was exposed to light. On testing these lea ...
The 10.8-AA structure of Saccharomyces cerevisiae
... largest success has been achieved for the less complex bacterial enzyme (e.g., Escherichia coli, Bacillus stearothermophilus). Bacterial phosphofructokinases are homotetramers with a total molecular weight of 140 kDa (Blangy, 1968) and their activity is mainly regulated by only two effectors, an acti ...
... largest success has been achieved for the less complex bacterial enzyme (e.g., Escherichia coli, Bacillus stearothermophilus). Bacterial phosphofructokinases are homotetramers with a total molecular weight of 140 kDa (Blangy, 1968) and their activity is mainly regulated by only two effectors, an acti ...
Test 5 Ch 2 - Kenton County Schools
... ____ 11. Refer to the illustration above. Which of the following statements regarding the graph is true? a. Reaction 2 occurs faster than Reaction 3 because Reaction 2 requires more energy than Reaction 3. b. The difference between the graphs shown for Reaction 2 and Reaction 3 occurs because of a ...
... ____ 11. Refer to the illustration above. Which of the following statements regarding the graph is true? a. Reaction 2 occurs faster than Reaction 3 because Reaction 2 requires more energy than Reaction 3. b. The difference between the graphs shown for Reaction 2 and Reaction 3 occurs because of a ...
inclusion of a glycogen regulation mathematical model into a
... While we generally eat infrequently, metabolic processes within our body tightly regulate blood glucose levels. The metabolic system is comprised of various tissues, each of which contains specific regulatory pathways that determine the function of the tissue within the system. ...
... While we generally eat infrequently, metabolic processes within our body tightly regulate blood glucose levels. The metabolic system is comprised of various tissues, each of which contains specific regulatory pathways that determine the function of the tissue within the system. ...
Document
... • The following four tests comprise a series of important determinations that are collectively called the IMViC series of reactions • The IMViC series of reactions allows for the differentiation of the various members of Enterobacteriaceae. ...
... • The following four tests comprise a series of important determinations that are collectively called the IMViC series of reactions • The IMViC series of reactions allows for the differentiation of the various members of Enterobacteriaceae. ...
What is Xtend
... pyruvate or other TCA cycle intermediates that can be used for the production of glucose through gluconeogenesis. A ketogenic amino acid is metabolized via the fatty acid pathway and gives rise to actyl-CoA, a fatty acid precursor. Leucine is completely ketogenic, valine is completely glucogenic, an ...
... pyruvate or other TCA cycle intermediates that can be used for the production of glucose through gluconeogenesis. A ketogenic amino acid is metabolized via the fatty acid pathway and gives rise to actyl-CoA, a fatty acid precursor. Leucine is completely ketogenic, valine is completely glucogenic, an ...
Expression and activity of hexokinase in the early mouse embryo
... medium before being transferred into T6 medium (Whittingham, 1971) containing 5.5 mM glucose, 0.25 mM pyruvate and 2.5 mM lactate, and cultured under pre-equilibrated paraffin oil at 37°C in a humidified atmosphere of 5% CO2 in air. Extraction of poly (A)* mRNA mRNA was extracted from single preimpl ...
... medium before being transferred into T6 medium (Whittingham, 1971) containing 5.5 mM glucose, 0.25 mM pyruvate and 2.5 mM lactate, and cultured under pre-equilibrated paraffin oil at 37°C in a humidified atmosphere of 5% CO2 in air. Extraction of poly (A)* mRNA mRNA was extracted from single preimpl ...
PDF - Biotechnology for Biofuels
... processes, such as steam reforming of natural gas, release large quantities of CO2 and thereby contribute substantially to the greenhouse effect [1]. Consequently, scientific interest in recent years has focused on alternative methods of hydrogen production, in particular on the use of photosyntheti ...
... processes, such as steam reforming of natural gas, release large quantities of CO2 and thereby contribute substantially to the greenhouse effect [1]. Consequently, scientific interest in recent years has focused on alternative methods of hydrogen production, in particular on the use of photosyntheti ...
HS-SCI-APB-Unit 2 -- Chapter 8- Introduction to
... Metabolism as a whole manages the material and energy resources of the cell. Some metabolic pathways release energy by breaking down complex molecules to simpler compounds. These degradative processes are called catabolic pathways, or breal
... Metabolism as a whole manages the material and energy resources of the cell. Some metabolic pathways release energy by breaking down complex molecules to simpler compounds. These degradative processes are called catabolic pathways, or breal
Name____________________________ Student number
... 2. Which of the following statements is true of enzyme catalysts? A) To be effective, they must be present at the same concentration as their substrate. B) They can increase the equilibrium constant for a given reaction by a thousand-fold or more. •C) They lower the activation energy for conversion ...
... 2. Which of the following statements is true of enzyme catalysts? A) To be effective, they must be present at the same concentration as their substrate. B) They can increase the equilibrium constant for a given reaction by a thousand-fold or more. •C) They lower the activation energy for conversion ...
Enhancement of the Essential Amino Acid Composition of Food
... glycerate-3-phosphate, pyruvate, phosphoenol pyruvate, α-ketoglutarate, and oxaloacetate groups of amino acids. A chemical advantage of the integrative approach is that it is supported by the free energy changes in glycolysis and citric-glyoxylic acid cycles, the low exergonic reactions producing a ...
... glycerate-3-phosphate, pyruvate, phosphoenol pyruvate, α-ketoglutarate, and oxaloacetate groups of amino acids. A chemical advantage of the integrative approach is that it is supported by the free energy changes in glycolysis and citric-glyoxylic acid cycles, the low exergonic reactions producing a ...
UvA-DARE (Digital Academic Repository) Bacterial class A acid
... essential part in photosynthesis, carbohydrate and lipid metabolism, the nitrogen cycle, immune response, host-pathogen interactions, transmembrane signaling, activation of metabolites, cellular control by protein phosphorylation and in numerous other biochemical reactions. Further, phosphorus is pa ...
... essential part in photosynthesis, carbohydrate and lipid metabolism, the nitrogen cycle, immune response, host-pathogen interactions, transmembrane signaling, activation of metabolites, cellular control by protein phosphorylation and in numerous other biochemical reactions. Further, phosphorus is pa ...
Partial Purification and Characterization of the Maize Mitochondrial
... Patel and Roche, 1990; Randall et al., 1996). The importance of mtPDC in controlling primary carbon metabolism is reflected by the many literature reports. However, there are a limited number of reports describing research on plant mtPDCs (for review, see Randall et al., 1996). Furthermore, our unde ...
... Patel and Roche, 1990; Randall et al., 1996). The importance of mtPDC in controlling primary carbon metabolism is reflected by the many literature reports. However, there are a limited number of reports describing research on plant mtPDCs (for review, see Randall et al., 1996). Furthermore, our unde ...
Glycolysis
Glycolysis (from glycose, an older term for glucose + -lysis degradation) is the metabolic pathway that converts glucose C6H12O6, into pyruvate, CH3COCOO− + H+. The free energy released in this process is used to form the high-energy compounds ATP (adenosine triphosphate) and NADH (reduced nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide).Glycolysis is a determined sequence of ten enzyme-catalyzed reactions. The intermediates provide entry points to glycolysis. For example, most monosaccharides, such as fructose and galactose, can be converted to one of these intermediates. The intermediates may also be directly useful. For example, the intermediate dihydroxyacetone phosphate (DHAP) is a source of the glycerol that combines with fatty acids to form fat.Glycolysis is an oxygen independent metabolic pathway, meaning that it does not use molecular oxygen (i.e. atmospheric oxygen) for any of its reactions. However the products of glycolysis (pyruvate and NADH + H+) are sometimes disposed of using atmospheric oxygen. When molecular oxygen is used in the disposal of the products of glycolysis the process is usually referred to as aerobic, whereas if the disposal uses no oxygen the process is said to be anaerobic. Thus, glycolysis occurs, with variations, in nearly all organisms, both aerobic and anaerobic. The wide occurrence of glycolysis indicates that it is one of the most ancient metabolic pathways. Indeed, the reactions that constitute glycolysis and its parallel pathway, the pentose phosphate pathway, occur metal-catalyzed under the oxygen-free conditions of the Archean oceans, also in the absence of enzymes. Glycolysis could thus have originated from chemical constraints of the prebiotic world.Glycolysis occurs in most organisms in the cytosol of the cell. The most common type of glycolysis is the Embden–Meyerhof–Parnas (EMP pathway), which was discovered by Gustav Embden, Otto Meyerhof, and Jakub Karol Parnas. Glycolysis also refers to other pathways, such as the Entner–Doudoroff pathway and various heterofermentative and homofermentative pathways. However, the discussion here will be limited to the Embden–Meyerhof–Parnas pathway.The entire glycolysis pathway can be separated into two phases: The Preparatory Phase – in which ATP is consumed and is hence also known as the investment phase The Pay Off Phase – in which ATP is produced.↑ ↑ 2.0 2.1 ↑ ↑ ↑ ↑ ↑ ↑