Name - Humble ISD
... the _blood___ moves into body cells via _facilitated diffusion___. **TOTAL ATP GAIN IN CELLULAR RESPIRATION = ...
... the _blood___ moves into body cells via _facilitated diffusion___. **TOTAL ATP GAIN IN CELLULAR RESPIRATION = ...
Metabolism
... Alcohol + CO2 Propionic Acid Butyric Acid Acetic Acid Succinic Acid Butylene to Acetoin – basis for VP Test (Vogues-Proskauer) Chapter 5 ...
... Alcohol + CO2 Propionic Acid Butyric Acid Acetic Acid Succinic Acid Butylene to Acetoin – basis for VP Test (Vogues-Proskauer) Chapter 5 ...
Glycobiology is the study of the structure, biosynthesis, biology and
... Are nutrients naturally available in our diet? Nothing is better than getting your nutrients through your food Unfortunately studies conclude that our diet is poor in nutrients An argument against supplement use is that many of the formulations on the market have no clinical studies to support their ...
... Are nutrients naturally available in our diet? Nothing is better than getting your nutrients through your food Unfortunately studies conclude that our diet is poor in nutrients An argument against supplement use is that many of the formulations on the market have no clinical studies to support their ...
Week 1 – Cell structure and Function and Cell membranes
... supplied The process of respiration involves the synthesis of ATP using the energy from glucose There are three stages in aerobic respiration; glycolysis, Krebs cycle and the cytochrome system All the stages in respiration are controlled by enzymes Glycolysis Glycolysis takes place in the cy ...
... supplied The process of respiration involves the synthesis of ATP using the energy from glucose There are three stages in aerobic respiration; glycolysis, Krebs cycle and the cytochrome system All the stages in respiration are controlled by enzymes Glycolysis Glycolysis takes place in the cy ...
(pt=2) What is an acid?
... For short answer questions, be brief; full sentences are not necessary. Point value for each question is in parentheses. If a question is not clear to you, please ask for clarification. ...
... For short answer questions, be brief; full sentences are not necessary. Point value for each question is in parentheses. If a question is not clear to you, please ask for clarification. ...
FES 100 - Introduction to Forest Biology Exam 1: 100 points October
... or not living. a)______________________________________________________________________________ b)______________________________________________________________________________ c)______________________________________________________________________________ ...
... or not living. a)______________________________________________________________________________ b)______________________________________________________________________________ c)______________________________________________________________________________ ...
Metabolism—chapter 4
... --There are 20 different amino acids that can be put together to form all the proteins that we can make. The arrangements are specified by the ‘code’ (arrangements of the nucleotide bases) located on the DNA. However, proteins are made in the cytoplasm of the cell at the ribosomes, and DNA is locate ...
... --There are 20 different amino acids that can be put together to form all the proteins that we can make. The arrangements are specified by the ‘code’ (arrangements of the nucleotide bases) located on the DNA. However, proteins are made in the cytoplasm of the cell at the ribosomes, and DNA is locate ...
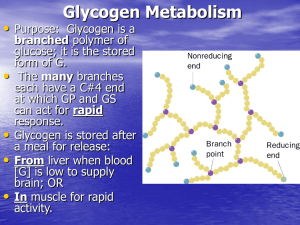
Glycogen Metabolism - http://www.utm.edu
... without the accumulation of glucose. It is said that “GP is the glucose sensor”: a) In the phospho (active) form, the P’s on GP are “buried” where PP1 can’t get at them. b) When G binds to active GP-P, its conformation changes, “exposing” the P’s so PP1 can “clip them” off. c) PP1 binds strongly to ...
... without the accumulation of glucose. It is said that “GP is the glucose sensor”: a) In the phospho (active) form, the P’s on GP are “buried” where PP1 can’t get at them. b) When G binds to active GP-P, its conformation changes, “exposing” the P’s so PP1 can “clip them” off. c) PP1 binds strongly to ...
Chapter 15 - FIU Faculty Websites
... 2. Ligation reactions – bond formation using free energy from ATP ...
... 2. Ligation reactions – bond formation using free energy from ATP ...
Supporting information
... cell samples in the 4 different nutrient conditions. The percentage of cells in each phase of the cell cycle (G1, S or G2) was calculated for control and treated samples in 4 different media conditions: A) 5 mM glucose, B) 1 mM glucose, C) 1 mM glucose without glutamine and D) 1mM glucose without gl ...
... cell samples in the 4 different nutrient conditions. The percentage of cells in each phase of the cell cycle (G1, S or G2) was calculated for control and treated samples in 4 different media conditions: A) 5 mM glucose, B) 1 mM glucose, C) 1 mM glucose without glutamine and D) 1mM glucose without gl ...
Cell Biology
... E. Its ability to proceed without an input of energy 17. Which of the following elements is not essential to aerobic cellular respiration? A. Phosphorus B. Magnesium C. Carbon D. Iron E. Lithium 18. What marks the stage of prometaphase in mitosis? I. Fragmentation of the nuclear envelope II. Creatio ...
... E. Its ability to proceed without an input of energy 17. Which of the following elements is not essential to aerobic cellular respiration? A. Phosphorus B. Magnesium C. Carbon D. Iron E. Lithium 18. What marks the stage of prometaphase in mitosis? I. Fragmentation of the nuclear envelope II. Creatio ...
DB QS
... Gluconeogenesis is a ubiquitous process, present in plants, animals, fungi, bacteria, and other microorganisms.[2] In vertebrates, gluconeogenesis takes place mainly in the liver and, to a lesser extent, in the cortex of the kidneys. Diabetic ketoacidosis arises because of a lack of insulin in the b ...
... Gluconeogenesis is a ubiquitous process, present in plants, animals, fungi, bacteria, and other microorganisms.[2] In vertebrates, gluconeogenesis takes place mainly in the liver and, to a lesser extent, in the cortex of the kidneys. Diabetic ketoacidosis arises because of a lack of insulin in the b ...
A2 revision
... Here you are not expected to know exactly how weedkillers work – the command word suggest tells you this. However, especially for a Stretch and Challenge question, you should use the information given to put forward a possible reason – but don’t take a wild guess! Notice that the answer to part (b) ...
... Here you are not expected to know exactly how weedkillers work – the command word suggest tells you this. However, especially for a Stretch and Challenge question, you should use the information given to put forward a possible reason – but don’t take a wild guess! Notice that the answer to part (b) ...
Amphibolic nature of Krebs Cycle
... • Proteins can also be broken down to feed into the citric acid cycle and generate energy • Under extreme starvation in animals or during senescence in plants polypeptides are cleaved to amino acids, amino group is cleaved off of amino acid forming an organic acid that can enter the citric acid cyc ...
... • Proteins can also be broken down to feed into the citric acid cycle and generate energy • Under extreme starvation in animals or during senescence in plants polypeptides are cleaved to amino acids, amino group is cleaved off of amino acid forming an organic acid that can enter the citric acid cyc ...
Chapter 2: Biochemistry
... acids and alcohols other than glycerol. Cholesterol is a steroid found in most animal tissues. It plays a role in the buildup of fatty deposits in arteries. Lipids have an extreme importance in many life activities. They are components of cell membranes along with other cell structures. Lipids also ...
... acids and alcohols other than glycerol. Cholesterol is a steroid found in most animal tissues. It plays a role in the buildup of fatty deposits in arteries. Lipids have an extreme importance in many life activities. They are components of cell membranes along with other cell structures. Lipids also ...
Oligonucleotide 5` End Labeling with Radiochemicals
... Synthetic oligonucleotides prepared with free 5’ and 3’ hydroxyl groups will not require pretreatment with bacterial alkaline or calf intestinal phosphatise. End labelling of oligos is also much simpler than double stranded DNA molecules because there is no need to modify reaction conditions dependi ...
... Synthetic oligonucleotides prepared with free 5’ and 3’ hydroxyl groups will not require pretreatment with bacterial alkaline or calf intestinal phosphatise. End labelling of oligos is also much simpler than double stranded DNA molecules because there is no need to modify reaction conditions dependi ...
Key Area 8 Respiration
... respiration in the absence of oxygen that takes place in animals. Success Criteria: Be able to name the process of respiration in the absence of oxygen Be able to describe the process of respiration in the absence of oxygen . Be able to name the conditions that an animal would be in to carry out thi ...
... respiration in the absence of oxygen that takes place in animals. Success Criteria: Be able to name the process of respiration in the absence of oxygen Be able to describe the process of respiration in the absence of oxygen . Be able to name the conditions that an animal would be in to carry out thi ...
Glucose Support Formula
... • Gymnema sylvestre, an herb used for over 2,000 years in India and standardized to contain 75% gymnemic acids, to nutritionally support the insulin producing cells of the pancreas.* • Alpha lipoic acid, a versatile nutrient that provides powerful antioxidant activity and sustains healthy glucose ...
... • Gymnema sylvestre, an herb used for over 2,000 years in India and standardized to contain 75% gymnemic acids, to nutritionally support the insulin producing cells of the pancreas.* • Alpha lipoic acid, a versatile nutrient that provides powerful antioxidant activity and sustains healthy glucose ...
BIO 1109 – Principles of Biology Midterm examination 2
... 4.1 Solar energy is stored in ATP and this compound during photosynthesis ___NADPH_______ 4.2 This metabolic process produces both NADH and FADH2. __Krebs/citric acid___________ 4.3 The traits Mendel studies in garden peas showed this kind of dominace. ___Complete______ 4.4 These vents in the deepes ...
... 4.1 Solar energy is stored in ATP and this compound during photosynthesis ___NADPH_______ 4.2 This metabolic process produces both NADH and FADH2. __Krebs/citric acid___________ 4.3 The traits Mendel studies in garden peas showed this kind of dominace. ___Complete______ 4.4 These vents in the deepes ...
Highlights from the Maltese Lipids Intervention: He went over his in
... 2. Know how fat is disgested and how Triacylglycerols (TGs) are transported in the blood. 3. Know the ACC slide on page 288 in combination with one on page 280. Know that AMP activates Protein Kinase A and ATP deactivates PKA. Know actions of insulin vs. glucagon 4. For glycerol pathway, don’t worry ...
... 2. Know how fat is disgested and how Triacylglycerols (TGs) are transported in the blood. 3. Know the ACC slide on page 288 in combination with one on page 280. Know that AMP activates Protein Kinase A and ATP deactivates PKA. Know actions of insulin vs. glucagon 4. For glycerol pathway, don’t worry ...
Sheldon Biology Semester I Review Sheet
... object, go to medium and then high keeping the organism in the center of the field of view, only use the fine adjustment on high power. Lab practical??? Can you do this? Review microscope lab…. ...
... object, go to medium and then high keeping the organism in the center of the field of view, only use the fine adjustment on high power. Lab practical??? Can you do this? Review microscope lab…. ...
Worked solutions: Chapter 2 Human biochemistry
... amylopectin both 1-1,4 and 1-1,6 linkages form between 1-glucose monomers. Cellulose has a 2-1,4 linkage; that is, carbon 1 of a 2-glucose molecule forms a glycoside (ether) linkage with carbon 4 of an 1-glucose. Glycogen is a highly branched polymer with a similar structure to amylopectin, but more ...
... amylopectin both 1-1,4 and 1-1,6 linkages form between 1-glucose monomers. Cellulose has a 2-1,4 linkage; that is, carbon 1 of a 2-glucose molecule forms a glycoside (ether) linkage with carbon 4 of an 1-glucose. Glycogen is a highly branched polymer with a similar structure to amylopectin, but more ...
Comments on metabolic needs for glucose and the role of
... stored in polymeric form (glycogen) is dictated by osmotic pressure considerations. That stored fat is about eight times more calorically dense than glycogen, when attendant water is factored in, accounts for the predominance of fat as a storage form of calories and, also, for the fact that ingested ...
... stored in polymeric form (glycogen) is dictated by osmotic pressure considerations. That stored fat is about eight times more calorically dense than glycogen, when attendant water is factored in, accounts for the predominance of fat as a storage form of calories and, also, for the fact that ingested ...
Glycolysis
Glycolysis (from glycose, an older term for glucose + -lysis degradation) is the metabolic pathway that converts glucose C6H12O6, into pyruvate, CH3COCOO− + H+. The free energy released in this process is used to form the high-energy compounds ATP (adenosine triphosphate) and NADH (reduced nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide).Glycolysis is a determined sequence of ten enzyme-catalyzed reactions. The intermediates provide entry points to glycolysis. For example, most monosaccharides, such as fructose and galactose, can be converted to one of these intermediates. The intermediates may also be directly useful. For example, the intermediate dihydroxyacetone phosphate (DHAP) is a source of the glycerol that combines with fatty acids to form fat.Glycolysis is an oxygen independent metabolic pathway, meaning that it does not use molecular oxygen (i.e. atmospheric oxygen) for any of its reactions. However the products of glycolysis (pyruvate and NADH + H+) are sometimes disposed of using atmospheric oxygen. When molecular oxygen is used in the disposal of the products of glycolysis the process is usually referred to as aerobic, whereas if the disposal uses no oxygen the process is said to be anaerobic. Thus, glycolysis occurs, with variations, in nearly all organisms, both aerobic and anaerobic. The wide occurrence of glycolysis indicates that it is one of the most ancient metabolic pathways. Indeed, the reactions that constitute glycolysis and its parallel pathway, the pentose phosphate pathway, occur metal-catalyzed under the oxygen-free conditions of the Archean oceans, also in the absence of enzymes. Glycolysis could thus have originated from chemical constraints of the prebiotic world.Glycolysis occurs in most organisms in the cytosol of the cell. The most common type of glycolysis is the Embden–Meyerhof–Parnas (EMP pathway), which was discovered by Gustav Embden, Otto Meyerhof, and Jakub Karol Parnas. Glycolysis also refers to other pathways, such as the Entner–Doudoroff pathway and various heterofermentative and homofermentative pathways. However, the discussion here will be limited to the Embden–Meyerhof–Parnas pathway.The entire glycolysis pathway can be separated into two phases: The Preparatory Phase – in which ATP is consumed and is hence also known as the investment phase The Pay Off Phase – in which ATP is produced.↑ ↑ 2.0 2.1 ↑ ↑ ↑ ↑ ↑ ↑