A is for Aortic Arch:
... A is for Aortic Arch: Arteries are blood vessels that carry blood from the heart. Arteries are part of the circulatory system (that carries the blood to the various parts of the body). The heart is the pump that pushes the blood out through the arteries to tiny blood vessels called capillaries (that ...
... A is for Aortic Arch: Arteries are blood vessels that carry blood from the heart. Arteries are part of the circulatory system (that carries the blood to the various parts of the body). The heart is the pump that pushes the blood out through the arteries to tiny blood vessels called capillaries (that ...
HUMAN Body systems and Major Organs
... 7.Integumentary: Protection from infection, sense of touch A. Skin – sense pain/pleasure, hot/cold, shallow/deep pressure ...
... 7.Integumentary: Protection from infection, sense of touch A. Skin – sense pain/pleasure, hot/cold, shallow/deep pressure ...
human body 2 review sheet - Hicksville Public Schools
... ANTI –A TYPE B ANTI-B TYPE A 9. What eventually happens to fluid that leaks from capillaries? RETURNS TO BLOOD THROUGH THE LYMPHATIC SYSTEM 10. What is the function of lymph nodes? ...
... ANTI –A TYPE B ANTI-B TYPE A 9. What eventually happens to fluid that leaks from capillaries? RETURNS TO BLOOD THROUGH THE LYMPHATIC SYSTEM 10. What is the function of lymph nodes? ...
Wednesday 5/18
... Wednesday 5/18 • Learning Goal: Explain how the cardiovascular system functions as the transport system of the body. ...
... Wednesday 5/18 • Learning Goal: Explain how the cardiovascular system functions as the transport system of the body. ...
Components of Blood - Hicksville Public Schools / Homepage
... lymph. Lymph Nodes are small knobs of tissue that filter the lymph that passes through. ...
... lymph. Lymph Nodes are small knobs of tissue that filter the lymph that passes through. ...
Practice Questions for Exam IV
... Practice Questions: Exam IV Respiratory Control and the Renal System 1. What does the ventral respiratory group within the medulla oblongata do? a) triggers inspiration b) decreased ventilation rate c) nothing d) for forced breathing e) inhibits apneustic center, sets limits to over inflation of lun ...
... Practice Questions: Exam IV Respiratory Control and the Renal System 1. What does the ventral respiratory group within the medulla oblongata do? a) triggers inspiration b) decreased ventilation rate c) nothing d) for forced breathing e) inhibits apneustic center, sets limits to over inflation of lun ...
Fifth Grade
... • Plasma is the liquid component of the blood. • Blood pressure is a way to monitor the health of your circulatory system. • Heart disease kills more people than any other disease and that we can help keep our heart healthy by exercising, eating healthy and not smoking. ...
... • Plasma is the liquid component of the blood. • Blood pressure is a way to monitor the health of your circulatory system. • Heart disease kills more people than any other disease and that we can help keep our heart healthy by exercising, eating healthy and not smoking. ...
Unit XIV: Excretion
... good and bad substances - water, glucose, amino acids, salts, urea = filtrate – 180 L per day - ___________ – filtrate passes into ___________ – reabsorb ______ by osmosis, reabsorb good substances (_______ and __________) by active transport - Left over fluid is ________ – some water, salts, and ur ...
... good and bad substances - water, glucose, amino acids, salts, urea = filtrate – 180 L per day - ___________ – filtrate passes into ___________ – reabsorb ______ by osmosis, reabsorb good substances (_______ and __________) by active transport - Left over fluid is ________ – some water, salts, and ur ...
Name - Mr. Lesiuk
... ____4. Give two reasons why being bi-concave is advantageous for an erythrocyte? ___ 5. Erythrocytes are the only cells in the body that lack this organelle? ___ 6. Where in the body do all blood cells originate? ___ 7. How long does a typical R.B.C. (erythrocyte) live? ____8. What triggers the incr ...
... ____4. Give two reasons why being bi-concave is advantageous for an erythrocyte? ___ 5. Erythrocytes are the only cells in the body that lack this organelle? ___ 6. Where in the body do all blood cells originate? ___ 7. How long does a typical R.B.C. (erythrocyte) live? ____8. What triggers the incr ...
Skeletal System
... nutrients the body needs Usable nutrients are transported by the blood Waste the body cannot use = poop ...
... nutrients the body needs Usable nutrients are transported by the blood Waste the body cannot use = poop ...
BLOOD
... a) dissolved proteins : albumin : help to draw the water from tissues into blood globulins : ( immunoglobulins ) : impotant for immunity fibrinogen : participate in blood clotting b) glucose : important as energy store ( normal blood glucose level is 4,4 – 5,5 mmol/ l) c) other substances : amino ac ...
... a) dissolved proteins : albumin : help to draw the water from tissues into blood globulins : ( immunoglobulins ) : impotant for immunity fibrinogen : participate in blood clotting b) glucose : important as energy store ( normal blood glucose level is 4,4 – 5,5 mmol/ l) c) other substances : amino ac ...
Lesson #2
... Found in circulatory system throughout the body Veins carry blood back to the heart Hollow tubes ...
... Found in circulatory system throughout the body Veins carry blood back to the heart Hollow tubes ...
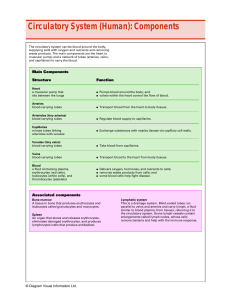
Circulatory System (Human): Components
... parallel to veins and arteries and carry lymph, a fluid similar to blood plasma, from tissues, returning it to the circulatory system. Some lymph vessels contain enlargements called lymph nodes, whose cells remove bacteria and help with the immune response. ...
... parallel to veins and arteries and carry lymph, a fluid similar to blood plasma, from tissues, returning it to the circulatory system. Some lymph vessels contain enlargements called lymph nodes, whose cells remove bacteria and help with the immune response. ...
Slide 1
... 1. carries oxygen from lungs to body cells and carries carbon dioxide to lungs to be exhaled 2. carries waste products from cells to kidneys 3. transports nutrients and other substances to body cells 4. cells and molecules in blood fight infections and help heal wounds ...
... 1. carries oxygen from lungs to body cells and carries carbon dioxide to lungs to be exhaled 2. carries waste products from cells to kidneys 3. transports nutrients and other substances to body cells 4. cells and molecules in blood fight infections and help heal wounds ...
The Circulatory System
... the body • Carries carbon dioxide from the body cells to the lungs to be exhaled • Carries waste to the kidneys to be disposed of • Carries nutrients to body cells • Contains immune system cells and molecules that ...
... the body • Carries carbon dioxide from the body cells to the lungs to be exhaled • Carries waste to the kidneys to be disposed of • Carries nutrients to body cells • Contains immune system cells and molecules that ...
Body Systems
... Function- when you breathe, the air you inhale supplies oxygen to the blood and gets rid of carbon dioxide Organs- pharynx, larynx, trachea, bronchi, alveoli, and diaphragm Pharynx- provides a passage way for food, liquid, and air Larynx- provides an airway for oxygen from the vocal cords Trachea- ...
... Function- when you breathe, the air you inhale supplies oxygen to the blood and gets rid of carbon dioxide Organs- pharynx, larynx, trachea, bronchi, alveoli, and diaphragm Pharynx- provides a passage way for food, liquid, and air Larynx- provides an airway for oxygen from the vocal cords Trachea- ...
Comparative Anatomy
... Since the worm has many cells NOT in contact with the external environment, it needs a circulatory system to distribute materials throughout its body. It Possesses a CLOSED circulatory system: It has blood vessels to contain the blood. Contains red pigment called hemoglobin. ...
... Since the worm has many cells NOT in contact with the external environment, it needs a circulatory system to distribute materials throughout its body. It Possesses a CLOSED circulatory system: It has blood vessels to contain the blood. Contains red pigment called hemoglobin. ...
Take it Home Tuesday #8 Name
... _____nervous system Breaks down food into nutrients small enough to be absorbed by cells. _____respiratory system E. Carries oxygen and nutrients to most body cells; picks up waste carbon dioxide to deliver back to the lungs. 2) Describe one way that two or more body systems work together. ...
... _____nervous system Breaks down food into nutrients small enough to be absorbed by cells. _____respiratory system E. Carries oxygen and nutrients to most body cells; picks up waste carbon dioxide to deliver back to the lungs. 2) Describe one way that two or more body systems work together. ...
Homeostasis

Homeostasis or homoeostasis (homeo- + -stasis) is the property of a system in which variables are regulated so that internal conditions remain stable and relatively constant. Examples of homeostasis include the regulation of temperature and the balance between acidity and alkalinity (pH). It is a process that maintains the stability of the human body's internal environment in response to changes in external conditions.The concept was described by French physiologist Claude Bernard in 1865 and the word was coined by Walter Bradford Cannon in 1926. Although the term was originally used to refer to processes within living organisms, it is frequently applied to automatic control systems such as thermostats. Homeostasis requires a sensor to detect changes in the condition to be regulated, an effector mechanism that can vary that condition, and a negative feedback connection between the two.