Reading Guide - Belle Vernon Area School District
... 24. Describe how breathing is regulated. Include the role of each of the following. a. Medulla ________________________________________________________________ b. pH ____________________________________________________________________ c. Carotid arteries ____________________________________________ ...
... 24. Describe how breathing is regulated. Include the role of each of the following. a. Medulla ________________________________________________________________ b. pH ____________________________________________________________________ c. Carotid arteries ____________________________________________ ...
Chapter 9
... Energy stored in food is used by the mitochondria and changed to a form of energy that the cell can use to grow and do work Half the energy stored in glucose is released as thermal energy (heat) The process requires oxygen and produces carbon dioxide and water ...
... Energy stored in food is used by the mitochondria and changed to a form of energy that the cell can use to grow and do work Half the energy stored in glucose is released as thermal energy (heat) The process requires oxygen and produces carbon dioxide and water ...
Circulatory & Respiratory Systems
... – Transport O2 , CO2 & waste – Distributes nutrients & hormones – Regulates body temperature – Protects against blood loss & disease ...
... – Transport O2 , CO2 & waste – Distributes nutrients & hormones – Regulates body temperature – Protects against blood loss & disease ...
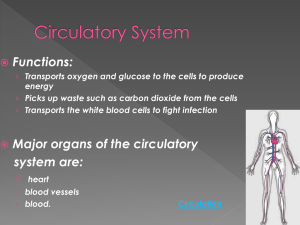
THE CIRCULATORY SYSTEM
... THE HEART • The heart is an organ that pumps the blood through the circulatory system. It allows the blood is always in movement. It’s formed by the myocardial, a cardiac muscular tissue. The heart is made up of four chambers, the two large are the ventricles and the other two are called auricles. ...
... THE HEART • The heart is an organ that pumps the blood through the circulatory system. It allows the blood is always in movement. It’s formed by the myocardial, a cardiac muscular tissue. The heart is made up of four chambers, the two large are the ventricles and the other two are called auricles. ...
Chapter 3 - Body Systems - podcasts.shelbyed.k12.al.
... 12. What do the villi in the small intestine do? They provide more surface area to absorb food. 13. Be able to label the ventricles and the atriums of the heart. 14. Be able to label the parts of the respiratory system. Short Answer: 15. Where do the respiratory and the circulatory systems work toge ...
... 12. What do the villi in the small intestine do? They provide more surface area to absorb food. 13. Be able to label the ventricles and the atriums of the heart. 14. Be able to label the parts of the respiratory system. Short Answer: 15. Where do the respiratory and the circulatory systems work toge ...
Hematologic System
... (about 5.6 liters in a 72 Kg man). This proportion is less in women, while in children is greater (gradually decreasing until the adult level is reached). ...
... (about 5.6 liters in a 72 Kg man). This proportion is less in women, while in children is greater (gradually decreasing until the adult level is reached). ...
Circulatory & Respiratory Systems
... top of the heart; collect blood as it enters b. Ventricles- large chambers on the bottom of the heart; pump blood out of the heart 2. Valves- one way doors; make the sound of the heartbeat ...
... top of the heart; collect blood as it enters b. Ventricles- large chambers on the bottom of the heart; pump blood out of the heart 2. Valves- one way doors; make the sound of the heartbeat ...
Benchmark 3 Study Guide
... What are neurotransmitters, where are they found and what is their job? How can we tell the type of neuron that is in use? The brain is divided into 3 part o Name them o What are each part in control of in the body o Be able to identify them Review the passage of a nerve impulse along the ax ...
... What are neurotransmitters, where are they found and what is their job? How can we tell the type of neuron that is in use? The brain is divided into 3 part o Name them o What are each part in control of in the body o Be able to identify them Review the passage of a nerve impulse along the ax ...
Notes template for Circulatory system
... Slide 1 – What do the Circulatory and Respiratory system do together/ Slide 2 - What do blood vessels do? What kind of tissue make up blood vessels? Why are they mad of this kid of tissue? Why are red blood cells important? Thinking about what we’ve written: review these answers and respond to this ...
... Slide 1 – What do the Circulatory and Respiratory system do together/ Slide 2 - What do blood vessels do? What kind of tissue make up blood vessels? Why are they mad of this kid of tissue? Why are red blood cells important? Thinking about what we’ve written: review these answers and respond to this ...
The Human Body Review - Effingham County Schools
... • Smooth Musclesinvoluntary muscle that moves food through the digestive tract and controls blood flow. •Cardiac MuscleOnly found in the ...
... • Smooth Musclesinvoluntary muscle that moves food through the digestive tract and controls blood flow. •Cardiac MuscleOnly found in the ...
The Circulatory System
... Some white blood cells surround and consume harmful microbes. Some produce chemicals called antibodies that fight infection. ...
... Some white blood cells surround and consume harmful microbes. Some produce chemicals called antibodies that fight infection. ...
Blocked and normal arteries
... straws are pointing down so that the water can flow out. Pour in the coloured water. 7. The coloured water will flow out both straws but at different rates ...
... straws are pointing down so that the water can flow out. Pour in the coloured water. 7. The coloured water will flow out both straws but at different rates ...
Lecture PowerPoint
... Understanding the Organization of the Body Cells: fundamental units of all living organisms. Cells are specialized to specific functions in the body. There is a division of labor. Some cells produce mineral for bone, some cells produce protein for muscle contraction, etc. Tissues: Tissues are group ...
... Understanding the Organization of the Body Cells: fundamental units of all living organisms. Cells are specialized to specific functions in the body. There is a division of labor. Some cells produce mineral for bone, some cells produce protein for muscle contraction, etc. Tissues: Tissues are group ...
Cardiovascular System Notes
... Capillaries =Exchanges nutrients and waste products with the body’s cells. -Capillary walls are 1 cell thick -Nutrients and wastes are exchanged are exchanged through a process called diffusion -Diffusion is movement of substances from an area of higher concentration to an area of lower concentratio ...
... Capillaries =Exchanges nutrients and waste products with the body’s cells. -Capillary walls are 1 cell thick -Nutrients and wastes are exchanged are exchanged through a process called diffusion -Diffusion is movement of substances from an area of higher concentration to an area of lower concentratio ...
Copyright © Glencoe/McGraw-Hill, a division of the McGraw
... 1. The ____________ is a tubelike passageway used by food, liquid, and air; lower end has a tissue flap called the epiglottis, to prevent food or liquid from entering the airway. 2. Air passes through the ___________, which contains the vocal cords used to speak. 3. ____________—tube held open by ri ...
... 1. The ____________ is a tubelike passageway used by food, liquid, and air; lower end has a tissue flap called the epiglottis, to prevent food or liquid from entering the airway. 2. Air passes through the ___________, which contains the vocal cords used to speak. 3. ____________—tube held open by ri ...
Compl
... 1. Name 2 major processes that the liver does to promote homeostasis with the human body. ...
... 1. Name 2 major processes that the liver does to promote homeostasis with the human body. ...
File
... Antarctic fishes, where temperatures can drop below the freezing point of unprotected body fluids (about -0.7oC). ...
... Antarctic fishes, where temperatures can drop below the freezing point of unprotected body fluids (about -0.7oC). ...
Excretory System
... 1. Carbon dioxide (lungs) 2. Sweat (skin) 3. Urine (kidneys) 4. Excrement also known as POOP (large intestines) (tears, ear wax, snot, gas) (vomit and pus when sick or have an infection) ...
... 1. Carbon dioxide (lungs) 2. Sweat (skin) 3. Urine (kidneys) 4. Excrement also known as POOP (large intestines) (tears, ear wax, snot, gas) (vomit and pus when sick or have an infection) ...
Chapter 2 - Bison Academy
... Red blood cells are the oxygen carrying cells and are produced by the bone marrow. Hemoglobin, the oxygen carrying compound, makes up 95% of the RBC’s dry weight. Oxygen enters the blood by diffusion across lung membranes. Once in the blood, almost all the oxygen is transported by the hemoglobin loc ...
... Red blood cells are the oxygen carrying cells and are produced by the bone marrow. Hemoglobin, the oxygen carrying compound, makes up 95% of the RBC’s dry weight. Oxygen enters the blood by diffusion across lung membranes. Once in the blood, almost all the oxygen is transported by the hemoglobin loc ...
Homeostasis

Homeostasis or homoeostasis (homeo- + -stasis) is the property of a system in which variables are regulated so that internal conditions remain stable and relatively constant. Examples of homeostasis include the regulation of temperature and the balance between acidity and alkalinity (pH). It is a process that maintains the stability of the human body's internal environment in response to changes in external conditions.The concept was described by French physiologist Claude Bernard in 1865 and the word was coined by Walter Bradford Cannon in 1926. Although the term was originally used to refer to processes within living organisms, it is frequently applied to automatic control systems such as thermostats. Homeostasis requires a sensor to detect changes in the condition to be regulated, an effector mechanism that can vary that condition, and a negative feedback connection between the two.