Human Organ Systems
... lymph nodes and vessels, white blood cells mouth, esophagus, stomach, liver, pancreas, small and large intestines kidneys, ureters, bladder, urethra, skin, lungs brain, spinal cord, nerves, sense organs, receptors ...
... lymph nodes and vessels, white blood cells mouth, esophagus, stomach, liver, pancreas, small and large intestines kidneys, ureters, bladder, urethra, skin, lungs brain, spinal cord, nerves, sense organs, receptors ...
Circulatory System
... 5 types of leukocytes: 1. Neutrophils – phagocytize bacteria by secreting an enzyme called lysozyme 2. Eosinophils – remove toxins & defend the body from allergic reactions by producing ...
... 5 types of leukocytes: 1. Neutrophils – phagocytize bacteria by secreting an enzyme called lysozyme 2. Eosinophils – remove toxins & defend the body from allergic reactions by producing ...
What is Homeostasis?
... What is Homeostasis? Homeostasis is… the equilibrium of the internal environment within an organism. Disturbances in Homeostasis cause decreased function of the cell, organism and population. In essence, homeostasis is the desired constancy that allows the body to function in the most efficient ...
... What is Homeostasis? Homeostasis is… the equilibrium of the internal environment within an organism. Disturbances in Homeostasis cause decreased function of the cell, organism and population. In essence, homeostasis is the desired constancy that allows the body to function in the most efficient ...
Physiology
... The E.C.F. contains large amounts of sodium, chloride and bicarbonate ions, plus nutrients for cells, such as oxygen, glucose, fatty acids and amino acids …etc. The I.C.F. differs significantly from the E.C.F. particularly, it contains large amount of potassium, magnesium and phosphate ions instead ...
... The E.C.F. contains large amounts of sodium, chloride and bicarbonate ions, plus nutrients for cells, such as oxygen, glucose, fatty acids and amino acids …etc. The I.C.F. differs significantly from the E.C.F. particularly, it contains large amount of potassium, magnesium and phosphate ions instead ...
1. The body`s transport system - CIS-Science-and
... veins and capillaries. Stretched end-to-end, that's three times around the world! They transport oxygen from the lungs, remove carbon dioxide from the cells and carry nutrients, hormones and water to all parts of the body. ...
... veins and capillaries. Stretched end-to-end, that's three times around the world! They transport oxygen from the lungs, remove carbon dioxide from the cells and carry nutrients, hormones and water to all parts of the body. ...
SUPER IMPORTANT! MATCH-UP your body`s organ systems and
... organs, provides a framework the muscles can use to provide movement, blood cells are formed within bones ...
... organs, provides a framework the muscles can use to provide movement, blood cells are formed within bones ...
Sample of - Test Bank Instant
... 3. A large volume of blood is transfused to a person whose baroreceptor blood pressure control system is not functioning and arterial blood pressure rises from the normal level of 100 to 160 mm Hg. If the same volume of blood is infused into the same person when the baroreceptor system is functionin ...
... 3. A large volume of blood is transfused to a person whose baroreceptor blood pressure control system is not functioning and arterial blood pressure rises from the normal level of 100 to 160 mm Hg. If the same volume of blood is infused into the same person when the baroreceptor system is functionin ...
Circulatory System Cloze
... All animals need to ________________ materials around to the different parts of their body. This is the job of the ________________ system. The circulatory system consists of a liquid called _______________, a pump called the ________________ and a series of vessels called _________________ and ____ ...
... All animals need to ________________ materials around to the different parts of their body. This is the job of the ________________ system. The circulatory system consists of a liquid called _______________, a pump called the ________________ and a series of vessels called _________________ and ____ ...
Circulatory/ Cardiovascular System
... Blood vessel that carries oxygen-rich blood away from the heart and to the body parts. ...
... Blood vessel that carries oxygen-rich blood away from the heart and to the body parts. ...
Chapter 33 Circulatory and Respiratory Systems
... 1-Which are the most numerous blood cells in the body? RED 2-The thymus organ produces which type of cells? T LYMPHOCYTES 3-Which organ removes old and damaged blood cells? SPLEEN 4-What type of molecule is cholesterol? FAT/LIPID 5-Which organ manufactures cholesterol? LIVER 6-How is carbon dioxide ...
... 1-Which are the most numerous blood cells in the body? RED 2-The thymus organ produces which type of cells? T LYMPHOCYTES 3-Which organ removes old and damaged blood cells? SPLEEN 4-What type of molecule is cholesterol? FAT/LIPID 5-Which organ manufactures cholesterol? LIVER 6-How is carbon dioxide ...
Textbook of Medical Physiology, 11 th Edition
... Full file at http://testbanksinstant.eu/ Test-Bank-for-Textbook-of-Medical-Physiology,-11th-Edition-ArthurC.-GuytonGuyton & Hall: Textbook of Medical Physiology, 11th Edition Test Bank Chapter 1: Functional Organization of the Human Body and Control of the "Internal Environment" Cells as the Living ...
... Full file at http://testbanksinstant.eu/ Test-Bank-for-Textbook-of-Medical-Physiology,-11th-Edition-ArthurC.-GuytonGuyton & Hall: Textbook of Medical Physiology, 11th Edition Test Bank Chapter 1: Functional Organization of the Human Body and Control of the "Internal Environment" Cells as the Living ...
Pg. 387 1-9 - Cobb Learning
... Opening: • Name the three types of muscles and tell me if they are voluntary or involuntary. ...
... Opening: • Name the three types of muscles and tell me if they are voluntary or involuntary. ...
Human Body Systems
... ____________liquid part of blood ____________liquid part ____________clotting What is blood pressure? ...
... ____________liquid part of blood ____________liquid part ____________clotting What is blood pressure? ...
Name - mrsboysbiology
... 14) What is the circulatory system that extends from the heart to the farthest reaches of the body? ...
... 14) What is the circulatory system that extends from the heart to the farthest reaches of the body? ...
Guyton and Hall Textbook of Medical Physiology
... 3. A large volume of blood is transfused to a person whose baroreceptor blood pressure control system is not functioning and arterial blood pressure rises from the normal level of 100 to 160 mm Hg. If the same volume of blood is infused into the same person when the baroreceptor system is functionin ...
... 3. A large volume of blood is transfused to a person whose baroreceptor blood pressure control system is not functioning and arterial blood pressure rises from the normal level of 100 to 160 mm Hg. If the same volume of blood is infused into the same person when the baroreceptor system is functionin ...
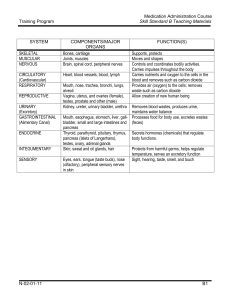
Body Systems, Organs and Functions
... Provides air (oxygen) to the cells; removes waste such as carbon dioxide Allow creation of new human being ...
... Provides air (oxygen) to the cells; removes waste such as carbon dioxide Allow creation of new human being ...
Chapter 38: Excretory System
... a. Collect water and filter body fluids b. Remove and concentrate waste products from body fluids and return other substances to body fluids as necessary for homeostasis c. Eliminate excretory products from the body - Include the kidneys (removes the most metabolic waste via urine),liver, lungs, and ...
... a. Collect water and filter body fluids b. Remove and concentrate waste products from body fluids and return other substances to body fluids as necessary for homeostasis c. Eliminate excretory products from the body - Include the kidneys (removes the most metabolic waste via urine),liver, lungs, and ...
Insulin Glucagon
... › role of the hypothalamus to control body temperature › role of sweat glands to control body temperature › role of the skin arterioles to control body temperature › role of shivering to control body temperature Include one advantage and one disadvantage of being warm blooded Criteria Evaluated: B a ...
... › role of the hypothalamus to control body temperature › role of sweat glands to control body temperature › role of the skin arterioles to control body temperature › role of shivering to control body temperature Include one advantage and one disadvantage of being warm blooded Criteria Evaluated: B a ...
homeostasis and feedback with video clip
... • Set point – what is the desired range? • Sensors – structures including receptors on target cells that will monitor levels relative to set point • Controller – determine if levels are within set point range and what response is necessary to return to range • Effector – parts of body that physicall ...
... • Set point – what is the desired range? • Sensors – structures including receptors on target cells that will monitor levels relative to set point • Controller – determine if levels are within set point range and what response is necessary to return to range • Effector – parts of body that physicall ...
Homeostasis

Homeostasis or homoeostasis (homeo- + -stasis) is the property of a system in which variables are regulated so that internal conditions remain stable and relatively constant. Examples of homeostasis include the regulation of temperature and the balance between acidity and alkalinity (pH). It is a process that maintains the stability of the human body's internal environment in response to changes in external conditions.The concept was described by French physiologist Claude Bernard in 1865 and the word was coined by Walter Bradford Cannon in 1926. Although the term was originally used to refer to processes within living organisms, it is frequently applied to automatic control systems such as thermostats. Homeostasis requires a sensor to detect changes in the condition to be regulated, an effector mechanism that can vary that condition, and a negative feedback connection between the two.