Chapter 37 Notes Circulatory and Respiratory Systems
... pressure in the arteries. This force is known as blood pressure. As the heart relaxes, blood pressure decreases. Through sensory receptors in several places of the body, your body regulates blood pressure by detecting different levels and sending impulses to the medulla oblongata region of the brain ...
... pressure in the arteries. This force is known as blood pressure. As the heart relaxes, blood pressure decreases. Through sensory receptors in several places of the body, your body regulates blood pressure by detecting different levels and sending impulses to the medulla oblongata region of the brain ...
Unit 6: Human Health And Physiology
... of collecting blood, pumping blood and opening and closing valves. • Atria- collect blood into heart • Ventricles- send blood out of the heart. • The direction of flow is controlled by atrioventricular and semilunar valves. ...
... of collecting blood, pumping blood and opening and closing valves. • Atria- collect blood into heart • Ventricles- send blood out of the heart. • The direction of flow is controlled by atrioventricular and semilunar valves. ...
File
... • Arteries – carry blood away from the heart. • Veins – returns blood to the heart. • Capillaries - connect veins and arteries. • Capillaries allow nutrients to pass through them into other cells of the body. ...
... • Arteries – carry blood away from the heart. • Veins – returns blood to the heart. • Capillaries - connect veins and arteries. • Capillaries allow nutrients to pass through them into other cells of the body. ...
File - biologywithsteiner
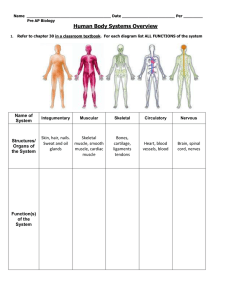
... Refer to chapter 30 in a classroom textbook. For each diagram list ALL FUNCTIONS of the system ...
... Refer to chapter 30 in a classroom textbook. For each diagram list ALL FUNCTIONS of the system ...
Circulatory and Respiratory Review
... Which Blood Cell? Defends the body against bacterial infection and invasion by foreign ...
... Which Blood Cell? Defends the body against bacterial infection and invasion by foreign ...
Respiration
... protein – large group of compounds that are essential constituents of living cells; consist of polymers of amino acids; essential in the diet of animals for growth and for repair of tissues; can be obtained from meat and eggs and milk ...
... protein – large group of compounds that are essential constituents of living cells; consist of polymers of amino acids; essential in the diet of animals for growth and for repair of tissues; can be obtained from meat and eggs and milk ...
Study Guide for Exam II
... What organ are stomata found on and what do they do? Why are stomata more open at night than in the day? Homeostasis What is homeostasis? How is a negative feedback loop used in homeostasis? Animals Name the 4 animal tissue types and describe their functions. How is each tissue type used in skin? Ca ...
... What organ are stomata found on and what do they do? Why are stomata more open at night than in the day? Homeostasis What is homeostasis? How is a negative feedback loop used in homeostasis? Animals Name the 4 animal tissue types and describe their functions. How is each tissue type used in skin? Ca ...
Circulatory and Respiratory Systems
... Pulmonary and Systemic Circulation • The flow of blood to the heart (pulmonary) then lungs, back to the heart, then out to the rest of the body (systemic) ...
... Pulmonary and Systemic Circulation • The flow of blood to the heart (pulmonary) then lungs, back to the heart, then out to the rest of the body (systemic) ...
Crossword for "Circulation and Excretion"
... The circulatory system is a transport system which brings digested food and oxygen to every part of the body and carries away metabolic wastes. The heart pumps blood which circulates in blood vessels. It has four chambers, the left and right atriums (auricles) and the left and right ventricles. Ther ...
... The circulatory system is a transport system which brings digested food and oxygen to every part of the body and carries away metabolic wastes. The heart pumps blood which circulates in blood vessels. It has four chambers, the left and right atriums (auricles) and the left and right ventricles. Ther ...
The Circulatory System - Resuscitation Academy
... contribute to the cleansing function of the respiratory system, for they, too, are lined with mucous membranes and ciliated cells that move mucus upward to the pharynx. ...
... contribute to the cleansing function of the respiratory system, for they, too, are lined with mucous membranes and ciliated cells that move mucus upward to the pharynx. ...
b5 clinic revision
... Gaseous exchange happens in the alveolithey are permeable, moist, large surface ...
... Gaseous exchange happens in the alveolithey are permeable, moist, large surface ...
BLOOD PHYSIOLOGY
... General Functions of blood 1.Transportation:. O2 from lungs --- cells cells , CO2 by cells ---- lungs 2.nutrients, electrolytes & water from gastrointestinal tract to cells ingested , waste products are transported from cells --- kidneys for elimination in urine ...
... General Functions of blood 1.Transportation:. O2 from lungs --- cells cells , CO2 by cells ---- lungs 2.nutrients, electrolytes & water from gastrointestinal tract to cells ingested , waste products are transported from cells --- kidneys for elimination in urine ...
Circulatory System Review
... 1. What are the basic needs of all living cells? a. Food (energy), water, gases (gas exchange), and waste removal are the basic needs of all living cells. 2. How do the cells in multi-cellular organisms get the resources they need to stay alive? a. Blood flowing through the circulatory system delive ...
... 1. What are the basic needs of all living cells? a. Food (energy), water, gases (gas exchange), and waste removal are the basic needs of all living cells. 2. How do the cells in multi-cellular organisms get the resources they need to stay alive? a. Blood flowing through the circulatory system delive ...
Cardiovascular Notes
... What Does C-V System do? Circulate blood throughout entire body for Transport of oxygen to cells Transport of CO2 away from cells Transport of nutrients (glucose) to cells Movement of immune system components (cells, antibodies) Transport of endocrine gland secretions ...
... What Does C-V System do? Circulate blood throughout entire body for Transport of oxygen to cells Transport of CO2 away from cells Transport of nutrients (glucose) to cells Movement of immune system components (cells, antibodies) Transport of endocrine gland secretions ...
Unit A, “Processes of Living Things”
... What do the villi do? Put nutrients into the blood After leaving the small intestine, food enters the _____large intestine __________. Eventually wastes are removed from the body. Name two other organs involved in digestion. What do they do? Liver – produces bile, which is stored in the gallbladder, ...
... What do the villi do? Put nutrients into the blood After leaving the small intestine, food enters the _____large intestine __________. Eventually wastes are removed from the body. Name two other organs involved in digestion. What do they do? Liver – produces bile, which is stored in the gallbladder, ...
Circulatory System
... arteries to cells - cells absorb O2 ; release CO2 & other wastes - some waste – eliminated by kidneys, etc - carries blood back to heart ...
... arteries to cells - cells absorb O2 ; release CO2 & other wastes - some waste – eliminated by kidneys, etc - carries blood back to heart ...
Cardiovascular Lab
... Closed Circulatory System: Transport efficiency is increased when there is a closed route for the transport of the blood back to the heart Heart (Pump) Blood Vessels (Tube network) Blood (Circulating ...
... Closed Circulatory System: Transport efficiency is increased when there is a closed route for the transport of the blood back to the heart Heart (Pump) Blood Vessels (Tube network) Blood (Circulating ...
Spring systems review
... 2. Muscles are necessary for body movement. 3. Nerve cells are known as neurons. 4. Arteries are vessels that carry blood away from the heart. 5. The respiratory system brings carbon dioxide to the body & eliminates oxygen. 6. The skin helps to regulate body temperature. 7. The veins are the only bl ...
... 2. Muscles are necessary for body movement. 3. Nerve cells are known as neurons. 4. Arteries are vessels that carry blood away from the heart. 5. The respiratory system brings carbon dioxide to the body & eliminates oxygen. 6. The skin helps to regulate body temperature. 7. The veins are the only bl ...
Principles of Homeostasis Maintaining Homeostasis
... The kidney is the primary regulator of fluid and ions. When large quantities of fluid must be excreted, the kidney produces large amounts of dilute urine. When water must be conserved, small amounts of concentrated urine are produced, ADH (antidiuretic hormone) causes more water to be reabsorbed fro ...
... The kidney is the primary regulator of fluid and ions. When large quantities of fluid must be excreted, the kidney produces large amounts of dilute urine. When water must be conserved, small amounts of concentrated urine are produced, ADH (antidiuretic hormone) causes more water to be reabsorbed fro ...
Human Body Fact Sheet - Scottish Wider Access Programme
... Blood that is rich in oxygen appears __________________ ...
... Blood that is rich in oxygen appears __________________ ...
Human Body Fact Sheet - Scottish Wider Access Programme
... Blood that is rich in oxygen appears __________________ ...
... Blood that is rich in oxygen appears __________________ ...
Investigation 1 “Living Cells”
... 1. Cell: the basic unit of life. 2. Oxygen: an atmospheric gas needed by most living cells. 3. Carbon Dioxide: a waste gas product by living cells. 4. Heart: a muscular organ that contracts rhythmically, producing a pulse with each contraction. a. The human heart has four chambers: the right atrium, ...
... 1. Cell: the basic unit of life. 2. Oxygen: an atmospheric gas needed by most living cells. 3. Carbon Dioxide: a waste gas product by living cells. 4. Heart: a muscular organ that contracts rhythmically, producing a pulse with each contraction. a. The human heart has four chambers: the right atrium, ...
Homeostasis

Homeostasis or homoeostasis (homeo- + -stasis) is the property of a system in which variables are regulated so that internal conditions remain stable and relatively constant. Examples of homeostasis include the regulation of temperature and the balance between acidity and alkalinity (pH). It is a process that maintains the stability of the human body's internal environment in response to changes in external conditions.The concept was described by French physiologist Claude Bernard in 1865 and the word was coined by Walter Bradford Cannon in 1926. Although the term was originally used to refer to processes within living organisms, it is frequently applied to automatic control systems such as thermostats. Homeostasis requires a sensor to detect changes in the condition to be regulated, an effector mechanism that can vary that condition, and a negative feedback connection between the two.