Function of the blood
... The plasma is also responsible for the transportation of hormones, which have been secreted by the endocrine glands, to the target organs. Hormones like erythropoietin, which are responsible for stimulating the production of erythrocytes, are transported in plasma. Other hormones like testosterone, ...
... The plasma is also responsible for the transportation of hormones, which have been secreted by the endocrine glands, to the target organs. Hormones like erythropoietin, which are responsible for stimulating the production of erythrocytes, are transported in plasma. Other hormones like testosterone, ...
The Circulatory System
... Function - transport The blood transports nutrients from the digestive system and lungs to the tissues. Also transports waste products to the lungs and urinary systems. ...
... Function - transport The blood transports nutrients from the digestive system and lungs to the tissues. Also transports waste products to the lungs and urinary systems. ...
circ and homeo
... • Animals capable of temperature regulation within a given range are deemed homeotherms (alternatively homiotherms or homotherms). They have the ability to regulate temperature via negative feedback control which is outlined below • Temperature fluctuations in the body are recognized by thermorecept ...
... • Animals capable of temperature regulation within a given range are deemed homeotherms (alternatively homiotherms or homotherms). They have the ability to regulate temperature via negative feedback control which is outlined below • Temperature fluctuations in the body are recognized by thermorecept ...
Circulatory System
... We maintain a healthy system by… • Eating healthy foods such as fruits and vegetables, grain, and dairy products. • Exercising a little bit each day ...
... We maintain a healthy system by… • Eating healthy foods such as fruits and vegetables, grain, and dairy products. • Exercising a little bit each day ...
Levels of Organization Student Handout
... 3. Cardiovascular (Circulatory) – Delivers food/oxygen to body cells; carries carbon dioxide away from cells. (heart, arteries, veins, capillaries) 4. Muscular – Allows for movement. (muscles, tendons) Examples of muscles: tricep, bicep, quadricep, hamstring 5. Digestive – Food is broken down into s ...
... 3. Cardiovascular (Circulatory) – Delivers food/oxygen to body cells; carries carbon dioxide away from cells. (heart, arteries, veins, capillaries) 4. Muscular – Allows for movement. (muscles, tendons) Examples of muscles: tricep, bicep, quadricep, hamstring 5. Digestive – Food is broken down into s ...
Circulatory System Exam
... 2. What kind of blood cell carries oxygen? What allows them to do this? 3. Name the three types of blood cells: 4. Describe the function of each type of blood cell. 5. What is the main function of the circulatory system? 6. Name the three types of blood vessels and state their function. 7. Why does ...
... 2. What kind of blood cell carries oxygen? What allows them to do this? 3. Name the three types of blood cells: 4. Describe the function of each type of blood cell. 5. What is the main function of the circulatory system? 6. Name the three types of blood vessels and state their function. 7. Why does ...
Mammalian Diving Reflex
... Adaptations for Diving • Medulla oblongata- part of brain that deals with autonomic functions – Less sensitive to CO2 levels in blood, so they can stay submerged longer without feeling the “need” to inhale ...
... Adaptations for Diving • Medulla oblongata- part of brain that deals with autonomic functions – Less sensitive to CO2 levels in blood, so they can stay submerged longer without feeling the “need” to inhale ...
Structural levels of organization:
... o come together to form cells o smallest unit of living things o basic structure of all living things cellular level examined in chapter 3. tissues o groups of similar cells with common function o 4 basic types o come together to make up… organs o complex functions become possible organ system o gro ...
... o come together to form cells o smallest unit of living things o basic structure of all living things cellular level examined in chapter 3. tissues o groups of similar cells with common function o 4 basic types o come together to make up… organs o complex functions become possible organ system o gro ...
Human Homeostasis Study Aid Circulatory System Main Connective
... Integrates information from various senses Conscious thought, mood/personality Smell, sound Sight Muscle coordination and balance Involuntary functions (internal organs) ...
... Integrates information from various senses Conscious thought, mood/personality Smell, sound Sight Muscle coordination and balance Involuntary functions (internal organs) ...
PowerPoint Presentation - Burlington Area Schools
... smallest unit of living things o basic structure of all living things cellular level examined in chapter 3. ...
... smallest unit of living things o basic structure of all living things cellular level examined in chapter 3. ...
day 5 intro to circulation
... consists of 3 general components 1) Blood: a fluid that transports nutrients, wastes, oxygen, carbon dioxide and hormones 2) A system of blood vessels that contain the blood 3) The heart: the pump that pushes the fluid through the blood vessels ...
... consists of 3 general components 1) Blood: a fluid that transports nutrients, wastes, oxygen, carbon dioxide and hormones 2) A system of blood vessels that contain the blood 3) The heart: the pump that pushes the fluid through the blood vessels ...
THE HUMAN ENDOCRINE SYSTEM Refer to the diagram of the
... sweating to lower the body temperature back to normal. ♦ Positive feedback mechanisms are those in which the stimulus causes a change that increases, rather than decreases, the original stimulus. An example of positive feedback is the action potential of a nerve cell. ...
... sweating to lower the body temperature back to normal. ♦ Positive feedback mechanisms are those in which the stimulus causes a change that increases, rather than decreases, the original stimulus. An example of positive feedback is the action potential of a nerve cell. ...
Biology Final Exam Review Topic 4: The Human Body I
... A) Moves _________through the body to the organs and cells that need them. B) Transported material includes: 1. ___________and __________from intestines to all cells of body. 2. ________from lungs to all cells of the body. 3. ________from glands to target cells 4. ________from all cells to the excre ...
... A) Moves _________through the body to the organs and cells that need them. B) Transported material includes: 1. ___________and __________from intestines to all cells of body. 2. ________from lungs to all cells of the body. 3. ________from glands to target cells 4. ________from all cells to the excre ...
Respiration Case Study
... Acute Mountain Sickness is also known as altitude sickness. AMS is an illness that affects people like mountain climbers or skiers at high altitudes. 2. What causes this illness? This is caused by low oxygen levels and decreased air pressure. These produce adverse effects from the decrease in alveol ...
... Acute Mountain Sickness is also known as altitude sickness. AMS is an illness that affects people like mountain climbers or skiers at high altitudes. 2. What causes this illness? This is caused by low oxygen levels and decreased air pressure. These produce adverse effects from the decrease in alveol ...
Cardiovascular System
... the heart. • Arteries have a thick wall . • Each heart beat pumps blood into your arteries at high pressure. • This is your blood pressure. • Oxygen rich blood ...
... the heart. • Arteries have a thick wall . • Each heart beat pumps blood into your arteries at high pressure. • This is your blood pressure. • Oxygen rich blood ...
The ABCs of CVTs
... disease where the immune system produces antibodies to attack and destroy its own red blood cells. When the destruction of the red blood cells is faster than production of red blood cells an anemia results. ...
... disease where the immune system produces antibodies to attack and destroy its own red blood cells. When the destruction of the red blood cells is faster than production of red blood cells an anemia results. ...
Evolution of the Circulatory System
... • Blood vessel pumps blood through peristalsis to large sinuses where organs are bathed in blood. • Only works in small organisms where cells are close to environment. ...
... • Blood vessel pumps blood through peristalsis to large sinuses where organs are bathed in blood. • Only works in small organisms where cells are close to environment. ...
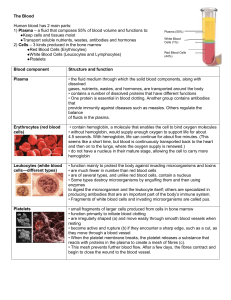
Red Blood Cells (Erythrocytes)
... 1) Plasma – a fluid that composes 55% of blood volume and functions to: ●Keep cells and tissues moist ●Transport soluble nutrients, wastes, antibodies and hormones 2) Cells – 3 kinds produced in the bone marrow ●Red Blood Cells (Erythrocytes) ●White Blood Cells (Leucocytes and Lymphocytes) ...
... 1) Plasma – a fluid that composes 55% of blood volume and functions to: ●Keep cells and tissues moist ●Transport soluble nutrients, wastes, antibodies and hormones 2) Cells – 3 kinds produced in the bone marrow ●Red Blood Cells (Erythrocytes) ●White Blood Cells (Leucocytes and Lymphocytes) ...
Science Test 2 – How does the body transport materials1
... 4. (2 p) What is the importance of the left and the right sides of the heart? The Systemic circulation departs from the left side of the heart, the pulmonary circulation departs from the right side of the heart. 5. (2 p) Mary is not feeling well, so her mother took her to the doctor. The doctor orde ...
... 4. (2 p) What is the importance of the left and the right sides of the heart? The Systemic circulation departs from the left side of the heart, the pulmonary circulation departs from the right side of the heart. 5. (2 p) Mary is not feeling well, so her mother took her to the doctor. The doctor orde ...
Chp.6 Circulatory System 2
... – Contain cup-like valves to prevent back flow, and carry blood containing waste products from capillaries back to heart – Located closer to outer surface off body than arteries ...
... – Contain cup-like valves to prevent back flow, and carry blood containing waste products from capillaries back to heart – Located closer to outer surface off body than arteries ...
Triple Science Biology - The Thomas Cowley High School
... – Atria (singular- Atrium) Bottom chambers ventricles. Left hand side pumps oxygenated blood to body – wall much thicker. sound Lubb Dubb – valves. How heart works. ...
... – Atria (singular- Atrium) Bottom chambers ventricles. Left hand side pumps oxygenated blood to body – wall much thicker. sound Lubb Dubb – valves. How heart works. ...
intro to anatom
... (eyes, ears, touch receptors, taste buds, and smell receptors) Major organs are the brain, spinal cord, and all of the major nerves. ...
... (eyes, ears, touch receptors, taste buds, and smell receptors) Major organs are the brain, spinal cord, and all of the major nerves. ...
Homeostasis

Homeostasis or homoeostasis (homeo- + -stasis) is the property of a system in which variables are regulated so that internal conditions remain stable and relatively constant. Examples of homeostasis include the regulation of temperature and the balance between acidity and alkalinity (pH). It is a process that maintains the stability of the human body's internal environment in response to changes in external conditions.The concept was described by French physiologist Claude Bernard in 1865 and the word was coined by Walter Bradford Cannon in 1926. Although the term was originally used to refer to processes within living organisms, it is frequently applied to automatic control systems such as thermostats. Homeostasis requires a sensor to detect changes in the condition to be regulated, an effector mechanism that can vary that condition, and a negative feedback connection between the two.