* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Human Homeostasis Study Aid Circulatory System Main Connective
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
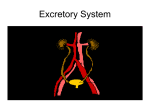
Human Homeostasis Study Aid Circulatory System Main Connective Tissue Involved in this system Where blood is manufactured Four components of this tissue and function of each Blood Bone marrow Red blood cells – carry O2 and CO2 White blood cells – immune response Platelets-blood clotting Plasma – liquid to carry everything including dissolve materials Cell transport used by: Red blood cells White blood cells Function of the heart Flow of blood through the heart down to the kidney Excretory System Includes these organs Main organ of excretory system Function of this organ (dialysis-artificially) Main filtration unit Three steps of blood filtration Red blood cells – use diffusion White blood cells – use active transport (endocytosis) Pump the blood around the body Deoxygenated blood from the body is carried to the heart through the superior and inferior vena cava and received by the right atrium, pumped to the right ventricle, pumped through the pulmonary artery to the lungs for gas exchange, oxygenated blood returns to the heart though the pulmonary vein and is received by the left atrium, pumped to the left ventricle, pumped through the aorta which connects to other arteries including the renal artery (Veins carry to the heart, arteries away) Lungs (gas exchange), skin (releases urea and salts in sweat), kidney (filters blood waste) Kidneys Blood filtration Nephron Filtration (glomerulus, Bowman’s capsule), Reabsorption 99% reabsorbed (Loop of Henle), Excretion (collecting ducts to ureters, to bladder, to urethra) Trace blood through the kidney Renal artery, glomerulus, capillaries, renal vein Trace the filtrate through the kidney Identify where these transports happen in the process: Active transport Passive transport Renal artery, glomerulus, Bowman’s capsule, Loop of Henle, back to blood if reabsorbed, to collecting duct if not, ureter, bladder, urethra Active transport – to reabsorb dissolved materials back into the blood Passive transport – materials across the space between the glomerulus and Bowman’s capsule Osmosis – reabsorb water Human Homeostasis Study Aid Nervous System Basic cell Nerve Impulse description Central Nervous System Neuron Dendrites to cell body to axon to axon terminal. Synaptic vesicles merge with the axon terminal cell membrane and neurotransmitters exit through exocytosis, they diffuse across the synaptic cleft and attach to an ion pump to open it and allow ions to pass through Brain and Spinal cord Peripheral Nervous System Sensory Motor Somatic Autonomic Parasympathetic Sympathetic All other nerves Gather information and send it to the brain Send a signal from the brain to the body Conscious control ex. Skeletal muscle Unconscious control ex. Heart rate Decreases rates Increases rates Parts of the brain Cerebrum Parietal Lobe Frontal Lobe Temporal Lobe Occipital Lobe Cerebellum Brain Stem Conscious though Integrates information from various senses Conscious thought, mood/personality Smell, sound Sight Muscle coordination and balance Involuntary functions (internal organs) Endocrine System Uses what chemical signal Nonsteroid hormones Steroid hormones Is a system of Target tissues Pituitary Hypothalamus Negative Feedback loop Thyroid Parathyroid Adrenal Glands Pancreas Reproductive glands Hormones Amino acid composition/ cannot diffuse into a cell Lipid composition/ diffuse into the cell Glands Tissues that a hormone is meant to stimulate Gland in the brain that controls many other glands Operates the negative feedback loop/controls the pituitary Monitors the levels in different systems, when they are too low or high it sends a signal to the pituitary to secrete another hormone to a target tissue to change levels. When levels reach normal it sends a stop signal to the pituitary Regulates metabolism Regulates blood calcium levels Regulates blood pressure/reabsorption Regulates insulin/glucagon levels Regulates gamete production/secondary sex characteristics Human Homeostasis Study Aid Immune System Non-specific defense (innate) First line of defense Second line of defense Specific Immunity (acquired) Cellular immunity Antibody immunity Same reaction for all invaders (pathogens) Skin, mucus, tears Inflammatory response (white blood cells), Histamine (brings more fluid to the area), Fever (body temperature is raised) Body learns invaders/ as a specific response T-Cells produce memory cells and destroy pathogens B-cells produce antibodies, neutralize the pathogen, remember the pathogen Vaccines Artificially produce acquired immunity by exposure to a weakened antigen of a specific pathogen, can only help prevent the illness not a cure Allergic reaction Over response by the immune system



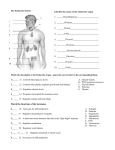



![Urinary System_student handout[1].](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/008293858_1-b77b303d5bfb3ec35a6e80f57f440bef-150x150.png)