Grade 10 Academic Science – Biology
... fungi and some protozoa. These pathogens enter our bodies through openings (e.g., eye, nose, mouth). To prevent invasions, the immune system has three lines of defense: (1) barriers (e.g., skin), (2) secretions (e.g., mucus, gastric juices) that wash away, expel or kill invaders and (3) prevention v ...
... fungi and some protozoa. These pathogens enter our bodies through openings (e.g., eye, nose, mouth). To prevent invasions, the immune system has three lines of defense: (1) barriers (e.g., skin), (2) secretions (e.g., mucus, gastric juices) that wash away, expel or kill invaders and (3) prevention v ...
FISH BODY SYSTEMS
... MUSCULAR/SKELETALENDOSKELETON made of bone for support/protection; VERTEBRAE = bones around nerve cord Large dorsal muscles make them top heavy so they float upside down when dead CIRCULATORY: CLOSED- vessels carry blood throughout body; VENTRAL HEART 2 main chambers ATRIUM & VENTRICLE (main blood p ...
... MUSCULAR/SKELETALENDOSKELETON made of bone for support/protection; VERTEBRAE = bones around nerve cord Large dorsal muscles make them top heavy so they float upside down when dead CIRCULATORY: CLOSED- vessels carry blood throughout body; VENTRAL HEART 2 main chambers ATRIUM & VENTRICLE (main blood p ...
The Digestive System
... About 8 million blood cells die in the human body every second, and the same number are born each second. Within a tiny droplet of blood, there are some 5 million red blood cells, 300 000 platelets and 10 000 white cells. It takes about 20 seconds for a red blood cell to circle the whole body. Red b ...
... About 8 million blood cells die in the human body every second, and the same number are born each second. Within a tiny droplet of blood, there are some 5 million red blood cells, 300 000 platelets and 10 000 white cells. It takes about 20 seconds for a red blood cell to circle the whole body. Red b ...
Red blood cells - Maria Regina School
... • Based on Rh factor – People who lack Rh factor (negative type), – Have Rh factor are positive (like being O+) – If lack Rh but receive Rh positive blood, body will produce antibodies against blood which can cause blood clots. ...
... • Based on Rh factor – People who lack Rh factor (negative type), – Have Rh factor are positive (like being O+) – If lack Rh but receive Rh positive blood, body will produce antibodies against blood which can cause blood clots. ...
Kidney - MrsGorukhomework
... Osmoregulation *this is a homeostatic mechanism – if reabsorption is not able to maintain a balance – when they ask for osmoregulation and/or homeostasis, this is what they want.* Osmoregulation is maintaining water balance in blood, tissues and cytoplasm in living organisms. The kidneys are ‘told’ ...
... Osmoregulation *this is a homeostatic mechanism – if reabsorption is not able to maintain a balance – when they ask for osmoregulation and/or homeostasis, this is what they want.* Osmoregulation is maintaining water balance in blood, tissues and cytoplasm in living organisms. The kidneys are ‘told’ ...
SYSTEM FUNCTIONS MAIN ORGANS Skeletal Muscular Digestive
... Label the following diagrams using the words provided. Alveoli Larynx Diaphragm Lung Bronchus Trachea ...
... Label the following diagrams using the words provided. Alveoli Larynx Diaphragm Lung Bronchus Trachea ...
The Circulatory System - Singapore Asia Publishers
... • The circulatory system consists of the heart, blood and blood vessels. • The heart pumps a supply of blood to the various parts of the body. • Blood is made up of plasma, red blood cells, white blood cells and platelets. • Blood travels in blood vessels. They are the arteries, veins and capill ...
... • The circulatory system consists of the heart, blood and blood vessels. • The heart pumps a supply of blood to the various parts of the body. • Blood is made up of plasma, red blood cells, white blood cells and platelets. • Blood travels in blood vessels. They are the arteries, veins and capill ...
Excretory System Notes
... Kidneys- remove urea and other waste material from blood. Urine- a watery fluid that contain urea and other wastes Urea- a chemical that comes from the breakdown of proteins Ureters- narrow tubes where urine flows from the kidneys Urinary bladder- where urine is carried to ( stores urine) Urethra- w ...
... Kidneys- remove urea and other waste material from blood. Urine- a watery fluid that contain urea and other wastes Urea- a chemical that comes from the breakdown of proteins Ureters- narrow tubes where urine flows from the kidneys Urinary bladder- where urine is carried to ( stores urine) Urethra- w ...
Circulatory System - Bingham-5th-2012
... of the arterial wall (usually medium and larger arteries) due to the formation of plaque feromaor atheroma. Arrhythmia: The major symptom of cardiac arrhythmia is irregular heart rhythm, in which beats abnormally, either at a slower rate or faster rate. ...
... of the arterial wall (usually medium and larger arteries) due to the formation of plaque feromaor atheroma. Arrhythmia: The major symptom of cardiac arrhythmia is irregular heart rhythm, in which beats abnormally, either at a slower rate or faster rate. ...
Res
... What do external and cellular respiration mean? What occurs during each process? What are the two waste products of respiration? How are oxygen and carbon dioxide transported in the body? (HINT: refer to the circulatory system) What is the relationship between the respiratory and circulatory ...
... What do external and cellular respiration mean? What occurs during each process? What are the two waste products of respiration? How are oxygen and carbon dioxide transported in the body? (HINT: refer to the circulatory system) What is the relationship between the respiratory and circulatory ...
Physiology of blood system. Red blood cells. Respiratory pigments
... metabolic diseases (congenital and acquired porphyria, etc.) It may be the reserve pigments, which give the tissue oxygen in a small oxygen condition. ...
... metabolic diseases (congenital and acquired porphyria, etc.) It may be the reserve pigments, which give the tissue oxygen in a small oxygen condition. ...
Maintaining Life and Homeostasis Vocabulary
... though the outside world is continuously changing Indicates dynamic state of equilibrium Not unchanging: internal conditions change and vary but always stay within relatively narrow limits Every organ system plays a role: blood levels or nutrients; blood pressure/heart activity constant; waste ...
... though the outside world is continuously changing Indicates dynamic state of equilibrium Not unchanging: internal conditions change and vary but always stay within relatively narrow limits Every organ system plays a role: blood levels or nutrients; blood pressure/heart activity constant; waste ...
File
... and are the smallest vessels in the body. The _______________ vessels take blood to and from the lungs. The _______________ is the largest artery delivering oxygen _____________ blood to the body. The _______________ is the largest vein delivering oxygen _____________ blood to the heart. The ...
... and are the smallest vessels in the body. The _______________ vessels take blood to and from the lungs. The _______________ is the largest artery delivering oxygen _____________ blood to the body. The _______________ is the largest vein delivering oxygen _____________ blood to the heart. The ...
Diffusion and Osmosis in the Human Body
... vasopressin, an anti-diuretic hormone (ADH). When the blood has a high concentration of sodium ions, the hypothalamus and pituitary gland (both in the brain) triggers the release of ADH which would tell the kidneys to reabsorb more water to help rehydrate the body. This is an example of maintaining ...
... vasopressin, an anti-diuretic hormone (ADH). When the blood has a high concentration of sodium ions, the hypothalamus and pituitary gland (both in the brain) triggers the release of ADH which would tell the kidneys to reabsorb more water to help rehydrate the body. This is an example of maintaining ...
Science final vocabulary
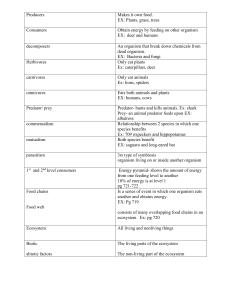
... Energy pyramid- shows the amount of energy from one feeding level to another 10% of energy is at level 1 pg 721-722 Is a series of event in which one organism eats another and obtains energy. EX: Pg 719 ...
... Energy pyramid- shows the amount of energy from one feeding level to another 10% of energy is at level 1 pg 721-722 Is a series of event in which one organism eats another and obtains energy. EX: Pg 719 ...
Human Anatomy - Centennial College Libraries
... The central nervous system consists of the brain and the spinal cord. The peripheral nervous system consists of the efferent neurons (to the brain) and afferent neurons (away from the brain). ...
... The central nervous system consists of the brain and the spinal cord. The peripheral nervous system consists of the efferent neurons (to the brain) and afferent neurons (away from the brain). ...
Body Fluids and Fluid Compartments
... the bloodstream and flows out into the tissue spaces, causing edema and possibly a shutdown of the circulatory system. When aldosterone concentrations are high, most of the remaining Na+ are reabsorbed. Generally each Na+ reabsorbed, Cl- follows and K+ is secreted into the nitrate. Thus, as the sod ...
... the bloodstream and flows out into the tissue spaces, causing edema and possibly a shutdown of the circulatory system. When aldosterone concentrations are high, most of the remaining Na+ are reabsorbed. Generally each Na+ reabsorbed, Cl- follows and K+ is secreted into the nitrate. Thus, as the sod ...
circulatory system
... Systemic and pulmonary circulation When the heart contracts it pushes the blood out into two major loops or cycles. In the systemic loop, the blood circulates into the body’s systems, bringing oxygen to all its organs, structures and tissues and collecting carbon dioxide waste. In the pulmonary loop ...
... Systemic and pulmonary circulation When the heart contracts it pushes the blood out into two major loops or cycles. In the systemic loop, the blood circulates into the body’s systems, bringing oxygen to all its organs, structures and tissues and collecting carbon dioxide waste. In the pulmonary loop ...
The Circulatory System
... Some white blood cells surround and consume harmful microbes. Some produce chemicals called antibodies that fight infection. ...
... Some white blood cells surround and consume harmful microbes. Some produce chemicals called antibodies that fight infection. ...
Human Body Study Guide - Effingham County Schools
... 2. The central nervous system is made up of your ___________________ which coordinates all body functions, and the __________________ which transmits messages from the brain to the rest of the body. 3. A nerve cell is also called a ________________ and are cells that transmit messages throughout the ...
... 2. The central nervous system is made up of your ___________________ which coordinates all body functions, and the __________________ which transmits messages from the brain to the rest of the body. 3. A nerve cell is also called a ________________ and are cells that transmit messages throughout the ...
Structure or term √ Function Digestive System System responsible
... Allows for a wide range of motions (hips and shoulders) Can only flex or extend in one direction (elbows or knees) The tissue that acts as a buffer between bones ...
... Allows for a wide range of motions (hips and shoulders) Can only flex or extend in one direction (elbows or knees) The tissue that acts as a buffer between bones ...
Homeostasis

Homeostasis or homoeostasis (homeo- + -stasis) is the property of a system in which variables are regulated so that internal conditions remain stable and relatively constant. Examples of homeostasis include the regulation of temperature and the balance between acidity and alkalinity (pH). It is a process that maintains the stability of the human body's internal environment in response to changes in external conditions.The concept was described by French physiologist Claude Bernard in 1865 and the word was coined by Walter Bradford Cannon in 1926. Although the term was originally used to refer to processes within living organisms, it is frequently applied to automatic control systems such as thermostats. Homeostasis requires a sensor to detect changes in the condition to be regulated, an effector mechanism that can vary that condition, and a negative feedback connection between the two.