* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download The Human Body Review - Effingham County Schools
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
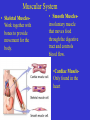
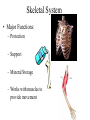
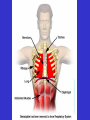
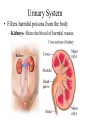
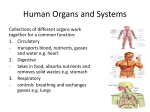
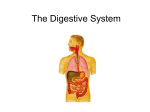
The Human Body Review Levels of Organization Section 7- 4 Muscle cell muscle tissue Organ Organ system These Organ Systems function together to maintain homeostasis – a stable internal environment Go to Section: The Integumentary System A. Major Organs – Skin – Hair – Nails B. Major Functions – Protection – keeps moisture in and pathogens out – Sensory input – nerves in skin allow you to sense your environment – Temperature regulation – sweat produced by glands in the skin cool the body – Waste removal – chemicals can be removed along with sweat Muscular System • Skeletal MusclesWork together with bones to provide movement for the body. • Smooth Musclesinvoluntary muscle that moves food through the digestive tract and controls blood flow. •Cardiac MuscleOnly found in the heart Skeletal System • Major Functions: – Protection – Support – Mineral Storage – Works with muscles to provide movement Nervous System Major Function: To control all activities of the body • Neurons- Nerve cells that transport signals • Major organs: - Central Nervous System- Brain and Spinal Cord -Peripheral Nervous System- Nerves that relay messages between the CNS and the rest of your body Digestive System Major Function: To break down food (mechanically and chemically) into molecules that the body can use. Organs: Mouth- mechanical and chemical digestion takes place Esophagus- tube leading to stomach Stomach- Mechanical and chemical digestion Small Intestines- Chemical digestion and absorbs Nutrients into blood stream Large Intestines- Absorbs water into blood stream Respiratory System Major Functuion- To supply the cells of the body with oxygen and get rid of carbon dioxide wastes Major organs: Trachea- tube that leads to the lungs Lungs- cavities that hold oxygen or carbon dioxide wastes Alveoli- sacs inside lungs where gas exchange takes place. Diaphragm- relaxes and contracts to draw oxygen into the lungs and expell carbondioxide out of the lungs. Urinary System • Filters harmful poisons from the body – Kidneys- filters the blood of harmful wastes Circulatory System • Transports material to and from the cells in the body. • Organs– Blood- transports nutrients, oxygen and cellular wastes throughout the body using red blood cells – Heart- Pumps blood through the vessels in the body – Blood Vessels- Transport system • Veins transport blood to heart • Arteries transport blood away from the heart • Capillaries- the exchange site at cells Circulatory System Major Transport System of nutrients and wastes to and from every cell in the body. Reproductive System • To enable organisms to carry on life by producing offspring. • Meiosis- The production of sex cells (gametes) which are haploid cells – Female gamete- Eggs – Male gamete- Sperm ALLOWS FOR GENETIC VARIATION!!!