* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download HUMAN Body systems and Major Organs
Survey
Document related concepts
Developmental biology wikipedia , lookup
Human embryogenesis wikipedia , lookup
Hematopoietic stem cell wikipedia , lookup
Human genetic resistance to malaria wikipedia , lookup
Hematopoietic stem cell transplantation wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
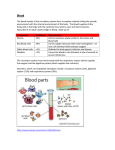
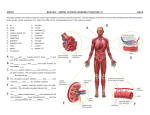
HUMAN Body systems and Major Organs 1.Circulatory: Move gas, water, nutrients, waste around body\ A. Heart – pumps blood B. Blood vessels – control where blood moves 1. Arteries - Away from heart 2. Veins - Return to heart, one way valves 3. Capillaries – leaky vessels that are site of cellular connection C. Blood – carries nutrients and gasses 1. Red Blood Cells – carries O2 to and CO2 away from cells 2. White BC – Fight infection 3. Platelets – clotting factor 4. Plasma – carries water, nutrients, dissolved gasses to and wastes away from cells 2. Respiratory: Gas exchange A. Lungs – Allows O2 into and CO2 out of body at Alveoli 3. Digestive: Break down, absorb nutrients, excretes solid waste A. Stomach - stores food (6 hrs), breaks down proteins B. Small Intestine – site of digestion and absorption of nutrients (villi) C. Large Intestine – reabsorb water, eliminate solid waste D. Liver – break down toxins (poisons); make digestive enzymes (bile) E. Pancreas – make digestive enzymes, insulin F. Gall Bladder – store bile Esophagus –tube to stomach Salivary glands – begin breakdown of starch 4. Skeletal: Protection, structure, support, movement A. Bones - Protection, structure, support, movement, adult stem cells make blood cells B. Ligaments – connect bone to bone C. Cartilage - cushions bones from each other 5. Muscular: Muscles (3 types) Movement. A. Skeletal - moves attached to 2 bones (contract/relax) Tendons attach bone to muscle B. Smooth - one way movement C. Cardiac (heart) – many endings, multi-nulceated 6. Urinary: Filter waste from blood, salt balance A. Kidneys Filter blood and maintain water and salt balance at nephron B. Urinary bladder – stores urine, reabsorbs water 7.Integumentary: Protection from infection, sense of touch A. Skin – sense pain/pleasure, hot/cold, shallow/deep pressure 8. Reproductive: Produce offspring A. Ovaries – make eggs B. Testes – make sperm 9. Nervous: Controls body through nerves (neurons) A. Brain – thought, memory, analysis and control of body B. Spinal Cord – information to and from body, some control (reflexes) C. Peripheral nervous system – sensory input, muscle movement D. Sensory organs – sight, sound, taste, smell 10. Endocrine: Control body through hormones (+ or -) A. Glands (Pituitary thyroid pancreas, etc.) produce hormones 11. Immune: Fight disease, infection A. Spleen – breaks down blood cells, reabsorbs them B. White blood cells – Eat foreign organisms 12. Lymphatic: Collecting system – absorbs material released form circulatory A. Lymph nodes – points of connection B. Lymph vessels - collect fluid from circulatory system C. Spleen – connection point for lymph system