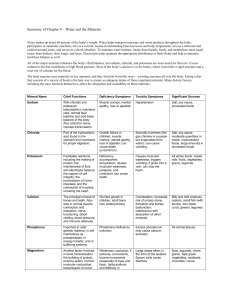
Circulatory System
... So narrow that red blood cells have to go through single file, allowing for lots of diffusion to take place (red blood cells carry oxygen and hemoglobin, which is essential for gas exchange (2) Oxygen, carbon dioxide, and other lipid soluble small substances can diffuse through endothelial cell memb ...
... So narrow that red blood cells have to go through single file, allowing for lots of diffusion to take place (red blood cells carry oxygen and hemoglobin, which is essential for gas exchange (2) Oxygen, carbon dioxide, and other lipid soluble small substances can diffuse through endothelial cell memb ...
Chapter 40 Study Guide Answers
... – Extensively branched or folded surfaces to increase surface area – Interstitial fluid, blood, ...
... – Extensively branched or folded surfaces to increase surface area – Interstitial fluid, blood, ...
excretion - biorocks
... reabsorbing materials from the blood. The kidney has an auto-regulation mechanism o The rate of filtration and reabsorption responds to changes in blood pressure and the composition of the blood ...
... reabsorbing materials from the blood. The kidney has an auto-regulation mechanism o The rate of filtration and reabsorption responds to changes in blood pressure and the composition of the blood ...
3rd Nine Weeks Review
... 29. What are the two main functions of the respiratory system? a) brings oxygen into the body b) releases carbon dioxide and water from the body 30. What occurs in the alveoli? gas exchange 31. Put the following in the correct order according to the path of air: bronchi, nostrils, trachea, lungs, ph ...
... 29. What are the two main functions of the respiratory system? a) brings oxygen into the body b) releases carbon dioxide and water from the body 30. What occurs in the alveoli? gas exchange 31. Put the following in the correct order according to the path of air: bronchi, nostrils, trachea, lungs, ph ...
The Body in Action – Summary
... 7. Training allows a person to exercise more vigorously and for much longer time before muscle fatigue sets in. Fitness training improves your body’s efficiency in several ways: - makes your heart able to pump more blood every beat - increases the flow of blood through the muscles - increases your l ...
... 7. Training allows a person to exercise more vigorously and for much longer time before muscle fatigue sets in. Fitness training improves your body’s efficiency in several ways: - makes your heart able to pump more blood every beat - increases the flow of blood through the muscles - increases your l ...
Organization and Regulation of Human Body Systems Circulatory, Respiratory, Immune, Integumentary
... lungs decrease The air pressure within the lungs increases Air flows into the lungs ...
... lungs decrease The air pressure within the lungs increases Air flows into the lungs ...
Document
... 13. Muscles are made of many fibers that are held together by _____________________. 14. Cardiac muscle is only found in the ______________, whereas smooth muscle is found in the _____________________. 15. In a complete sentence, explain the difference between resistance exercise and aerobic exercis ...
... 13. Muscles are made of many fibers that are held together by _____________________. 14. Cardiac muscle is only found in the ______________, whereas smooth muscle is found in the _____________________. 15. In a complete sentence, explain the difference between resistance exercise and aerobic exercis ...
the transport system
... transports nutrients, water, and oxygen to your body cells and carries away wastes such as carbon dioxide that body cells produce. ...
... transports nutrients, water, and oxygen to your body cells and carries away wastes such as carbon dioxide that body cells produce. ...
Chapter 6 and 7 Questions_2
... These disorders are caused by poor lifestyle habits or disease. One such disorder may lead to colon cancer. It is caused by ... a) b) c) d) ...
... These disorders are caused by poor lifestyle habits or disease. One such disorder may lead to colon cancer. It is caused by ... a) b) c) d) ...
Circulatory System - El Camino College
... transporting substances over long distances It takes 1 second for glucose to diffuse 100 micro meters It will take 3 hours to diffuse 1 cm! ...
... transporting substances over long distances It takes 1 second for glucose to diffuse 100 micro meters It will take 3 hours to diffuse 1 cm! ...
Summary of Chapter 9 – Water and the Minerals
... cushion around joints, and serves as a shock absorber. To maintain water balance, intake from liquids, foods, and metabolism must equal losses from kidneys, skin, lungs, and feces. Electrolytes help maintain the appropriate distribution of body fluids and help to maintain acid-base balance as well. ...
... cushion around joints, and serves as a shock absorber. To maintain water balance, intake from liquids, foods, and metabolism must equal losses from kidneys, skin, lungs, and feces. Electrolytes help maintain the appropriate distribution of body fluids and help to maintain acid-base balance as well. ...
File - LC Biology 2012-2013
... Excretion is the removal of waste products of metabolism from the body. The excretory system plays a role in homeostasis: (i) by maintaining the composition of an organism's fluids, including fluid balance and chemistry. (ii) by preventing the accumulation of poisonous wastes which might interfe ...
... Excretion is the removal of waste products of metabolism from the body. The excretory system plays a role in homeostasis: (i) by maintaining the composition of an organism's fluids, including fluid balance and chemistry. (ii) by preventing the accumulation of poisonous wastes which might interfe ...
Systems 2 - Attica Central School
... a. When you sweat b. When nutrients pass through the wall into the blood. c. When the liver produces juices ...
... a. When you sweat b. When nutrients pass through the wall into the blood. c. When the liver produces juices ...
Organ Systems - Montville.net
... Name an organ system and list as many organs as you can think of that are within that system. ...
... Name an organ system and list as many organs as you can think of that are within that system. ...
Body Systems Song - Association of Classical Christian Schools
... From cells to organs to the big systems Each part has a job to do. To breathe the air goes in the nose; It’s warmed, cleaned and moistened. The trachea leads to the lungs, Bronchial tubes and the air sacs. The circulatory system, it moves our blood. Arteries carry oxygen to cells, Veins bring back t ...
... From cells to organs to the big systems Each part has a job to do. To breathe the air goes in the nose; It’s warmed, cleaned and moistened. The trachea leads to the lungs, Bronchial tubes and the air sacs. The circulatory system, it moves our blood. Arteries carry oxygen to cells, Veins bring back t ...
Chapter 6 - loyolaunit1biology
... In plants, ergastic substances is the term used (instead of excretory products) This term refers to the products of photosynthesis as well as waste products. Wastes are often stored in vacuoles (dissolved in water) and cell walls Plants are able to shed parts of themselves to rid themselves of ...
... In plants, ergastic substances is the term used (instead of excretory products) This term refers to the products of photosynthesis as well as waste products. Wastes are often stored in vacuoles (dissolved in water) and cell walls Plants are able to shed parts of themselves to rid themselves of ...
Powerpoint
... • Air enters the body through the nose and moves into space called the nasal cavities. • It then goes through the pharynx, or the throat. • From there, air goes through the trachea. • After that, air moves into the bronchi, which lead directly to the lungs. • The lungs are the main organs of the res ...
... • Air enters the body through the nose and moves into space called the nasal cavities. • It then goes through the pharynx, or the throat. • From there, air goes through the trachea. • After that, air moves into the bronchi, which lead directly to the lungs. • The lungs are the main organs of the res ...
4 - Bulldogbiology.com
... functions. 4.1 Explain generally how the digestive system (mouth, pharynx, esophagus, stomach, small and large intestines, rectum) converts macromolecules from food into smaller molecules that can be used by cells for energy and for repair and growth. ...
... functions. 4.1 Explain generally how the digestive system (mouth, pharynx, esophagus, stomach, small and large intestines, rectum) converts macromolecules from food into smaller molecules that can be used by cells for energy and for repair and growth. ...
Week 1 – Cell structure and Function and Cell membranes
... - the capillaries are near to every alveoli so gases do not have to travel very far - there are many capillaries which gives a large surface area ...
... - the capillaries are near to every alveoli so gases do not have to travel very far - there are many capillaries which gives a large surface area ...
Circulatory System Red
... Takes blood from aorta to blood vessels and down to the capillary beds in the different parts of the body where the oxygen is distributed among the cells (1). o The now deoxygenated blood is taken through the veins to the heart where it is pumped into the pulmonary circuit (1). o ...
... Takes blood from aorta to blood vessels and down to the capillary beds in the different parts of the body where the oxygen is distributed among the cells (1). o The now deoxygenated blood is taken through the veins to the heart where it is pumped into the pulmonary circuit (1). o ...
Visual Study Guide: Ch 13
... • Identify the right and left sides of the heart • Know the name and function of each of the 4 chambers • Identify the septum, valves, and aorta and describe their functions • Describe the two loop system blood takes through the body ...
... • Identify the right and left sides of the heart • Know the name and function of each of the 4 chambers • Identify the septum, valves, and aorta and describe their functions • Describe the two loop system blood takes through the body ...
Homeostasis

Homeostasis or homoeostasis (homeo- + -stasis) is the property of a system in which variables are regulated so that internal conditions remain stable and relatively constant. Examples of homeostasis include the regulation of temperature and the balance between acidity and alkalinity (pH). It is a process that maintains the stability of the human body's internal environment in response to changes in external conditions.The concept was described by French physiologist Claude Bernard in 1865 and the word was coined by Walter Bradford Cannon in 1926. Although the term was originally used to refer to processes within living organisms, it is frequently applied to automatic control systems such as thermostats. Homeostasis requires a sensor to detect changes in the condition to be regulated, an effector mechanism that can vary that condition, and a negative feedback connection between the two.