Evolution
... 8. Evidence of once living things ______fossils___________________. 9. Catastrophism – floods and earthquakes have shaped land and caused species to go extinct 10. Uniformitarianism – geological processes that shaped Earth in the past have stayed the same throughout time. 11. Charles Darwin – develo ...
... 8. Evidence of once living things ______fossils___________________. 9. Catastrophism – floods and earthquakes have shaped land and caused species to go extinct 10. Uniformitarianism – geological processes that shaped Earth in the past have stayed the same throughout time. 11. Charles Darwin – develo ...
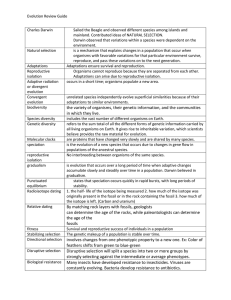
Evolution Review Guide Charles Darwin Sailed the Beagle and
... refers to the sum total of all the different forms of genetic information carried by all living organisms on Earth. It gives rise to inheritable variation, which scientists believe provides the raw material for evolution. are proteins that have changed very slowly and are shared by many species. is ...
... refers to the sum total of all the different forms of genetic information carried by all living organisms on Earth. It gives rise to inheritable variation, which scientists believe provides the raw material for evolution. are proteins that have changed very slowly and are shared by many species. is ...
Speciation
... Any species with a multiple of the normal set of chromosomes is known as a polyploid Can be caused by mistakes in meiosis or mitosis If their offspring survive, they are usually unable to reproduce, but some can with other polyploids Ex. Wheat, cotton, apples, and bananas ...
... Any species with a multiple of the normal set of chromosomes is known as a polyploid Can be caused by mistakes in meiosis or mitosis If their offspring survive, they are usually unable to reproduce, but some can with other polyploids Ex. Wheat, cotton, apples, and bananas ...
Mechanisms of Evolution
... Founder Effect: result of migration (Darwin’s finches) Ex. Amish and Mennonites: people rarely marry outside their own communities; Old Order Amish—high frequency of 6-finger dwarfism—can trace ancestry back to one of the founders of the ...
... Founder Effect: result of migration (Darwin’s finches) Ex. Amish and Mennonites: people rarely marry outside their own communities; Old Order Amish—high frequency of 6-finger dwarfism—can trace ancestry back to one of the founders of the ...
Chapter 7.1 , 7.2, and 7.3
... Evolution is the process in which inherited characteristics within a population change over generations, sometimes developing into new species. Scientists continue to develop theories to explain how evolution happens. Evidence that organisms evolve can be found by comparing living organisms to ...
... Evolution is the process in which inherited characteristics within a population change over generations, sometimes developing into new species. Scientists continue to develop theories to explain how evolution happens. Evidence that organisms evolve can be found by comparing living organisms to ...
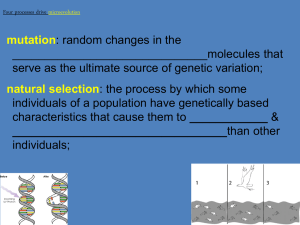
mutation: random changes in the that serve as the ultimate source of
... populations (____________________ into or out of a region); genetic drift: change in genetic composition that results by ______________, especially in __________ ____________________ . Example: Cheetahs, low genetic diversity ...
... populations (____________________ into or out of a region); genetic drift: change in genetic composition that results by ______________, especially in __________ ____________________ . Example: Cheetahs, low genetic diversity ...
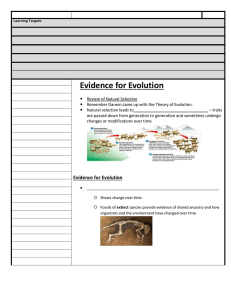
Evidence for Evolution
... Remember Darwin came up with the Theory of Evolution. Natural selection leads to_________________________________ – traits are passed down from generation to generation and sometimes undergo changes or modifications over time ...
... Remember Darwin came up with the Theory of Evolution. Natural selection leads to_________________________________ – traits are passed down from generation to generation and sometimes undergo changes or modifications over time ...
Evidence for Evolution
... DNA and the universal code • DNA is the genetic molecule for every organism on earth • All organisms use A, T, G, and C which is called the universal code • DNA makes proteins out of 20 amino acids • Mutations cause changes to DNA sequences and amino acid sequences ...
... DNA and the universal code • DNA is the genetic molecule for every organism on earth • All organisms use A, T, G, and C which is called the universal code • DNA makes proteins out of 20 amino acids • Mutations cause changes to DNA sequences and amino acid sequences ...
Evolution Jeopardy
... blackened with soot. Moths that were darker in color blended in with their environment better than lightcolored moths. This is an example of ...
... blackened with soot. Moths that were darker in color blended in with their environment better than lightcolored moths. This is an example of ...
Science Understandings - IHMC Public Cmaps (3)
... Although species my look very different, the similarities become apparent when analyzing the internal structures of organisms Although species my look very different, the similarities become apparent when analyzing their common ancestry (fossil record) Diversity of species develops gradually over ma ...
... Although species my look very different, the similarities become apparent when analyzing the internal structures of organisms Although species my look very different, the similarities become apparent when analyzing their common ancestry (fossil record) Diversity of species develops gradually over ma ...
Review for Evolution Test
... 3. What is the difference between microevolution and macroevolution? 4. How does natural selection lead to adaptation? 5. How do the forelimbs of a bat, whale, cat, and human contribute evidence to support the hypothesis that these mammals evolved from a common ancestor? 6. Why are islands prime loc ...
... 3. What is the difference between microevolution and macroevolution? 4. How does natural selection lead to adaptation? 5. How do the forelimbs of a bat, whale, cat, and human contribute evidence to support the hypothesis that these mammals evolved from a common ancestor? 6. Why are islands prime loc ...
File
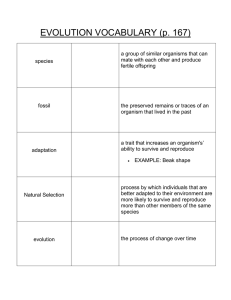
... the most likely to survive and pass on their genes. Fossils help us because they show us remains or imprints of once-living organisms. A group of organisms that can mate with each other to produce fertile offspring are called species. Speciation can occur through reproductive isolation and then the ...
... the most likely to survive and pass on their genes. Fossils help us because they show us remains or imprints of once-living organisms. A group of organisms that can mate with each other to produce fertile offspring are called species. Speciation can occur through reproductive isolation and then the ...
Evolution Quiz Study Guide
... Charles Darwin – published a book entitled On the Origin of Species; learned about the living things he saw on his voyage to the Galapagos Islands ...
... Charles Darwin – published a book entitled On the Origin of Species; learned about the living things he saw on his voyage to the Galapagos Islands ...
Exam II Vocabulary Review
... A visual representation of the evolutionary history of populations, genes, or species Change in the allele frequencies within a population over time (generations) The process by which similar traits evolve independently in unrelated lineages Similarity in structure due to common descent ...
... A visual representation of the evolutionary history of populations, genes, or species Change in the allele frequencies within a population over time (generations) The process by which similar traits evolve independently in unrelated lineages Similarity in structure due to common descent ...
Charles Darwin
... An English naturalist who, along with Alfred Russell Wallace, developed the theory of evolution through natural selection. It is this name that is most closely associated with the theory of evolution. Species ...
... An English naturalist who, along with Alfred Russell Wallace, developed the theory of evolution through natural selection. It is this name that is most closely associated with the theory of evolution. Species ...
here - My Haiku
... 4. _____________________ Body part of organisms which have similar function but do not share a common ancestor 5. _____________________ Evolutionary pattern in which distantly-related organisms evolve similar traits 6. _____________________ A group of similar organisms that can mate and produce fert ...
... 4. _____________________ Body part of organisms which have similar function but do not share a common ancestor 5. _____________________ Evolutionary pattern in which distantly-related organisms evolve similar traits 6. _____________________ A group of similar organisms that can mate and produce fert ...
Evolution1
... A process of change through time Existing forms have evolved from earlier forms Diversity leads to evolution ...
... A process of change through time Existing forms have evolved from earlier forms Diversity leads to evolution ...
Evidence for evolution ppt evidence for evolution ppt
... Fossils: • Document patterns of evolution • Provide physical evidence of changes in various groups of organisms • Show that present day organisms are different than those of long ago • Show that extinctions have occurred ...
... Fossils: • Document patterns of evolution • Provide physical evidence of changes in various groups of organisms • Show that present day organisms are different than those of long ago • Show that extinctions have occurred ...
Evolution Review Answer Key
... 5) Compare and contrast convergent and divergent evolution, give an example for each. Convergent, different ancestor adapting to similar environments - sharks/dolphins Divergent, common ancestor adapting to different environments – dolphins/humans ...
... 5) Compare and contrast convergent and divergent evolution, give an example for each. Convergent, different ancestor adapting to similar environments - sharks/dolphins Divergent, common ancestor adapting to different environments – dolphins/humans ...
Evidence of common descent

Evidence of common descent of living organisms has been discovered by scientists researching in a variety of disciplines over many decades and has demonstrated common descent of all life on Earth developing from a last universal ancestor. This evidence explicates that evolution does occur, and is able to show the natural processes by which the biodiversity of life on Earth developed. Additionally, this evidence supports the modern evolutionary synthesis—the current scientific theory that explains how and why life changes over time. Evolutionary biologists document evidence of common descent by making testable predictions, testing hypotheses, and developing theories that illustrate and describe its causes.Comparison of the DNA genetic sequences of organisms has revealed that organisms that are phylogenetically close have a higher degree of DNA sequence similarity than organisms that are phylogenetically distant. Further evidence for common descent comes from genetic detritus such as pseudogenes, regions of DNA that are orthologous to a gene in a related organism, but are no longer active and appear to be undergoing a steady process of degeneration from cumulative mutations.Fossils are important for estimating when various lineages developed in geologic time. As fossilization is an uncommon occurrence, usually requiring hard body parts and death near a site where sediments are being deposited, the fossil record only provides sparse and intermittent information about the evolution of life. Scientific evidence of organisms prior to the development of hard body parts such as shells, bones and teeth is especially scarce, but exists in the form of ancient microfossils, as well as impressions of various soft-bodied organisms. The comparative study of the anatomy of groups of animals shows structural features that are fundamentally similar or homologous, demonstrating phylogenetic and ancestral relationships with other organisms, most especially when compared with fossils of ancient extinct organisms. Vestigial structures and comparisons in embryonic development are largely a contributing factor in anatomical resemblance in concordance with common descent. Since metabolic processes do not leave fossils, research into the evolution of the basic cellular processes is done largely by comparison of existing organisms' physiology and biochemistry. Many lineages diverged at different stages of development, so it is possible to determine when certain metabolic processes appeared by comparing the traits of the descendants of a common ancestor. Universal biochemical organization and molecular variance patterns in all organisms also show a direct correlation with common descent.Further evidence comes from the field of biogeography because evolution with common descent provides the best and most thorough explanation for a variety of facts concerning the geographical distribution of plants and animals across the world. This is especially obvious in the field of insular biogeography. Combined with the theory of plate tectonics common descent provides a way to combine facts about the current distribution of species with evidence from the fossil record to provide a logically consistent explanation of how the distribution of living organisms has changed over time.The development and spread of antibiotic resistant bacteria, like the spread of pesticide resistant forms of plants and insects provides evidence that evolution due to natural selection is an ongoing process in the natural world. Alongside this, are observed instances of the separation of populations of species into sets of new species (speciation). Speciation has been observed directly and indirectly in the lab and in nature. Multiple forms of such have been described and documented as examples for individual modes of speciation. Furthermore, evidence of common descent extends from direct laboratory experimentation with the selective breeding of organisms—historically and currently—and other controlled experiments involving many of the topics in the article. This article explains the different types of evidence for evolution with common descent along with many specialized examples of each.