macromolecules - BHSBiology-Cox
... Proteins control the rate of reactions and regulate cell processes. Proteins are used to form bones and muscles Proteins transport substances into or out of cells or help to fight disease Made from CHON and sometimes S ...
... Proteins control the rate of reactions and regulate cell processes. Proteins are used to form bones and muscles Proteins transport substances into or out of cells or help to fight disease Made from CHON and sometimes S ...
PROTEIN SYNTHESIS
... separates the 2 strands • RNA polymerase then uses one strand of DNA as a template for assembling an mRNA complementary strand • This creates a strand of mRNA which can carry the genetic code out of the nucleus to complete the second step of protein synthesis. ...
... separates the 2 strands • RNA polymerase then uses one strand of DNA as a template for assembling an mRNA complementary strand • This creates a strand of mRNA which can carry the genetic code out of the nucleus to complete the second step of protein synthesis. ...
Close Reading for Macromolecules
... ____amino acids_____ acids together. Lipids are large, nonpolar (won't dissolve in water) molecules. Phospholipids make up cell membranes. Lipids also serve as waxy coverings (cuticle) on plants, pigments (chlorophyll), and steroids. Lipids have more carbon and hydrogen atoms than oxygen atoms. Fats ...
... ____amino acids_____ acids together. Lipids are large, nonpolar (won't dissolve in water) molecules. Phospholipids make up cell membranes. Lipids also serve as waxy coverings (cuticle) on plants, pigments (chlorophyll), and steroids. Lipids have more carbon and hydrogen atoms than oxygen atoms. Fats ...
Biomolecules
... • Organic molecules contain carbon • Carbon’s four valence electrons allow it to form up to four covalent bonds • Hydrocarbons consist only of C and H – Propane CH8 ...
... • Organic molecules contain carbon • Carbon’s four valence electrons allow it to form up to four covalent bonds • Hydrocarbons consist only of C and H – Propane CH8 ...
Notes - The University of Sydney
... involved in the coupling has a stronger affinity for the electron(s), hence we generate a partial charge or dipole, denoted as delta positive (δ+) or delta negative (δ-). It is not a complete swap and no true ion forms. But it gives the compound a polar character. The best and most important example ...
... involved in the coupling has a stronger affinity for the electron(s), hence we generate a partial charge or dipole, denoted as delta positive (δ+) or delta negative (δ-). It is not a complete swap and no true ion forms. But it gives the compound a polar character. The best and most important example ...
Enzymes - preabenagh
... How are proteins able to do so many things? 20 different kinds amino acids - different R-groups Non-polar ...
... How are proteins able to do so many things? 20 different kinds amino acids - different R-groups Non-polar ...
CHAPTER 4 HF` Cleavage and Deprotection Procedures for
... On completion of chemical synthesis of the peptide chain, the final step requires the removal from the solid-phase support and liberation of the protected side chains of the trifunctional amino acids (I). Many different approaches to this problem have been established, but the procedure most widely ...
... On completion of chemical synthesis of the peptide chain, the final step requires the removal from the solid-phase support and liberation of the protected side chains of the trifunctional amino acids (I). Many different approaches to this problem have been established, but the procedure most widely ...
Chapter Three: The Chemistry of Organic Molecules
... waxes, phospholipids, and steroids. • Many are insoluble in water because they lack polar groups. ...
... waxes, phospholipids, and steroids. • Many are insoluble in water because they lack polar groups. ...
In Word
... 4. Functions vary due primarily to different attached functional groups. IV. Proteins A. Amino Acids 1. Amino acids are the monomers that condense to form proteins, which are very large molecules with structural and metabolic functions. 2. Structural proteins include keratin, which makes up hair and ...
... 4. Functions vary due primarily to different attached functional groups. IV. Proteins A. Amino Acids 1. Amino acids are the monomers that condense to form proteins, which are very large molecules with structural and metabolic functions. 2. Structural proteins include keratin, which makes up hair and ...
Introduction: As the building blocks of proteins, amino acids play a
... 5. Add enough 0.5 N NaOH solution to the titration burette. It is recommended that you allow the first portion of NaOH solution to run through the burette to clear the bottom constriction from residual distilled water (Discard this volume). 6. Record the starting volume reading on the burette, and ...
... 5. Add enough 0.5 N NaOH solution to the titration burette. It is recommended that you allow the first portion of NaOH solution to run through the burette to clear the bottom constriction from residual distilled water (Discard this volume). 6. Record the starting volume reading on the burette, and ...
Amino Acids
... Amino acids are the building blocks of proteins; proteins are made of amino acids. When you ingest a protein your body breaks it down into the individual aminos, reorders them, re-folds them, and turns them into whatever is needed by the body at that time. From only 20 amino acids, the body is able ...
... Amino acids are the building blocks of proteins; proteins are made of amino acids. When you ingest a protein your body breaks it down into the individual aminos, reorders them, re-folds them, and turns them into whatever is needed by the body at that time. From only 20 amino acids, the body is able ...
Biology I Honors Chapter 3 Biochemistry I. Cells Contain Organic
... 4. Functions vary due primarily to different attached functional groups. IV. Proteins A. Amino Acids 1. Amino acids are the monomers that condense to form proteins, which are very large molecules with structural and metabolic functions. 2. Structural proteins include keratin, which makes up hair and ...
... 4. Functions vary due primarily to different attached functional groups. IV. Proteins A. Amino Acids 1. Amino acids are the monomers that condense to form proteins, which are very large molecules with structural and metabolic functions. 2. Structural proteins include keratin, which makes up hair and ...
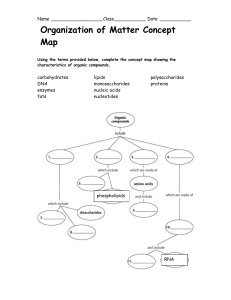
Polymers vs. monomers wkst. and concept map
... ________________________________________ 20. Your best friend tells you that they are deathly allergic to certain amino acids in food. Your mom has prepared dinner already, so you need to tell her not to serve what macromolecule to them? ...
... ________________________________________ 20. Your best friend tells you that they are deathly allergic to certain amino acids in food. Your mom has prepared dinner already, so you need to tell her not to serve what macromolecule to them? ...
essential amino acid
... Leucine Asparagine Lysine Aspartic acid Methionine Cysteine * Phenylalanine Glutamic acid Threonine Glutamine * Tryptophan Glycine Valine Ornithine * Proline * Selenocysteine * Serine * Taurine * Tyrosine * (*) Essential only in certain cases ...
... Leucine Asparagine Lysine Aspartic acid Methionine Cysteine * Phenylalanine Glutamic acid Threonine Glutamine * Tryptophan Glycine Valine Ornithine * Proline * Selenocysteine * Serine * Taurine * Tyrosine * (*) Essential only in certain cases ...
Macromolecules - Georgetown ISD
... 3. Carbon has how many electrons in its outer energy shell? 4. Carbon can form up to ______ covalent bonds with other atoms (elements) 5. Elements that carbon usually bonds with: _____, _____, _____, or _____. Example: ___________________ 6. Macromolecules are also called ___________________. 7. Mad ...
... 3. Carbon has how many electrons in its outer energy shell? 4. Carbon can form up to ______ covalent bonds with other atoms (elements) 5. Elements that carbon usually bonds with: _____, _____, _____, or _____. Example: ___________________ 6. Macromolecules are also called ___________________. 7. Mad ...
CHAPTER 3-Protein-In Class Activity
... PROTEIN: Draw the structure of amino acid (aa) and label each part’s name. Draw and show how two aa bind together and go through dehydration reaction. Condensation reactions bond the carboxyl group of one amino acid to the amino group of another to form a peptide bond There are _______different amin ...
... PROTEIN: Draw the structure of amino acid (aa) and label each part’s name. Draw and show how two aa bind together and go through dehydration reaction. Condensation reactions bond the carboxyl group of one amino acid to the amino group of another to form a peptide bond There are _______different amin ...
Organic Chemistry
... Each R-group side chain identifies the amino acid. There are 20 different side chains and therefore 20 different amino acids. 14. Two amino acids can be joined together to make a Dipeptide by the same reactions we talked about earlier known as Condensation reactions or Dehydration reactions. Why are ...
... Each R-group side chain identifies the amino acid. There are 20 different side chains and therefore 20 different amino acids. 14. Two amino acids can be joined together to make a Dipeptide by the same reactions we talked about earlier known as Condensation reactions or Dehydration reactions. Why are ...
Chapter 2 Summary
... 8. Phospholipids contain 2 fatty acid chains and a phosphate group; they are critical components of membranes. 9. PROTEINS are made from 21 amino acids. Amino acids have an amino group on one end and the carboxyl (acid) group in the other. They are different because of the 21 different side groups ...
... 8. Phospholipids contain 2 fatty acid chains and a phosphate group; they are critical components of membranes. 9. PROTEINS are made from 21 amino acids. Amino acids have an amino group on one end and the carboxyl (acid) group in the other. They are different because of the 21 different side groups ...
Inorganic Chemistry PP
... • Basic Structure Amino Acids • NH 2 = amino groups • COOH = carboxyl group ...
... • Basic Structure Amino Acids • NH 2 = amino groups • COOH = carboxyl group ...
Notes - Part 1.
... amino acid residues in the common secondary structures. R corresponds to the helix (also known as the 3.613 helix), This has 3.6 residues per turn. It is a righthanded helix, with the carbonyls pointing towards the C-terminus of the helix, and the sidechains and NH groups towards the N-terminus (s ...
... amino acid residues in the common secondary structures. R corresponds to the helix (also known as the 3.613 helix), This has 3.6 residues per turn. It is a righthanded helix, with the carbonyls pointing towards the C-terminus of the helix, and the sidechains and NH groups towards the N-terminus (s ...
Monomers are atoms or small molecules that bond together to form
... Monomers are atoms or small molecules that bond together to form more complex structures such as polymers. There are four main types of monomer, including sugars, amino acids, fatty acids, and nucleotides. Each of these monomer types play important roles in the existence and development of life, and ...
... Monomers are atoms or small molecules that bond together to form more complex structures such as polymers. There are four main types of monomer, including sugars, amino acids, fatty acids, and nucleotides. Each of these monomer types play important roles in the existence and development of life, and ...