Test Topics and Study Questions for Unit 7 DNA and Protein
... If the entire molecule is copied or just specific genes, what enzymes are involved, where in cell it occurs 9. Translate the codon on an mRNA molecule to determine the amino acid called for 10. Determine the anticodon on the tRNA molecule that is complementary to mRNA 11. Explain the role of the rib ...
... If the entire molecule is copied or just specific genes, what enzymes are involved, where in cell it occurs 9. Translate the codon on an mRNA molecule to determine the amino acid called for 10. Determine the anticodon on the tRNA molecule that is complementary to mRNA 11. Explain the role of the rib ...
Genetics Exam 3
... cell types. ________________________________ A chromosomal mutation in which there is a change in position of chromosome segments to a different location in the genome. ________________________________ A gene present in only one dose. ________________________________ An enzyme that introduces or eli ...
... cell types. ________________________________ A chromosomal mutation in which there is a change in position of chromosome segments to a different location in the genome. ________________________________ A gene present in only one dose. ________________________________ An enzyme that introduces or eli ...
The Structure of DNA DNA Has the Structure of a Winding Staircase
... • Adenine forms 2 hydrogen bonds with Thymine • Cytosine forms 3 hydrogen bonds with Guanine • The hydrogen bonds between the nitrogen bases keep the two strands of DNA together. • Each strand is complementary to the other. Ex. TCGAACT is complementary to ...
... • Adenine forms 2 hydrogen bonds with Thymine • Cytosine forms 3 hydrogen bonds with Guanine • The hydrogen bonds between the nitrogen bases keep the two strands of DNA together. • Each strand is complementary to the other. Ex. TCGAACT is complementary to ...
IB Molecular Biology Review Game
... What are the names of the 4 nitrogenous bases found in DNA? o Adenine, Thymine, Cytosine, Guanine In what way are the 2 halves of a DNA strand oriented toward each other? o Anti-parallel What kind of bond connects the phosphate of one nucleotide to the sugar of the next? o Phosphodiester bond ...
... What are the names of the 4 nitrogenous bases found in DNA? o Adenine, Thymine, Cytosine, Guanine In what way are the 2 halves of a DNA strand oriented toward each other? o Anti-parallel What kind of bond connects the phosphate of one nucleotide to the sugar of the next? o Phosphodiester bond ...
Prentice hall Biology Worksheets
... Short Answer On the lines provided, list the kinds of information that can be found by knowing the sequence of a DNA molecule. 4. __________________________________________________________________________________ 5. __________________________________________________________________________________ 6 ...
... Short Answer On the lines provided, list the kinds of information that can be found by knowing the sequence of a DNA molecule. 4. __________________________________________________________________________________ 5. __________________________________________________________________________________ 6 ...
SBI4U: Molecular Genetics Unit Review
... Leading strand is made continuously, lagging strand is made in small segments called okazaki fragments behind the leading strand 12. What are Okazaki fragments? See above 13. Describe the roles of the following enzymes/proteins in DNA replication: a. DNA helicase – unwinds DNA b. DNA gyrase – Reliev ...
... Leading strand is made continuously, lagging strand is made in small segments called okazaki fragments behind the leading strand 12. What are Okazaki fragments? See above 13. Describe the roles of the following enzymes/proteins in DNA replication: a. DNA helicase – unwinds DNA b. DNA gyrase – Reliev ...
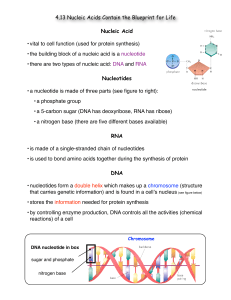
4.13 notes
... • a nucleotide is made of three parts (see figure to right): • a phosphate group • a 5-carbon sugar (DNA has deoxyribose, RNA has ribose) • a nitrogen base (there are five different bases available) RNA • is made of a single-stranded chain of nucleotides • is used to bond amino acids together during ...
... • a nucleotide is made of three parts (see figure to right): • a phosphate group • a 5-carbon sugar (DNA has deoxyribose, RNA has ribose) • a nitrogen base (there are five different bases available) RNA • is made of a single-stranded chain of nucleotides • is used to bond amino acids together during ...
Chapter 9
... Handouts – Online packets on DNA diagrams and Chromosomes – Genetics Revisited The Cellular Basis of Inheritance- Chapter 9 – Concept 9.4 Cancer cells grow and divide out of control. DNA and the Language of Life – Chapter 11- Concept 11.2 Nucleic acids store information in their sequences of chemica ...
... Handouts – Online packets on DNA diagrams and Chromosomes – Genetics Revisited The Cellular Basis of Inheritance- Chapter 9 – Concept 9.4 Cancer cells grow and divide out of control. DNA and the Language of Life – Chapter 11- Concept 11.2 Nucleic acids store information in their sequences of chemica ...
Eastern Intermediate High School
... Worksheet – Structure of DNA and Replication Directions: Label the diagram below with the following choices: ...
... Worksheet – Structure of DNA and Replication Directions: Label the diagram below with the following choices: ...
Mighty Miniscule DNA
... cell contains a nucleus which is filled with the directions for cell function, called DNA. ...
... cell contains a nucleus which is filled with the directions for cell function, called DNA. ...
DNA Prot Syn Engineer
... Explain how DNA replicates semiconservatively. How does the antiparallel structure of the double helix affect replication? In your answer, be sure to include discussion of leading strand, lagging strand, and Okazaki fragments. Discuss the purpose of the following enzymes: DNA polymerase, DNA ligase, ...
... Explain how DNA replicates semiconservatively. How does the antiparallel structure of the double helix affect replication? In your answer, be sure to include discussion of leading strand, lagging strand, and Okazaki fragments. Discuss the purpose of the following enzymes: DNA polymerase, DNA ligase, ...
DNA Replication, Transcription, Translation Notes (Central Dogma)
... 1. mRNA and tRNA transcribed from DNA in nucleus. 2. This RNA exits the ________ through pores. 3. _________ travels to _____________. 4. Free floating ___________ are brought to __________ by _______. 5. Protein always starts with ____________ (aug) AA 6. A second AA on tRNA enters ribosome. Codon ...
... 1. mRNA and tRNA transcribed from DNA in nucleus. 2. This RNA exits the ________ through pores. 3. _________ travels to _____________. 4. Free floating ___________ are brought to __________ by _______. 5. Protein always starts with ____________ (aug) AA 6. A second AA on tRNA enters ribosome. Codon ...
DNA and RNA
... • Avery and colleagues made an extract from the heat-killed bacteria then treated it with enzymes that destroyed proteins, lipids, CHOs, and RNA • Transformation still occurred • When DNA was destroyed, transformation did not occur • DNA stores and transmits the genetic information from one generati ...
... • Avery and colleagues made an extract from the heat-killed bacteria then treated it with enzymes that destroyed proteins, lipids, CHOs, and RNA • Transformation still occurred • When DNA was destroyed, transformation did not occur • DNA stores and transmits the genetic information from one generati ...
DNA, RNA, and Protein
... Replication • Occurs during S phase of cell cycle • DNA unwinds, in increments, via helicase • DNA polymerase makes 2 copies of DNA – Complementary base pairing: G=C; T=A – Leading strand has continuous replication – Lagging strand done in Okazaki fragments ...
... Replication • Occurs during S phase of cell cycle • DNA unwinds, in increments, via helicase • DNA polymerase makes 2 copies of DNA – Complementary base pairing: G=C; T=A – Leading strand has continuous replication – Lagging strand done in Okazaki fragments ...
DNA
... A always pairs with T and C always pairs with G. This is because of the number of bonds formed between the bases. Two hydrogen bonds form between A and T and three between C and G. Write the compliment for GGCTATTGGCA. ...
... A always pairs with T and C always pairs with G. This is because of the number of bonds formed between the bases. Two hydrogen bonds form between A and T and three between C and G. Write the compliment for GGCTATTGGCA. ...
Write True if the statement is true
... 1. DNA contains the sugar ribose. 2. Messenger RNA carries copies of the instructions for making proteins from DNA to other parts of the cell. 3. RNA polymerase transfers amino acids to ribosomes. 4. The process of transcription produces a complementary strand of RNA on a DNA template. 5. The enzyme ...
... 1. DNA contains the sugar ribose. 2. Messenger RNA carries copies of the instructions for making proteins from DNA to other parts of the cell. 3. RNA polymerase transfers amino acids to ribosomes. 4. The process of transcription produces a complementary strand of RNA on a DNA template. 5. The enzyme ...
Replisome
The replisome is a complex molecular machine that carries out replication of DNA. The replisome first unwinds double stranded DNA into two single strands. For each of the resulting single strands, a new complementary sequence of DNA is synthesized. The net result is formation of two new double stranded DNA sequences that are exact copies of the original double stranded DNA sequence.In terms of structure, the replisome is composed of two replicative polymerase complexes, one of which synthesizes the leading strand, while the other synthesizes the lagging strand. The replisome is composed of a number of proteins including helicase, RFC, PCNA, gyrase/topoisomerase, SSB/RPA, primase, DNA polymerase I, RNAse H, and ligase.