AP Biology Unit 4 Continued
... is correct! • Each strand acts as a template for the other, and so the mutation will propagate through successive generations. ...
... is correct! • Each strand acts as a template for the other, and so the mutation will propagate through successive generations. ...
Exam #3 Study Guide
... Frameshift mutations may be caused by A specific gene is always found on only one strand of the DNA double helix. The strand that is not being transcribed into mRNA is called the: Which of the following could have a role in the reason that few mistakes occur in the process of DNA replication? Finish ...
... Frameshift mutations may be caused by A specific gene is always found on only one strand of the DNA double helix. The strand that is not being transcribed into mRNA is called the: Which of the following could have a role in the reason that few mistakes occur in the process of DNA replication? Finish ...
DNA Replication Worksheet
... drawing. Pay attention to the specific coloring directions. Use chapter 6 in your book to help you. ...
... drawing. Pay attention to the specific coloring directions. Use chapter 6 in your book to help you. ...
AP Biology - HPHSAPBIO
... 4. Describe the semiconservative model of replication and the significance of the experiments by Matthew Meselson and Franklin Stahl. 5. Describe the process of DNA replication. Note the structure of the many origins of replication and replication forks and explain the role of DNA polymerase. 6. Def ...
... 4. Describe the semiconservative model of replication and the significance of the experiments by Matthew Meselson and Franklin Stahl. 5. Describe the process of DNA replication. Note the structure of the many origins of replication and replication forks and explain the role of DNA polymerase. 6. Def ...
Protein Synthesis Lab - Northwest ISD Moodle
... • Copy down the triplets of the complementary strand you are assigned. • Using the yarn, begin tying your complementary strand together. ...
... • Copy down the triplets of the complementary strand you are assigned. • Using the yarn, begin tying your complementary strand together. ...
DNA Unit Study Guide 2017 - Liberty Union High School District
... 5. How many bonds are there between A/T? __________ G/C? _________ 6. What are the chemicals that make up the backbone? ______________ & ___________________. 7. What is the enzyme responsible for unwinding the DNA so it can replicate? _____________________ 8. What is the enzyme responsible for makin ...
... 5. How many bonds are there between A/T? __________ G/C? _________ 6. What are the chemicals that make up the backbone? ______________ & ___________________. 7. What is the enzyme responsible for unwinding the DNA so it can replicate? _____________________ 8. What is the enzyme responsible for makin ...
Unit 4 Review: Molecular Genetics
... the list below: nucleotide cytosine guanine adenine thymine purine base pyrimidine base 5’ end of chain sugar-phosphate backbone 3’ end of chain hydrogen bonds deoxyribose phosphate group ...
... the list below: nucleotide cytosine guanine adenine thymine purine base pyrimidine base 5’ end of chain sugar-phosphate backbone 3’ end of chain hydrogen bonds deoxyribose phosphate group ...
What is the NUTRIENT needed for growth and repair
... Process of H bond formation when complementary base pairs bind ...
... Process of H bond formation when complementary base pairs bind ...
PARP inhibitors for cancer therapy Nicola Curtin Newcastle
... increasing the persistence of DNA damage in order to increase the antitumour activity of DNA damaging anticancer agents. Over the last 3 decades PARPi of increasing potency have been developed, virtually all contain the nicotinamide pharmacophore. PARPi increase the persistence of DNA single and dou ...
... increasing the persistence of DNA damage in order to increase the antitumour activity of DNA damaging anticancer agents. Over the last 3 decades PARPi of increasing potency have been developed, virtually all contain the nicotinamide pharmacophore. PARPi increase the persistence of DNA single and dou ...
ORGANELLES AND PROTEIN SYNTHESIS Worksheet #3
... A. Organelle Functions and Protein Synthesis 1) Organelle Functions: a. Define the function of the following items and indicate if it is an organelle or not CELLULAR STRUCTURES: Plasma Membrane ...
... A. Organelle Functions and Protein Synthesis 1) Organelle Functions: a. Define the function of the following items and indicate if it is an organelle or not CELLULAR STRUCTURES: Plasma Membrane ...
No Slide Title
... Here is an... DNA not only stores information, but accurately passes it on through replication & RNA transcription. ...
... Here is an... DNA not only stores information, but accurately passes it on through replication & RNA transcription. ...
Lecture 4, Exam III Worksheet Answers
... start/stop transcribing? What direction does it work in? RNA polymerase; larger than DNA polymerase, can take two nucleotides and add them together. Can make the beginning of a nucleotide without needing primase to make a primer; doesn’t need topoisomerase; doesn’t need helicase, because it has its ...
... start/stop transcribing? What direction does it work in? RNA polymerase; larger than DNA polymerase, can take two nucleotides and add them together. Can make the beginning of a nucleotide without needing primase to make a primer; doesn’t need topoisomerase; doesn’t need helicase, because it has its ...
Molecular Genetics DNA
... Semi-conservative – one half of DNA is old strand and other half is new Starts are replication origin (specific nucleotide sequence) – on strand will have many start points ...
... Semi-conservative – one half of DNA is old strand and other half is new Starts are replication origin (specific nucleotide sequence) – on strand will have many start points ...
Recitation 6 - MIT OpenCourseWare
... the protein DNA polymerase. DNA polymerase catalyzes the reaction of forming a phosphodiester bond between two deoxyribonucleotides. The start signal for DNA polymerase is an origin of replication, which is a site on DNA that may or may not be inside a gene. DNA polymerase proceeds down a piece of D ...
... the protein DNA polymerase. DNA polymerase catalyzes the reaction of forming a phosphodiester bond between two deoxyribonucleotides. The start signal for DNA polymerase is an origin of replication, which is a site on DNA that may or may not be inside a gene. DNA polymerase proceeds down a piece of D ...
Document
... Replicating the Ends of DNA Molecules • Limitations of DNA polymerase create problems for the linear DNA of eukaryotic chromosomes • The usual replication machinery provides no way to complete the 5 ends, so repeated rounds of replication produce shorter DNA molecules with uneven ends • This is n ...
... Replicating the Ends of DNA Molecules • Limitations of DNA polymerase create problems for the linear DNA of eukaryotic chromosomes • The usual replication machinery provides no way to complete the 5 ends, so repeated rounds of replication produce shorter DNA molecules with uneven ends • This is n ...
DNA Test Study Guide
... Human cells have ________chromosomes, or two sets of _________. One set came from the ___________ and one from the ___________. Body cells we also call ________________Because our body cells’ chromosomes are found in pairs, we call them ___________. When arranged on a karyotype, you can see that the ...
... Human cells have ________chromosomes, or two sets of _________. One set came from the ___________ and one from the ___________. Body cells we also call ________________Because our body cells’ chromosomes are found in pairs, we call them ___________. When arranged on a karyotype, you can see that the ...
DNA - ScanlinMagnet
... REPLICATION Replication Process in which DNA copies itself before cell division Important so each new cell has a complete set of DNA molecules Base pairing “Chargaff’s Rules” explains how DNA can be replicated (copied) A=T&G=C Each strand has the information to reconstruct the other strand ...
... REPLICATION Replication Process in which DNA copies itself before cell division Important so each new cell has a complete set of DNA molecules Base pairing “Chargaff’s Rules” explains how DNA can be replicated (copied) A=T&G=C Each strand has the information to reconstruct the other strand ...
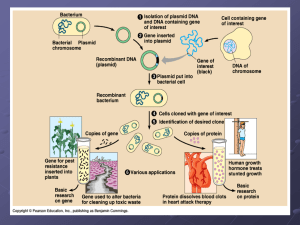
AP-ppt-PCR
... Problems Not all bacteria pick up plasmid-how do we distinguish? Annealing of human DNA to plasmid is random-how do we distinguish which plasmids have human DNA? ...
... Problems Not all bacteria pick up plasmid-how do we distinguish? Annealing of human DNA to plasmid is random-how do we distinguish which plasmids have human DNA? ...
DNA
... • Purines - Large organic bases – Adenine and Guanine • Pyrimidines - Small organic bases – Cytosine and Thymine, Uracil (RNA) ...
... • Purines - Large organic bases – Adenine and Guanine • Pyrimidines - Small organic bases – Cytosine and Thymine, Uracil (RNA) ...
Ch. 15
... manageable size using restriction enzymes. These restriction fragments can then be separated according to size, using gel electrophoresis or another similar technique. ...
... manageable size using restriction enzymes. These restriction fragments can then be separated according to size, using gel electrophoresis or another similar technique. ...
Replisome
The replisome is a complex molecular machine that carries out replication of DNA. The replisome first unwinds double stranded DNA into two single strands. For each of the resulting single strands, a new complementary sequence of DNA is synthesized. The net result is formation of two new double stranded DNA sequences that are exact copies of the original double stranded DNA sequence.In terms of structure, the replisome is composed of two replicative polymerase complexes, one of which synthesizes the leading strand, while the other synthesizes the lagging strand. The replisome is composed of a number of proteins including helicase, RFC, PCNA, gyrase/topoisomerase, SSB/RPA, primase, DNA polymerase I, RNAse H, and ligase.