Cell Theory Quiz Study Guide Name
... 17. The order of the nitrogen bases on the DNA molecule is known as the genetic _______. 18. In 1952, Rosalind ____________ discovered DNA is 2 chains of molecules. 19. In 1953, using the above scientist’s research, _____________ and ____________ made a model of DNA. 20. A _____________________ is a ...
... 17. The order of the nitrogen bases on the DNA molecule is known as the genetic _______. 18. In 1952, Rosalind ____________ discovered DNA is 2 chains of molecules. 19. In 1953, using the above scientist’s research, _____________ and ____________ made a model of DNA. 20. A _____________________ is a ...
Molecular Genetics - The Bronx High School of Science
... combined together (bacterial plasmid with human gene; glow in the dark rabbit, etc.) • How can we produce recombinant DNA? • Describe the function of restriction enzymes in creating recombinant DNA ...
... combined together (bacterial plasmid with human gene; glow in the dark rabbit, etc.) • How can we produce recombinant DNA? • Describe the function of restriction enzymes in creating recombinant DNA ...
The Blueprint of Life, From DNA to Protein
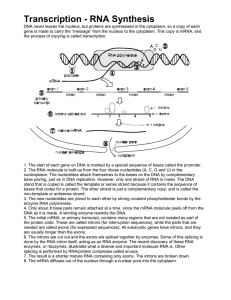
... – Gene expression • Expression involves two process – Transcription – Translation ...
... – Gene expression • Expression involves two process – Transcription – Translation ...
HSproteinsynth
... ·Instead of a long loop of DNA like a bacterium, cells of plants and animals have chromosomes that hold the DNA strands. Humans have 23 pairs of chromosomes, for a total of 46 chromosomes. Fruit flies have five pairs. Dogs have 39 pairs, and some plants have as many as 100. ...
... ·Instead of a long loop of DNA like a bacterium, cells of plants and animals have chromosomes that hold the DNA strands. Humans have 23 pairs of chromosomes, for a total of 46 chromosomes. Fruit flies have five pairs. Dogs have 39 pairs, and some plants have as many as 100. ...
MOLECULAR BIOLOGY.rtf
... Transcription—copies one of the DNA strands from the 3’end, and makes RNA beginning at its 5’end. The new RNA is complementary (A=U and G=C) and antiparallel to the coding strand of DNA Transcription is catalyzed in the nucleus by RNA polymerase 3 types of RNA mRNA—Is the template read to make prote ...
... Transcription—copies one of the DNA strands from the 3’end, and makes RNA beginning at its 5’end. The new RNA is complementary (A=U and G=C) and antiparallel to the coding strand of DNA Transcription is catalyzed in the nucleus by RNA polymerase 3 types of RNA mRNA—Is the template read to make prote ...
Section 10-1
... 1. The three parts are a deoxyribose sugar, a phosphate group, and a nitrogenous base. The phosphate group and the base are connected to different parts of the sugar. 2. Since guanine and cytosine are complementary, another 15% of the nucleotides must contain cytosine. The remaining 70% of the nucle ...
... 1. The three parts are a deoxyribose sugar, a phosphate group, and a nitrogenous base. The phosphate group and the base are connected to different parts of the sugar. 2. Since guanine and cytosine are complementary, another 15% of the nucleotides must contain cytosine. The remaining 70% of the nucle ...
Molecular Genetics 2- Central Dogma PDQ
... 6. How does replication of the leading strand differ from replication of the lagging strand? Why can’t both strands of DNA be replicated in the same fashion? 7. Diagram the replication fork. Include: a. the leading strand b. the lagging strand c. prime orientation of both parent strand and both daug ...
... 6. How does replication of the leading strand differ from replication of the lagging strand? Why can’t both strands of DNA be replicated in the same fashion? 7. Diagram the replication fork. Include: a. the leading strand b. the lagging strand c. prime orientation of both parent strand and both daug ...
AP Bio Molecular Genetics Review Sheet
... Which nucleotides match with which nucleotides? What is the main rule about nucleotide composition of DNA? What does it mean when you say that the strands that make up DNA are antiparallel? What is the role of DNA ligase in the elongation of the lagging strand during DNA replication? What is the sim ...
... Which nucleotides match with which nucleotides? What is the main rule about nucleotide composition of DNA? What does it mean when you say that the strands that make up DNA are antiparallel? What is the role of DNA ligase in the elongation of the lagging strand during DNA replication? What is the sim ...
DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid ) **Long molecule made up of units
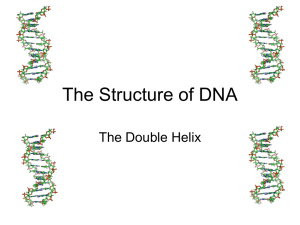
... **Double Helix- 2 strands of DNA wound around each other in the shape of a spiral staircase. **Hydrogen bonds formed between 2 nitrogenous bases all the way up and down the strand to hold the two strands together. **Hydrogen bonds can only form between certain base pairs: This is called base pairing ...
... **Double Helix- 2 strands of DNA wound around each other in the shape of a spiral staircase. **Hydrogen bonds formed between 2 nitrogenous bases all the way up and down the strand to hold the two strands together. **Hydrogen bonds can only form between certain base pairs: This is called base pairing ...
2016 N2 Week 4
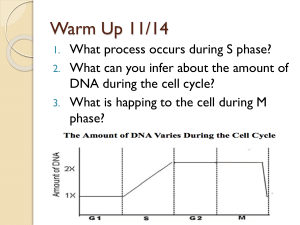
... 2. Bacteria reproduce by mitosis. 3. Cells must divide to replace other cells. 4. Stem cells are specialized. 5. The cell cycle includes interphase only. ...
... 2. Bacteria reproduce by mitosis. 3. Cells must divide to replace other cells. 4. Stem cells are specialized. 5. The cell cycle includes interphase only. ...
Study_Guide
... Describe, with the aid of diagrams, how hydrogen bonding between complementary base pairs (A to T, G to C) on two antiparallel DNA polynucleotides leads to the formation of a DNA molecule and how the twisting of DNA produces its ‘double-helix’ shape. Outline, with the aid of diagrams, how DNA re ...
... Describe, with the aid of diagrams, how hydrogen bonding between complementary base pairs (A to T, G to C) on two antiparallel DNA polynucleotides leads to the formation of a DNA molecule and how the twisting of DNA produces its ‘double-helix’ shape. Outline, with the aid of diagrams, how DNA re ...
Test Study Guide
... 15. What is the center of the chromosome called? 16. What are the tips of a chromosome called? 17. What problem occurs at the tips of chromosomes during replication? 18. What enzyme attempts to “fix” this problem? How? ...
... 15. What is the center of the chromosome called? 16. What are the tips of a chromosome called? 17. What problem occurs at the tips of chromosomes during replication? 18. What enzyme attempts to “fix” this problem? How? ...
Bio101 Topic 5 - Nucleic Acids
... purines and they have a double cycle. Cytosine C, Thymine, T and Uracil are called pyrimidines and they have a single cycle. ...
... purines and they have a double cycle. Cytosine C, Thymine, T and Uracil are called pyrimidines and they have a single cycle. ...
assignment DNA - UniMAP Portal
... _____________ A mutagen that causes insertions _____________ A mutagen that causes the formation of pyrimidine dimmers ...
... _____________ A mutagen that causes insertions _____________ A mutagen that causes the formation of pyrimidine dimmers ...
Key to the 13 Word Challenge Word Definition Neil 9e Hydrophyte
... Endosymbiosis Process in which unicellular organisms engulfed other cells that became endosymbionts and ultimately organelles in the host cell. Examples: ...
... Endosymbiosis Process in which unicellular organisms engulfed other cells that became endosymbionts and ultimately organelles in the host cell. Examples: ...
Name ______ Date - Net Start Class
... of DNA led to the idea that DNA — a. Robert Hooke; and is a very long molecule b. Gregor Mendel; can copy itself c. Charles Darwin; contains paired bases d. Watson & Crick is a double helix ...
... of DNA led to the idea that DNA — a. Robert Hooke; and is a very long molecule b. Gregor Mendel; can copy itself c. Charles Darwin; contains paired bases d. Watson & Crick is a double helix ...
Chapter 2: How Chromosomes Work
... 10. new cell formation—cells reproduce by dividing; the new cells contain the exact same genetic information as the original cell, and the new cells are called daughter cells 11. DNA replication—process of making exact copies of DNA; DNA replication is the first step of the cell cycle 12. DNA replic ...
... 10. new cell formation—cells reproduce by dividing; the new cells contain the exact same genetic information as the original cell, and the new cells are called daughter cells 11. DNA replication—process of making exact copies of DNA; DNA replication is the first step of the cell cycle 12. DNA replic ...
DNA Notes Part 1
... A. DNA is copied before a cell divides so that each new cell has it’s own genetic copy. B. There are 4 main steps: STEP 1: - DNA is unzipped by the enzyme HELICASE and now two single strands begin to unwind. - Hydrogen bonds are broken. ...
... A. DNA is copied before a cell divides so that each new cell has it’s own genetic copy. B. There are 4 main steps: STEP 1: - DNA is unzipped by the enzyme HELICASE and now two single strands begin to unwind. - Hydrogen bonds are broken. ...
Replisome
The replisome is a complex molecular machine that carries out replication of DNA. The replisome first unwinds double stranded DNA into two single strands. For each of the resulting single strands, a new complementary sequence of DNA is synthesized. The net result is formation of two new double stranded DNA sequences that are exact copies of the original double stranded DNA sequence.In terms of structure, the replisome is composed of two replicative polymerase complexes, one of which synthesizes the leading strand, while the other synthesizes the lagging strand. The replisome is composed of a number of proteins including helicase, RFC, PCNA, gyrase/topoisomerase, SSB/RPA, primase, DNA polymerase I, RNAse H, and ligase.