Molecular Bio
... Leading strand: synthesis toward the replication fork (only in a 5’ to 3’ direction from the 3’ to 5’ master strand) Lagging strand: synthesis away from the replication fork (Okazaki fragments); joined by DNA ligase (must wait for 3’ end to open; again in a 5’ to 3’ direction) Initiation: Primer (sh ...
... Leading strand: synthesis toward the replication fork (only in a 5’ to 3’ direction from the 3’ to 5’ master strand) Lagging strand: synthesis away from the replication fork (Okazaki fragments); joined by DNA ligase (must wait for 3’ end to open; again in a 5’ to 3’ direction) Initiation: Primer (sh ...
a14DNAGenMat
... • James Watson and Francis Crick determined that DNA is a double helix in 1953. ...
... • James Watson and Francis Crick determined that DNA is a double helix in 1953. ...
Lab Biology - Chapter 10
... 1. DNA makes exact copies of itself. a. the 2 nucleotide chains separate between base pairs. b. DNA polymerases ( enzymes ) move along separated chains and cause new chains of DNA to assemble and bond to existing nucleotides. c. Sequences remain exact. Ex: if original chain is: A T T C C G then new ...
... 1. DNA makes exact copies of itself. a. the 2 nucleotide chains separate between base pairs. b. DNA polymerases ( enzymes ) move along separated chains and cause new chains of DNA to assemble and bond to existing nucleotides. c. Sequences remain exact. Ex: if original chain is: A T T C C G then new ...
Things to Cover for Exam 1
... What is the central dogman of gene expression? Desribe Chargaff’s rules. (What does A pair with? T? G? C?) What is the complementary mRNA strand to the following DNA strand: TTCCAGCCGAAT Why is DNA replication considered a semi-conservative process? Ch. 12 “How Genes Work” What is the name ...
... What is the central dogman of gene expression? Desribe Chargaff’s rules. (What does A pair with? T? G? C?) What is the complementary mRNA strand to the following DNA strand: TTCCAGCCGAAT Why is DNA replication considered a semi-conservative process? Ch. 12 “How Genes Work” What is the name ...
Mitochondrial DNA - Winona Senior High School
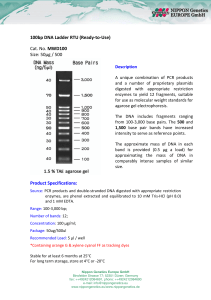
... • 25-50 cycles run to amplify DNA(each doubles the DNA) ...
... • 25-50 cycles run to amplify DNA(each doubles the DNA) ...
DNA and RNA study guide Answer Key
... 7. Before a cell divides, it must duplicate its own DNA in a process known as… DNA Replication 8. The genetic code in DNA depends upon the order or sequence of… Nitrogenous Bases 9. If one strand of DNA has the nitrogenous base sequence ATCGT, the sequence of bases on the COMPLEMENTARY STRAND of DNA ...
... 7. Before a cell divides, it must duplicate its own DNA in a process known as… DNA Replication 8. The genetic code in DNA depends upon the order or sequence of… Nitrogenous Bases 9. If one strand of DNA has the nitrogenous base sequence ATCGT, the sequence of bases on the COMPLEMENTARY STRAND of DNA ...
1. Fill in the blanks of the following diagram of photosynthesis. 2
... a. Splitting of water for electrons b. Has the highest energy state electrons c. Is at the beginning of the electron transport chain d. Receives electrons PC e. P700 f. P680 g. Ferredoxin h. Pheophytin ...
... a. Splitting of water for electrons b. Has the highest energy state electrons c. Is at the beginning of the electron transport chain d. Receives electrons PC e. P700 f. P680 g. Ferredoxin h. Pheophytin ...
(null): Quick Facts on DNA RNA Protein Synthesis
... helix as a template. The double-stranded molecule of DNA separates along the hydrogen bonds. An enzyme called RNA polymerase adds in corresponding base pairs. However, instead of using Thymine to match up with Adenine, Uracil is used. For RNA, the base paring rules are A-U and G-C. At the end of thi ...
... helix as a template. The double-stranded molecule of DNA separates along the hydrogen bonds. An enzyme called RNA polymerase adds in corresponding base pairs. However, instead of using Thymine to match up with Adenine, Uracil is used. For RNA, the base paring rules are A-U and G-C. At the end of thi ...
Topic 6: DNA and its Processes
... helix as a template. The double-stranded molecule of DNA separates along the hydrogen bonds. An enzyme called RNA polymerase adds in corresponding base pairs. However, instead of using Thymine to match up with Adenine, Uracil is used. For RNA, the base paring rules are A-U and G-C. At the end of thi ...
... helix as a template. The double-stranded molecule of DNA separates along the hydrogen bonds. An enzyme called RNA polymerase adds in corresponding base pairs. However, instead of using Thymine to match up with Adenine, Uracil is used. For RNA, the base paring rules are A-U and G-C. At the end of thi ...
File - High School Biology
... 12. The double coiled, “staircase” shape of DNA is called a __________________. Replication. 13. The process of __________________ produces a new copy of an organism’s genetic information, which is passed on to a new cell. 14. Create a matching (complementary) DNA sequence for the following strand: ...
... 12. The double coiled, “staircase” shape of DNA is called a __________________. Replication. 13. The process of __________________ produces a new copy of an organism’s genetic information, which is passed on to a new cell. 14. Create a matching (complementary) DNA sequence for the following strand: ...
chapter 14 15 16 study guide
... DNA replication: prokaryote has circular DNA; one origin of replication; smaller genome; faster replication; doesn’t have a telomere because it is circular Eukaryotic: linear dna, double helix, multiple origins of replication, more complicated lots of enzymes, have telomeres, histones RNA primase: s ...
... DNA replication: prokaryote has circular DNA; one origin of replication; smaller genome; faster replication; doesn’t have a telomere because it is circular Eukaryotic: linear dna, double helix, multiple origins of replication, more complicated lots of enzymes, have telomeres, histones RNA primase: s ...
Replisome
The replisome is a complex molecular machine that carries out replication of DNA. The replisome first unwinds double stranded DNA into two single strands. For each of the resulting single strands, a new complementary sequence of DNA is synthesized. The net result is formation of two new double stranded DNA sequences that are exact copies of the original double stranded DNA sequence.In terms of structure, the replisome is composed of two replicative polymerase complexes, one of which synthesizes the leading strand, while the other synthesizes the lagging strand. The replisome is composed of a number of proteins including helicase, RFC, PCNA, gyrase/topoisomerase, SSB/RPA, primase, DNA polymerase I, RNAse H, and ligase.