Chapter 14 Glycolysis Glucose 2 Pyruvate → → → 2 Lactate (sent to
... This reaction is coupled to the hydrolysis of ATP which results in an energetically favorable reaction (large, negative ΔG= irreversible rxn). This reaction is not unique to glycolysis. In fact, all glucose is phosphorylated once it enters the cell, no matter what its ultimate fate is (glycolysis, g ...
... This reaction is coupled to the hydrolysis of ATP which results in an energetically favorable reaction (large, negative ΔG= irreversible rxn). This reaction is not unique to glycolysis. In fact, all glucose is phosphorylated once it enters the cell, no matter what its ultimate fate is (glycolysis, g ...
Chapter 1 The Framework of Biology
... ATP is made across the inner membrane of mitochondria. Oxidative phosphorylation involves an electron transport chain embedded in a mitochondrial membrane in which H+ ions are concentrated on one side of the membrane using high-energy electrons from NADH and FADH2. ATP is formed by ATP synthase powe ...
... ATP is made across the inner membrane of mitochondria. Oxidative phosphorylation involves an electron transport chain embedded in a mitochondrial membrane in which H+ ions are concentrated on one side of the membrane using high-energy electrons from NADH and FADH2. ATP is formed by ATP synthase powe ...
macromolecules new
... • 2 peptides is called a dipeptide • 3-9 peptides is called a polypeptide • Many amino acids with lots of folding is called a protein ...
... • 2 peptides is called a dipeptide • 3-9 peptides is called a polypeptide • Many amino acids with lots of folding is called a protein ...
Problem Set 5 (Due February 25th) 1. Show how glucose can be
... spectrophotometrically – I noticed that the experimental section refers to another paper, so I apologize if this gave you a headache. e. Figure 5 has a lot of important information. i. What does this figure tell us about Glucose-1-phosphate and AMP – are they activators or inhibitors? They are activ ...
... spectrophotometrically – I noticed that the experimental section refers to another paper, so I apologize if this gave you a headache. e. Figure 5 has a lot of important information. i. What does this figure tell us about Glucose-1-phosphate and AMP – are they activators or inhibitors? They are activ ...
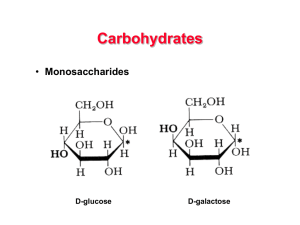
Carbohydrates
... • The simplest type of carbohydrate is a simple sugar called a monosaccharide. Contains ONE sugar molecule. • Examples are glucose and fructose) ...
... • The simplest type of carbohydrate is a simple sugar called a monosaccharide. Contains ONE sugar molecule. • Examples are glucose and fructose) ...
Chemistry of Life Carbohydrates Lipids Nucleic Acids ATP – The
... Then those amino acids are put together to form proteins, which are used to build the structure of a cell and fuel all the cell’s functions. These three-letter combos are called codons. !Nucleotides make up codons; codons code for amino acids; amino acids are put together into proteins; proteins mak ...
... Then those amino acids are put together to form proteins, which are used to build the structure of a cell and fuel all the cell’s functions. These three-letter combos are called codons. !Nucleotides make up codons; codons code for amino acids; amino acids are put together into proteins; proteins mak ...
Chapter 9 / Energy-Releasing Pathways and Biosynthesis I
... X. The Versatility of Catabolism Use of nutrients other than carbohydrates in aerobic respiration can catabolize proteins and neutral fats --enter at different points along pathways XI. Aspects of Biosynthesis--Anabolism A. The body uses small molecules to build other substances B. These small molec ...
... X. The Versatility of Catabolism Use of nutrients other than carbohydrates in aerobic respiration can catabolize proteins and neutral fats --enter at different points along pathways XI. Aspects of Biosynthesis--Anabolism A. The body uses small molecules to build other substances B. These small molec ...
Where It Starts: Photosynthesis
... Calvin–Benson Cycle Cyclic pathway makes phosphorylated glucose • Uses energy from ATP, carbon and oxygen from CO2, and hydrogen and electrons from NADPH ...
... Calvin–Benson Cycle Cyclic pathway makes phosphorylated glucose • Uses energy from ATP, carbon and oxygen from CO2, and hydrogen and electrons from NADPH ...
2.3 Biomolecules Hon
... Organic: contains carbon and hydrogen ◦ All living things contain carbon (C), hydrogen (H), oxygen (O), nitrogen (N), phosphorus (P) and Sulfur (S) Monomer: created when C,H,O, N, P bond together to form small molecules Polymer: large compounds that are formed by joining monomers together ...
... Organic: contains carbon and hydrogen ◦ All living things contain carbon (C), hydrogen (H), oxygen (O), nitrogen (N), phosphorus (P) and Sulfur (S) Monomer: created when C,H,O, N, P bond together to form small molecules Polymer: large compounds that are formed by joining monomers together ...
Building Monomers of Macromolecules
... constructing each monomer, raise your hand to be checked to see if it correct. REMEMBER: Molecules are 3-dimensional so models will not always be flat! Background info: Living cells are made up of mostly water. The rest of the cell is largely made up of compounds that contain Carbon. Living things a ...
... constructing each monomer, raise your hand to be checked to see if it correct. REMEMBER: Molecules are 3-dimensional so models will not always be flat! Background info: Living cells are made up of mostly water. The rest of the cell is largely made up of compounds that contain Carbon. Living things a ...
Biochemistry Metabolic pathways - Limes-Institut-Bonn
... • Stores glycogen that can be made into glucose-6-phosphate, then glucose. • Makes glucose by gluconeogenesis (from pyruvate, de novo). • Synthesizes FA, cholesterol and bile salts. • Produces ketone bodies but cannot use them (no CoA transferase in the liver) • Only the liver and kidneys contain gl ...
... • Stores glycogen that can be made into glucose-6-phosphate, then glucose. • Makes glucose by gluconeogenesis (from pyruvate, de novo). • Synthesizes FA, cholesterol and bile salts. • Produces ketone bodies but cannot use them (no CoA transferase in the liver) • Only the liver and kidneys contain gl ...
Cellular Respiration
... There’s still 32 ATP left to get from the process (because aerobic produces a total of 36 ATP from each glucose). ...
... There’s still 32 ATP left to get from the process (because aerobic produces a total of 36 ATP from each glucose). ...
Carbohydrates
... *insulin low…GLUT4 in intracellular compartments; insulin high…GLUT4 translocates to membrane ...
... *insulin low…GLUT4 in intracellular compartments; insulin high…GLUT4 translocates to membrane ...
Cellular respiration *vs
... This fermentation occurs in the cytoplasm of the cell and produces only 2 molecules of ATP—Therefore, this is not as efficient of an energy path to follow. • So where does this fermentation occur—have you every been sore after a hard workout or from playing a sport you have not done for a long time? ...
... This fermentation occurs in the cytoplasm of the cell and produces only 2 molecules of ATP—Therefore, this is not as efficient of an energy path to follow. • So where does this fermentation occur—have you every been sore after a hard workout or from playing a sport you have not done for a long time? ...
doc 3.5.2 respiration revision Factual revision sheet for
... Relationship between respiration and photosynthesis: ...
... Relationship between respiration and photosynthesis: ...
Anaerobic Respiration
... NADH and ubiquinol from the Krebs cycle start a series of oxidation reduction reactions that move electrons through a series of carriers. The electron carriers together are called an “electron transport chain” ...
... NADH and ubiquinol from the Krebs cycle start a series of oxidation reduction reactions that move electrons through a series of carriers. The electron carriers together are called an “electron transport chain” ...
notes - is234
... the ultimate source of energy for all living things. Plants, algae, and some prokaryotes carry out Photosynthesis, the process during which sunlight’s energy is used to change CO₂ and H₂O into carbon compounds. Organisms that carry out photosynthesis are called Autotrophs or Producers . Heterotrophs ...
... the ultimate source of energy for all living things. Plants, algae, and some prokaryotes carry out Photosynthesis, the process during which sunlight’s energy is used to change CO₂ and H₂O into carbon compounds. Organisms that carry out photosynthesis are called Autotrophs or Producers . Heterotrophs ...
Answers to Test Your Understanding of Concepts
... be converted to glucose by the liver or be used in the synthesis of new proteins. Glucocorticoids thus promote an increase in blood glucose levels by stimulating gluconeogenesis. 3. Thyroxine stimulates the utilization of ATP by almost all cells. Since ATP exerts a negative feedback inhibition on ce ...
... be converted to glucose by the liver or be used in the synthesis of new proteins. Glucocorticoids thus promote an increase in blood glucose levels by stimulating gluconeogenesis. 3. Thyroxine stimulates the utilization of ATP by almost all cells. Since ATP exerts a negative feedback inhibition on ce ...
Chemistry of Life - Bilkent University
... nucleotides. • The main functions of nucleotides are information storage (DNA), protein synthesis (RNA), energy transfers (ATP and NAD), and signaling molecules (cAMP) • Nucleotides consist of a sugar, a nitrogenous base, and a phosphate. ...
... nucleotides. • The main functions of nucleotides are information storage (DNA), protein synthesis (RNA), energy transfers (ATP and NAD), and signaling molecules (cAMP) • Nucleotides consist of a sugar, a nitrogenous base, and a phosphate. ...
Biochemistry of Cells
... Fats in Organisms Most plants oils tend to be low in saturated fatty acids & exist as liquids at room temperature (oils) Fats Dietary fat consists largely of the molecule triglyceride composed of glycerol and three fatty acid chains Steroids The carbon skeleton of steroids is bent to form 4 fused ri ...
... Fats in Organisms Most plants oils tend to be low in saturated fatty acids & exist as liquids at room temperature (oils) Fats Dietary fat consists largely of the molecule triglyceride composed of glycerol and three fatty acid chains Steroids The carbon skeleton of steroids is bent to form 4 fused ri ...
CARBOHYDRATE METABOLISM
... muscle and adipose tissue. Insulin increases the number and promotes the activity of GLUT-4 in skeletal muscle and adipose tissue. ...
... muscle and adipose tissue. Insulin increases the number and promotes the activity of GLUT-4 in skeletal muscle and adipose tissue. ...
Chapter 6 and 9 - Wando High School
... 27. The primary goal of cellular respiration is to build ___________. Explain how energy is released and stored with this molecule. ATP, When one of the three phosphates is released, energy is released. When a phosphate is bound to the remaining two phosphates, energy is stored. 28. What are the pro ...
... 27. The primary goal of cellular respiration is to build ___________. Explain how energy is released and stored with this molecule. ATP, When one of the three phosphates is released, energy is released. When a phosphate is bound to the remaining two phosphates, energy is stored. 28. What are the pro ...
1 - Wsfcs
... What type of molecule is this? __________________ This process is called a ___________________ ______________________. (on board) If you were to break this large molecule apart into the two original glucose molecules, the process would be ______________________ (on board). What would you have to add ...
... What type of molecule is this? __________________ This process is called a ___________________ ______________________. (on board) If you were to break this large molecule apart into the two original glucose molecules, the process would be ______________________ (on board). What would you have to add ...
Glucose

Glucose is a sugar with the molecular formula C6H12O6. The name ""glucose"" (/ˈɡluːkoʊs/) comes from the Greek word γλευκος, meaning ""sweet wine, must"". The suffix ""-ose"" is a chemical classifier, denoting a carbohydrate. It is also known as dextrose or grape sugar. With 6 carbon atoms, it is classed as a hexose, a sub-category of monosaccharides. α-D-glucose is one of the 16 aldose stereoisomers. The D-isomer (D-glucose) occurs widely in nature, but the L-isomer (L-glucose) does not. Glucose is made during photosynthesis from water and carbon dioxide, using energy from sunlight. The reverse of the photosynthesis reaction, which releases this energy, is a very important source of power for cellular respiration. Glucose is stored as a polymer, in plants as starch and in animals as glycogen.