Cellular Respiration: Obtaining Energy from Food
... muscles is the limiting factor in their performance (VO2 max) Your muscles need a continuous supply of energy to perform work (contract and relax) Muscle cells obtain this energy from the sugar glucose through a series of chemical reactions that depend upon a constant input of oxygen (O2) When there ...
... muscles is the limiting factor in their performance (VO2 max) Your muscles need a continuous supply of energy to perform work (contract and relax) Muscle cells obtain this energy from the sugar glucose through a series of chemical reactions that depend upon a constant input of oxygen (O2) When there ...
Blood Composition and Blood Glucose Testing
... the medical device being utilized. All FDA-cleared blood glucose meters include individualized instructions for use (IFU) that provide guidance on how and where on the body a test sample should be obtained. Adherence to the IFU is the best way to ensure accurate results and minimize risk of patient ...
... the medical device being utilized. All FDA-cleared blood glucose meters include individualized instructions for use (IFU) that provide guidance on how and where on the body a test sample should be obtained. Adherence to the IFU is the best way to ensure accurate results and minimize risk of patient ...
Cellular Energy hbio 09 tri 1
... categories and write down what each item in the category shares in common. 2. Why did you put them in those categories and what do they have in common. ...
... categories and write down what each item in the category shares in common. 2. Why did you put them in those categories and what do they have in common. ...
fuels and tissues
... Neurons: no glycogen stores, glycogen in glial cells excess carbohydrate not needed for immediate use is stored as glycogen or TAGs FATS stored as TAGs in adipocytes long term fuel reserve (~ 3 months depending on individual fat stores) liver: preferred fuel; synthesis of FA for export in ...
... Neurons: no glycogen stores, glycogen in glial cells excess carbohydrate not needed for immediate use is stored as glycogen or TAGs FATS stored as TAGs in adipocytes long term fuel reserve (~ 3 months depending on individual fat stores) liver: preferred fuel; synthesis of FA for export in ...
Chapter 13 Carbohydrate Metabolism
... form free glucose from glycogen. – They can carry out the first two steps of glycogenolysis to produce glucose 6-phosphate. – This form of glucose is the first intermediate in the glycolysis pathway, which produces energy. – Muscles therefore only use glycogen for energy production. • In the liver, ...
... form free glucose from glycogen. – They can carry out the first two steps of glycogenolysis to produce glucose 6-phosphate. – This form of glucose is the first intermediate in the glycolysis pathway, which produces energy. – Muscles therefore only use glycogen for energy production. • In the liver, ...
Type 2 Diabetes
... Increased liberation of glucose into circulation from liver. Therefore there is an extracellular glucose excess and in many cells an intracellular glucose deficiency – “starvation in the midst of plenty”. ...
... Increased liberation of glucose into circulation from liver. Therefore there is an extracellular glucose excess and in many cells an intracellular glucose deficiency – “starvation in the midst of plenty”. ...
GLUCONEOGENESIS, GLYCOGEN SYNTHESIS & DEGRADATION
... The carboxyl is transferred from this ~P intermediate to of a ureido group of the biotin ring. Overall: biotin + ATP + HCO3 carboxybiotin + ADP + Pi ...
... The carboxyl is transferred from this ~P intermediate to of a ureido group of the biotin ring. Overall: biotin + ATP + HCO3 carboxybiotin + ADP + Pi ...
Science of running
... • Increase stroke volume – amount of blood that can be pushed from the heart • Increase the amount of oxygen in the blood (Iron) • Increase the amount of capillaries that move the blood to the muscles ...
... • Increase stroke volume – amount of blood that can be pushed from the heart • Increase the amount of oxygen in the blood (Iron) • Increase the amount of capillaries that move the blood to the muscles ...
Cellular Respiration
... Electron carriers that were reduced in glycolysis are oxidized in fermentation so that they can return to glycolysis process ...
... Electron carriers that were reduced in glycolysis are oxidized in fermentation so that they can return to glycolysis process ...
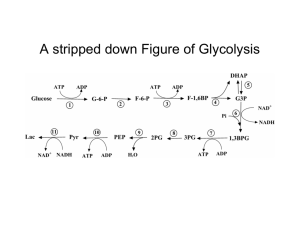
Figure 17-3 Degradation of glucose via the glycolytic pathway.
... by NADH. Thus, no net oxidation occurs in glycolysis = fermentation; another organic serving as electron acceptor. •lactate, end-product under anaerobic conditions, diffuses thru cell membrane as waste into blood - salvaged by liver and rebuilt to form glucose (gluconeogenesis). This occurs in skele ...
... by NADH. Thus, no net oxidation occurs in glycolysis = fermentation; another organic serving as electron acceptor. •lactate, end-product under anaerobic conditions, diffuses thru cell membrane as waste into blood - salvaged by liver and rebuilt to form glucose (gluconeogenesis). This occurs in skele ...
Chapter 7
... The Final Steps of Catabolism • All energy-yieldiing nutrients proceed down three different pathways that lead to the point where acetyl CoA enters the TCA cycle. These reactions take place in the mitochondria. • The TCA-Oxalacetate is the first 4-carbon compound to enter the TCA cycle. And cannot ...
... The Final Steps of Catabolism • All energy-yieldiing nutrients proceed down three different pathways that lead to the point where acetyl CoA enters the TCA cycle. These reactions take place in the mitochondria. • The TCA-Oxalacetate is the first 4-carbon compound to enter the TCA cycle. And cannot ...
Biochemistry PowerPoint
... up chemical reactions without being affected by the reactions themselves. Enzyme: a protein that increases the rate of reactions by lowering the activation energy. ...
... up chemical reactions without being affected by the reactions themselves. Enzyme: a protein that increases the rate of reactions by lowering the activation energy. ...
Nutrition
... 1) glucose catabolism is inhibited 2) glucose conversion to glycogen (glycogenesis) or to fat (lipogenesis) is stimulated B) When ATP or glucose levels drop the body can then convert glycogen back to glucose 1) glycogenolysis – production of glucose from glycogen 2) gluconeogenesis – formation of gl ...
... 1) glucose catabolism is inhibited 2) glucose conversion to glycogen (glycogenesis) or to fat (lipogenesis) is stimulated B) When ATP or glucose levels drop the body can then convert glycogen back to glucose 1) glycogenolysis – production of glucose from glycogen 2) gluconeogenesis – formation of gl ...
Metabolism and Energetics
... Beta oxidation is a repeating 4 step process in which sequential 2-C groups (“acetyl groups”) are cut from the long chain; they are attached to a carrier (CoA) and then shuttled into the mitochondria These 2-C groups are then burned in the ...
... Beta oxidation is a repeating 4 step process in which sequential 2-C groups (“acetyl groups”) are cut from the long chain; they are attached to a carrier (CoA) and then shuttled into the mitochondria These 2-C groups are then burned in the ...
Biomolecules - Mercer Island School District
... __________________________. An _____ group from one subunit is linked with a ______ on the other subunit, forming _________. The subunits are linked covalently together. ...
... __________________________. An _____ group from one subunit is linked with a ______ on the other subunit, forming _________. The subunits are linked covalently together. ...
B4 The Processes of Life
... makes large food molecules using carbon dioxide and water and it happens in plants as well as some micro organisms: That’s a nice plant. I’m going to put it in the sun and give it lots of water and air… ...
... makes large food molecules using carbon dioxide and water and it happens in plants as well as some micro organisms: That’s a nice plant. I’m going to put it in the sun and give it lots of water and air… ...
glycogen, calcification
... Extensive microvascular calcification and occlusion/thrombosis lead to violaceous skin lesions, which progress to nonhealing ulcers with secondary infection, often leading to sepsis and death. The lower extremities are predominantly involved (roughly 90% of ...
... Extensive microvascular calcification and occlusion/thrombosis lead to violaceous skin lesions, which progress to nonhealing ulcers with secondary infection, often leading to sepsis and death. The lower extremities are predominantly involved (roughly 90% of ...
File
... Although constituting only 0.5% of body mass, kidneys consume 10% of the oxygen used in cellular respiration. Much of the glucose that is reabsorbed is carried into the kidney cells by the sodium-glucose cotransporter. ...
... Although constituting only 0.5% of body mass, kidneys consume 10% of the oxygen used in cellular respiration. Much of the glucose that is reabsorbed is carried into the kidney cells by the sodium-glucose cotransporter. ...
ch 9 Cellular_Respiration
... • Occurs in the inner mitochondrial membrane • Electrons stored in NADH and FADH2 from glycolysis and the CAC are transported to the ETC • Oxygen is the final ...
... • Occurs in the inner mitochondrial membrane • Electrons stored in NADH and FADH2 from glycolysis and the CAC are transported to the ETC • Oxygen is the final ...
Biomolecules - VCS1-to-1
... Macromolecules • Each macromolecule is made up of smaller organic molecules. • These smaller molecules are called monomers. • Monomers that are bonded together are called polymers. ...
... Macromolecules • Each macromolecule is made up of smaller organic molecules. • These smaller molecules are called monomers. • Monomers that are bonded together are called polymers. ...
2. tissue - specific metabolism - cmb
... bloodstream transports what may be one organ's waste product but another organ's fuel (for example, lactate from muscle to liver). 2. Blood transports oxygen from lungs to tissues, enabling exergonic oxidative pathways to occur, followed by transport of the resultant CO2 back to the lungs for exhal ...
... bloodstream transports what may be one organ's waste product but another organ's fuel (for example, lactate from muscle to liver). 2. Blood transports oxygen from lungs to tissues, enabling exergonic oxidative pathways to occur, followed by transport of the resultant CO2 back to the lungs for exhal ...
Nutrition PowerPoint
... 3.2.1 Outline the terms metabolism, anabolism, aerobic catabolism and aerobic catabolism . ...
... 3.2.1 Outline the terms metabolism, anabolism, aerobic catabolism and aerobic catabolism . ...
clin sys MENU v 8
... ELITech Clinical Systems offers a broad and growing menu of liquid-stable reagents backed by more than 25 years of experience in assay development and reagent manufacturing. ELITech reagents are: ...
... ELITech Clinical Systems offers a broad and growing menu of liquid-stable reagents backed by more than 25 years of experience in assay development and reagent manufacturing. ELITech reagents are: ...
Glucose

Glucose is a sugar with the molecular formula C6H12O6. The name ""glucose"" (/ˈɡluːkoʊs/) comes from the Greek word γλευκος, meaning ""sweet wine, must"". The suffix ""-ose"" is a chemical classifier, denoting a carbohydrate. It is also known as dextrose or grape sugar. With 6 carbon atoms, it is classed as a hexose, a sub-category of monosaccharides. α-D-glucose is one of the 16 aldose stereoisomers. The D-isomer (D-glucose) occurs widely in nature, but the L-isomer (L-glucose) does not. Glucose is made during photosynthesis from water and carbon dioxide, using energy from sunlight. The reverse of the photosynthesis reaction, which releases this energy, is a very important source of power for cellular respiration. Glucose is stored as a polymer, in plants as starch and in animals as glycogen.