* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Science of running
Adenosine triphosphate wikipedia , lookup
Gaseous signaling molecules wikipedia , lookup
Citric acid cycle wikipedia , lookup
Photosynthetic reaction centre wikipedia , lookup
Oxidative phosphorylation wikipedia , lookup
Metalloprotein wikipedia , lookup
Microbial metabolism wikipedia , lookup
Evolution of metal ions in biological systems wikipedia , lookup
Basal metabolic rate wikipedia , lookup
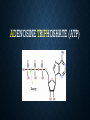
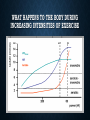
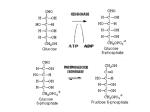
SCIENCE OF RUNNING Your body’s ability to adapt to stresses and strengthen itself is a miracle! What is required for your body to move? ADENOSINE TRIPHOSHATE (ATP) Energy CREATINE PHOSPHATE + ADP Positives • Immediate source of energy • Oxygen is not necessary (anaerobic) • Quick bursts of energy Negatives • Limited amount of storage of creating phosphate in the muscles • Does not endure for long-term low intensity activities? ANAEROBIC GLYCOLYSIS Positives • Does not require oxygen (anaerobic) • Produces two molecules of Pyruvate which can be used in aerobic metabolism • Produces hydrogen which in the presence of oxygen starts aerobic metabolism • Produces ATP quite rapidly for activities that last between 30 seconds and 3 minutes Negatives • Glucose is required (glycolysis is the splitting of glucose molecules) • When oxygen is not present, hydrogen bonds to Pyruvate to form Lactic Acid which must be cleared out of the blood stream through the liver. AEROBIC GLYCOLYSIS Positives • Requires the presence of oxygen • Uses Hydrogen and Pyruvate (Lactic Acid) • Produces 38 molecules of ATP from one glucose molecule • Can use fat as a source of energy • No negative waste products • As long as fuel is present, aerobic glycolysis can continue for long periods of exercise Negatives • Very slow process CPT DEVELOPMENT • Why develop this system? • How do you develop the CPT system? • When is the ideal time to focus on this system? ANAEROBIC GLYCOLYSIS DEVELOPMENT • Why develop this system? • How do you develop the anaerobic energy system? • When is the ideal time to focus on this system? • What are the physiological effects of training this system? AEROBIC DEVELOPMENT • Why develop this system? • How do you develop the aerobic energy system? • When is the ideal time to focus on this system? • What are the physiological effects of developing this system? • How do you know when you move from aerobic to anaerobic training? WHAT HAPPENS TO THE BODY DURING INCREASING INTENSITIES OF EXERCISE ENERGY SYSTEM BY DISTANCE LIMITING FACTORS OF PERFORMANCE • Transporting oxygen to the muscles • Increase stroke volume – amount of blood that can be pushed from the heart • Increase the amount of oxygen in the blood (Iron) • Increase the amount of capillaries that move the blood to the muscles • Utilizing oxygen that is transported to the muscle cells • Increase the size and number of mitochondria • Increase the body’s ability to clear lactic acid from the blood stream • Mentally train the body to experience more discomfort SUPERCOMPENSATION THEORY CREATING A TRAINING PLAN • What energy system should be the focus at each part of the season? • How do you provide the correct stimulus? • How much stress should be presented to the body? • How can you help the body during the supercompensation phase? • What factors will limit the amount of stress that can be presented to the body and how can you increase these limits? • ***Listen to your body…this cannot be overstated***