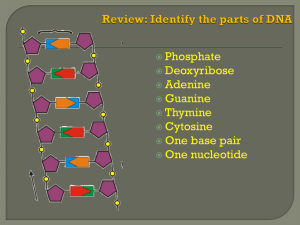
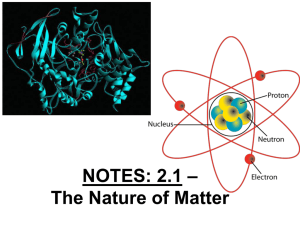
Section 2.3 and 2.4 Guided Notes
... Structure is key to the function of enzymes. • If…… • The order of amino acids changes or • The temperature or pH changes to much Then….. • The protein will not function!! ...
... Structure is key to the function of enzymes. • If…… • The order of amino acids changes or • The temperature or pH changes to much Then….. • The protein will not function!! ...
Ei otsikkoa
... energy raises an electron from one energy level to another. Since bonding in complex ions involves always d orbitals, the electron transition occurs within the split d orbital. ...
... energy raises an electron from one energy level to another. Since bonding in complex ions involves always d orbitals, the electron transition occurs within the split d orbital. ...
Proteins
... The Structure of Molecules Determines the Function • Ex. Gloves have specific shape that gives them the ability to do certain things ...
... The Structure of Molecules Determines the Function • Ex. Gloves have specific shape that gives them the ability to do certain things ...
6.3 Life Substances
... Used by cells to store energy, insulate and in protective coatings Organic compound with many more carbon and hydrogen than carbohydrates ...
... Used by cells to store energy, insulate and in protective coatings Organic compound with many more carbon and hydrogen than carbohydrates ...
Ex. glucose, fructose and galactose: these are isomers
... B. Polypeptides: very long chains of amino acids. The amino acids in the chains interact with each other, forming different types of structures: 1.__________________________ 2.__________________________ 3.__________________________ C. The ___________________of a protein is greatly influenced by cond ...
... B. Polypeptides: very long chains of amino acids. The amino acids in the chains interact with each other, forming different types of structures: 1.__________________________ 2.__________________________ 3.__________________________ C. The ___________________of a protein is greatly influenced by cond ...
Biology Unit 2 Organic Notes The Chemistry of Carbon Organic
... Nucleic acids are polymers assembled from individual monomers known as nucleotides. ...
... Nucleic acids are polymers assembled from individual monomers known as nucleotides. ...
Biological (organic) Molecules
... Used for energy storage and to build cell structures Broken down through cellular respiration to create energy (ATP) ...
... Used for energy storage and to build cell structures Broken down through cellular respiration to create energy (ATP) ...
Chemical Bond – a force that holds two atoms together, the bond
... Ionic Bond – an electrostatic force between two different atomic elements (atomic nonmetal and an atomic metal) in which the atomic nonmetal steals the available electron/s for bonding from the atomic metal, thus creating a positive cation on the atomic metal, and a negative anion from atomic non me ...
... Ionic Bond – an electrostatic force between two different atomic elements (atomic nonmetal and an atomic metal) in which the atomic nonmetal steals the available electron/s for bonding from the atomic metal, thus creating a positive cation on the atomic metal, and a negative anion from atomic non me ...
1A - The changing atom History of the atom • The model of the atom
... As the atom has the same number of protons and electrons it will have the same chemical properties. They are all hydrogen atoms because they all have the same number of protons Hydrogen can be used as an example:- ...
... As the atom has the same number of protons and electrons it will have the same chemical properties. They are all hydrogen atoms because they all have the same number of protons Hydrogen can be used as an example:- ...
Enzymes and Temperature
... They can also help to keep the pH at a constant level as you investigate another factor. ...
... They can also help to keep the pH at a constant level as you investigate another factor. ...
Life Science
... Active transport: requires energy to be expended by the cell. Often moving substances from low concentration to high concentration. Often uses “Transport Proteins” which grab molecules outside the cell and pull them inside the cell: example insulin requires a transport protein to enter the cell. Pas ...
... Active transport: requires energy to be expended by the cell. Often moving substances from low concentration to high concentration. Often uses “Transport Proteins” which grab molecules outside the cell and pull them inside the cell: example insulin requires a transport protein to enter the cell. Pas ...
Life Science Chapter 1 Part 2 Chemical Compounds in Cells
... Atoms bind together w/ 2 basic types of bonds: Ionic – atom “steals” electrons (ie NaCl) - metal + nonmetal Covalent – atoms “share” electrons ie (C6H12O6) – 2 or more nonmetals ...
... Atoms bind together w/ 2 basic types of bonds: Ionic – atom “steals” electrons (ie NaCl) - metal + nonmetal Covalent – atoms “share” electrons ie (C6H12O6) – 2 or more nonmetals ...
C1 - Metals Quiz
... solution is either electrolysed or scrap iron is added to displace the copper ions What are the pros and cons of phytomining? Pro: heat released during burning of plants can be used to heat houses or produce electricity. Plants absorb CO2 during photosynthesis. Cons: not continuous/Batch process so ...
... solution is either electrolysed or scrap iron is added to displace the copper ions What are the pros and cons of phytomining? Pro: heat released during burning of plants can be used to heat houses or produce electricity. Plants absorb CO2 during photosynthesis. Cons: not continuous/Batch process so ...
Notes
... • Identify the three subatomic particles found in atoms. • Explain how all of the isotopes of an element are similar and how they are different. • Explain how compounds are different from their component elements. • Describe the two main types of chemical bonds ...
... • Identify the three subatomic particles found in atoms. • Explain how all of the isotopes of an element are similar and how they are different. • Explain how compounds are different from their component elements. • Describe the two main types of chemical bonds ...
Balancing Chemical Equations
... Balancing Chemical Equations Chemical reactions can be represented as: i) word equations: water hydrogen + oxygen ii) iii) ...
... Balancing Chemical Equations Chemical reactions can be represented as: i) word equations: water hydrogen + oxygen ii) iii) ...
Answers for extension worksheet – Chapter 7
... ribosome as a peptide bond forms between them. The first site holds incoming tRNA, the second site is where amino acids are linked to the polypeptide being formed and the third site is where the tRNA leaves the ribosome once its amino acid has detached. ...
... ribosome as a peptide bond forms between them. The first site holds incoming tRNA, the second site is where amino acids are linked to the polypeptide being formed and the third site is where the tRNA leaves the ribosome once its amino acid has detached. ...
Protein - PBworks
... Protein is an energy supplying nutrient made up of carbon, hydrogen, oxygen and nitrogen. The nitrogen is what makes it different from carbohydrates and fats. Proteins are formed from the combining of 20 different amino acids into different combinations and patterns. There are at least 30,000 differ ...
... Protein is an energy supplying nutrient made up of carbon, hydrogen, oxygen and nitrogen. The nitrogen is what makes it different from carbohydrates and fats. Proteins are formed from the combining of 20 different amino acids into different combinations and patterns. There are at least 30,000 differ ...
Unit 1: Biology Review
... essential to cell communication and muscle contraction. - All biological compounds contain a few common elements: C, H, O, N, P, S. - However, there are also other elements common to our body, but not always found in organic compounds: Ca, P, K, Na, Cl, Fe - Calcium = bones + teeth - Phosphorus = (a ...
... essential to cell communication and muscle contraction. - All biological compounds contain a few common elements: C, H, O, N, P, S. - However, there are also other elements common to our body, but not always found in organic compounds: Ca, P, K, Na, Cl, Fe - Calcium = bones + teeth - Phosphorus = (a ...
history of an atom Part 1
... Name: _________________________________ Date: ________________ Period: _______ Page#:_____ HISTORY OF THE ATOM NOTES PART 1 Dalton’s Atomic Theory: 1. All matter is made of indivisible and indestructible atoms. 2. All atoms of the same element are identical in their physical and chemical properties. ...
... Name: _________________________________ Date: ________________ Period: _______ Page#:_____ HISTORY OF THE ATOM NOTES PART 1 Dalton’s Atomic Theory: 1. All matter is made of indivisible and indestructible atoms. 2. All atoms of the same element are identical in their physical and chemical properties. ...
Metalloprotein

Metalloprotein is a generic term for a protein that contains a metal ion cofactor. A large number of all proteins are part of this category.