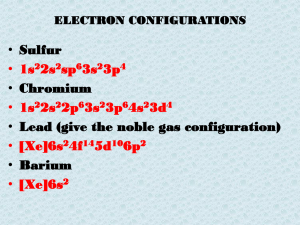
Syllabus Notes - Southwest High School
... 2.1.2 State that a variety of other elements are needed by living organisms including nitrogen, calcium, phosphorus, iron and sodium. 2.1.3 State one role for each of the elements mentioned in 2.1.2. (leave room) N protein, and nucleic acids (DNA), makes stuff POLAR. Ca bones and muscle contract ...
... 2.1.2 State that a variety of other elements are needed by living organisms including nitrogen, calcium, phosphorus, iron and sodium. 2.1.3 State one role for each of the elements mentioned in 2.1.2. (leave room) N protein, and nucleic acids (DNA), makes stuff POLAR. Ca bones and muscle contract ...
ALE 23. Balancing Redox Reactions
... How does one balance a reaction for both matter and charge? The Model Oxidation-reduction or Redox reactions involve the transfer of one or more electrons from one chemical species to another. Redox reactions are involved in the corrosion of metals, the combustion of fuels, the generation of electri ...
... How does one balance a reaction for both matter and charge? The Model Oxidation-reduction or Redox reactions involve the transfer of one or more electrons from one chemical species to another. Redox reactions are involved in the corrosion of metals, the combustion of fuels, the generation of electri ...
Here
... 1. Definition – two or more substances that combine to form a new compound 2. Generic formula – A + X -> AX B. Decomposition 1. Definition – a single compound undergoes a rxn to produce two or more simpler substances 2. Generic – AX -> A + X C. Single-Replacement 1. Definition – when one element tak ...
... 1. Definition – two or more substances that combine to form a new compound 2. Generic formula – A + X -> AX B. Decomposition 1. Definition – a single compound undergoes a rxn to produce two or more simpler substances 2. Generic – AX -> A + X C. Single-Replacement 1. Definition – when one element tak ...
Ch. 3 Study Guide
... 7. Carbohydrates perform three primary functions for cells. They are: A. B. C. 8. Compare and contrast monosaccharides, disaccharides, and polysaccharides ...
... 7. Carbohydrates perform three primary functions for cells. They are: A. B. C. 8. Compare and contrast monosaccharides, disaccharides, and polysaccharides ...
Chapter 7 and Protein Examples
... Heme is a protoporphyrin IX with an iron(II) atom in its center figure 12.12). The iron atom can form six coordinating ligand bonds. The iron is coordinated to 4 nitrogen groups within the heme structure The fifth coordinate bond is to a nitrogen of a distal His residue within the protein. O2 forms ...
... Heme is a protoporphyrin IX with an iron(II) atom in its center figure 12.12). The iron atom can form six coordinating ligand bonds. The iron is coordinated to 4 nitrogen groups within the heme structure The fifth coordinate bond is to a nitrogen of a distal His residue within the protein. O2 forms ...
ORGANIC CHEMISTRY 4 Types of Macromolecules
... Two types of nucleic acids – 1. DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) – double strand of genetic information 2. RNA (ribonucleic acid) – single strand copy of DNA used to build proteins Examples of nongenetic nucleotides - plays a major role in cell metabolism 1. ATP (adenosine triphosphate) – carries energy ...
... Two types of nucleic acids – 1. DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) – double strand of genetic information 2. RNA (ribonucleic acid) – single strand copy of DNA used to build proteins Examples of nongenetic nucleotides - plays a major role in cell metabolism 1. ATP (adenosine triphosphate) – carries energy ...
Carbon compounds - Sonoma Valley High School
... out the ‘amino’ and carboxyl group to label it? ...
... out the ‘amino’ and carboxyl group to label it? ...
Coefficients and Subscripts
... A subscript, like the 2 in H2O, tells how many of an atom there are in any one molecule of a compound, so H2O has 2 Hydrogens and 1 Oxygen atom per water molecule. A coefficient, on the other hand, tells you how many molecules of a compound you need to perform a chemical reaction. So if a chemical r ...
... A subscript, like the 2 in H2O, tells how many of an atom there are in any one molecule of a compound, so H2O has 2 Hydrogens and 1 Oxygen atom per water molecule. A coefficient, on the other hand, tells you how many molecules of a compound you need to perform a chemical reaction. So if a chemical r ...
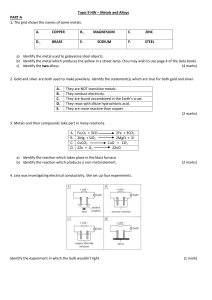
Topic 9 HW – Metals and Alloys PART A 1. The grid shows the
... 5. Kevin was investigating corrosion. He set up four experiments as shown in the grid below. ...
... 5. Kevin was investigating corrosion. He set up four experiments as shown in the grid below. ...
4. bonding - New Hartford Central Schools
... Either absorb or release energy when formed Create new species with chemical and physical properties unlike constituent atoms Form because atoms want to have complete outer shells ...
... Either absorb or release energy when formed Create new species with chemical and physical properties unlike constituent atoms Form because atoms want to have complete outer shells ...
Chemistry 199 - Oregon State chemistry
... Does Co3+ act as a Lewis acid? Draw the Lewis structure and explain. List and draw two additional Lewis acids. Yes, Co3+ like the transition metal ions acts as Lewis acids. They accept a pair (or several pairs) of electrons to form a new bond (several new bonds). On the left side of the structure be ...
... Does Co3+ act as a Lewis acid? Draw the Lewis structure and explain. List and draw two additional Lewis acids. Yes, Co3+ like the transition metal ions acts as Lewis acids. They accept a pair (or several pairs) of electrons to form a new bond (several new bonds). On the left side of the structure be ...
Catabolism vs Anabolism
... Providing or picking up protons to allow for more efficient reaction catalysis. Happens in Chymotrypsin! H+ provided by Ser195 OH group! ...
... Providing or picking up protons to allow for more efficient reaction catalysis. Happens in Chymotrypsin! H+ provided by Ser195 OH group! ...
Biological Molecules
... Starch (plants) and glycogen (animals) are formed so as not to interfere with cell chemistry and osmosis. They can be quickly broken down to glucose and used as energy. (hydrolysis) ...
... Starch (plants) and glycogen (animals) are formed so as not to interfere with cell chemistry and osmosis. They can be quickly broken down to glucose and used as energy. (hydrolysis) ...
Chapter 5
... Biologically important amino acids • Neurotransmitter AAs – Glycine, glutamate, taurine, aspartate ...
... Biologically important amino acids • Neurotransmitter AAs – Glycine, glutamate, taurine, aspartate ...
Design and Synthesis of a New Chelate for the Uranyl Ion
... Biological Chemistry Department, College of Judea and Samaria, Ariel, Israel The hard acid, large uranyl cation is expected to form stable complexes with diamino tetradentate dianionic open chain ligands. As the two axial position of the dioxo cation are occupied it was decided to design a flexible ...
... Biological Chemistry Department, College of Judea and Samaria, Ariel, Israel The hard acid, large uranyl cation is expected to form stable complexes with diamino tetradentate dianionic open chain ligands. As the two axial position of the dioxo cation are occupied it was decided to design a flexible ...
ch 7 organic power point
... The water molecule “adds” to the doublebonded carbon atoms by placing an H- on one carbon and an –OH group on the other. H ...
... The water molecule “adds” to the doublebonded carbon atoms by placing an H- on one carbon and an –OH group on the other. H ...
Introducing Transition Metals
... sub-levels are very close in energy. It is relatively easy to lose electrons from either of these sub-levels. The oxidation state of the metal in a compound is noted as a Roman numeral after the name of the metal. ...
... sub-levels are very close in energy. It is relatively easy to lose electrons from either of these sub-levels. The oxidation state of the metal in a compound is noted as a Roman numeral after the name of the metal. ...
Writing formulas and naming ionic bonds
... NH4OH Aluminum chlorate Al(ClO3)3 Lead(II) sulfide Pb3S2 Magnesium hydroxide Mg(OH)2 ...
... NH4OH Aluminum chlorate Al(ClO3)3 Lead(II) sulfide Pb3S2 Magnesium hydroxide Mg(OH)2 ...
Coordination Number 2
... Transition metal complexes with the coordination number 1 are rare. In the case of main group elements this coordination number is more common, e.g. in HF, IF. It can be also observed in the gas phase. In the following reference (this journal is in the library) a compound had been reported which is ...
... Transition metal complexes with the coordination number 1 are rare. In the case of main group elements this coordination number is more common, e.g. in HF, IF. It can be also observed in the gas phase. In the following reference (this journal is in the library) a compound had been reported which is ...
The Chemistry of Life – Matter and Energy
... pH scale – measures concentration of H+ (hydrogen ion) in solution • Ranges from 0 to 14 ...
... pH scale – measures concentration of H+ (hydrogen ion) in solution • Ranges from 0 to 14 ...
Metals and non-metals III IMPORTANT POINTS Non-metals
... 1. a. Magnesium, chromium and sodium are all metals, hence, they react with oxygen to form basic oxides b. Chromium, as it is a transition metal. Metals have high density and coloured compounds are formed by transition metals. c. Bromine - the formula is Br2, that is, two atoms of bromine. d. Bromin ...
... 1. a. Magnesium, chromium and sodium are all metals, hence, they react with oxygen to form basic oxides b. Chromium, as it is a transition metal. Metals have high density and coloured compounds are formed by transition metals. c. Bromine - the formula is Br2, that is, two atoms of bromine. d. Bromin ...
Name Due date ______ Strive for a 5 – AP Biology Review Unit 1
... 20. A student added a strong acid to a beaker containing a solution with a functional protein. After adding the acid, the protein no longer functioned. Explain how adding the acid altered the protein’s structure and function. Be sure to include the following terms in your answer: protons, 3D structu ...
... 20. A student added a strong acid to a beaker containing a solution with a functional protein. After adding the acid, the protein no longer functioned. Explain how adding the acid altered the protein’s structure and function. Be sure to include the following terms in your answer: protons, 3D structu ...
NUR101ModB
... Atom nucleus is the center core of the atom and contains protons and neutrons. Protons are positively charged particles within the nucleus of an atom. Neutrons are electrically neutral particles within the nucleus of an atom. Electrons are negatively charged particles orbiting the nucleus of ...
... Atom nucleus is the center core of the atom and contains protons and neutrons. Protons are positively charged particles within the nucleus of an atom. Neutrons are electrically neutral particles within the nucleus of an atom. Electrons are negatively charged particles orbiting the nucleus of ...
Metalloprotein

Metalloprotein is a generic term for a protein that contains a metal ion cofactor. A large number of all proteins are part of this category.