Chem Reactions (and Balancing Equations)
... (s) after the formula –solid Cu(s) (g) after the formula –gas H2 (g) (l) after the formula -liquid H2O(l) (aq) after the formula - dissolved in water, an aqueous solution. CaCl2 (aq) • used after a product indicates a gas (same as (g)) O2 • used after a product indicates a solid (same as (s)) ...
... (s) after the formula –solid Cu(s) (g) after the formula –gas H2 (g) (l) after the formula -liquid H2O(l) (aq) after the formula - dissolved in water, an aqueous solution. CaCl2 (aq) • used after a product indicates a gas (same as (g)) O2 • used after a product indicates a solid (same as (s)) ...
Chapter 2 Molecules to enzymes Short Answer
... f. triplets of nucleotides on mRNA are codons; g. translation converts mRNA sequence of information into a specific amino acid chain (polypeptide); h. (each class of) tRNA carries a specific triplet of (three) bases called an anticodon; i. anticodons bind to codons by complementary base pairing; j. ...
... f. triplets of nucleotides on mRNA are codons; g. translation converts mRNA sequence of information into a specific amino acid chain (polypeptide); h. (each class of) tRNA carries a specific triplet of (three) bases called an anticodon; i. anticodons bind to codons by complementary base pairing; j. ...
Protein Structure
... • The tertiary structure is the final specific geometric shape that a protein assumes. • This final shape is determined and stabilized by a variety of bonding interactions between the side chains of the amino acids • These bonding interactions between side chains may cause a number of folds, bends, ...
... • The tertiary structure is the final specific geometric shape that a protein assumes. • This final shape is determined and stabilized by a variety of bonding interactions between the side chains of the amino acids • These bonding interactions between side chains may cause a number of folds, bends, ...
Basic Chemistry - Biology with Radjewski
... undergo chemical reactions to fill their outer shells. • They can attain stability by sharing electrons with other atoms (covalent bond) or by losing or gaining electrons (ionic bond) • The atoms are then bonded together into molecules. • Octet rule—atoms with at least two electron shells form stabl ...
... undergo chemical reactions to fill their outer shells. • They can attain stability by sharing electrons with other atoms (covalent bond) or by losing or gaining electrons (ionic bond) • The atoms are then bonded together into molecules. • Octet rule—atoms with at least two electron shells form stabl ...
UNIT 9: CO-ORDINATION COMPOUNDS
... Ambidentate ligand: A ligand that can ligate through two different atoms, one at a time. Ex-NO2- ; SCNv) Coordination number: The no. of ligand donor atoms to which the metal is directly bonded through sigma bonds only. It is commonly 4 or 6. vi) Counter ions: The ionisable groups written outside th ...
... Ambidentate ligand: A ligand that can ligate through two different atoms, one at a time. Ex-NO2- ; SCNv) Coordination number: The no. of ligand donor atoms to which the metal is directly bonded through sigma bonds only. It is commonly 4 or 6. vi) Counter ions: The ionisable groups written outside th ...
Protein engineering of aldolase: Directed evolution
... important for functioning of the enzyme. These studies have added to our knowledge of the mechanism of this enzyme. ii) Directed evolution of aldolase A powerful technique to create mutant enzymes with novel properties is directed evolution, which mimicks the process that created naturally occuring ...
... important for functioning of the enzyme. These studies have added to our knowledge of the mechanism of this enzyme. ii) Directed evolution of aldolase A powerful technique to create mutant enzymes with novel properties is directed evolution, which mimicks the process that created naturally occuring ...
Chemistry in Living Things - Mercer Island School District
... Quaternary structure: Proteins that have more than one polypeptide chain joined together. Animation: http://www.stolaf.edu/people/giannini/flashanimat/proteins/ protein%20structure.swf ...
... Quaternary structure: Proteins that have more than one polypeptide chain joined together. Animation: http://www.stolaf.edu/people/giannini/flashanimat/proteins/ protein%20structure.swf ...
Proteins
... Proteins • . essential life substance of all living matter . • act as structural unit to build our bodies . • specific structural chemical units amino acids • amino [alkaline substance carbon, hydrogen ,o2& NH2. ...
... Proteins • . essential life substance of all living matter . • act as structural unit to build our bodies . • specific structural chemical units amino acids • amino [alkaline substance carbon, hydrogen ,o2& NH2. ...
Transition elements – electron configurations
... Some ligands combine more strongly with transition metal ions than others. A ligand that binds strongly can displace a ligand that binds more weakly. This is called ligand substitution. You can see ligand substitution in experiments because different ligands change the colour of the solution as a di ...
... Some ligands combine more strongly with transition metal ions than others. A ligand that binds strongly can displace a ligand that binds more weakly. This is called ligand substitution. You can see ligand substitution in experiments because different ligands change the colour of the solution as a di ...
Title - Iowa State University
... 10. How does competitive inhibition affect enzyme function? a. A regulatory molecule binds at a location other than the active site and changes the shape of the enzyme in a way that makes the active site available to the enzyme’s natural substrates. b. Regulatory molecules that are similar in size a ...
... 10. How does competitive inhibition affect enzyme function? a. A regulatory molecule binds at a location other than the active site and changes the shape of the enzyme in a way that makes the active site available to the enzyme’s natural substrates. b. Regulatory molecules that are similar in size a ...
LOYOLA COLLEGE (AUTONOMOUS), CHENNAI – 600 034 Part A
... 6. Differentiate LDL from HDL. 7. What is chemi-osmotic hypothesis? 8. Comment on auto oxidation. 9. Write a note on Zimmermann reaction. 10. What are anti oxidants? ...
... 6. Differentiate LDL from HDL. 7. What is chemi-osmotic hypothesis? 8. Comment on auto oxidation. 9. Write a note on Zimmermann reaction. 10. What are anti oxidants? ...
Physical Properties - Winthrop Chemistry, Physics, and Geology
... • Stretches of charged amino acids will disrupt a helix as will a stretch of amino acids with bulky side chains – Charge repulsion and steric repulsion ...
... • Stretches of charged amino acids will disrupt a helix as will a stretch of amino acids with bulky side chains – Charge repulsion and steric repulsion ...
Notes
... change in pH – do so by taking up excess H+ or OH- ions. •Help maintain pH in blood, stomach acid, urine, and intestinal fluid – example of how your body maintains ...
... change in pH – do so by taking up excess H+ or OH- ions. •Help maintain pH in blood, stomach acid, urine, and intestinal fluid – example of how your body maintains ...
A Mad Scientist`s Chemistry Presentation
... relatively strong positive charge. • It can attract the negative pole of other nearby molecules. • This attraction is called a hydrogen bond, even though it is not a true chemical bond. • Hydrogen bonds are very important in many compounds in living things. • For example, they help form the structur ...
... relatively strong positive charge. • It can attract the negative pole of other nearby molecules. • This attraction is called a hydrogen bond, even though it is not a true chemical bond. • Hydrogen bonds are very important in many compounds in living things. • For example, they help form the structur ...
Chapter 1-The Chemical Nature of Cells
... Ionic Compounds In nature, atoms will interact in such a way that they become more stable. When atoms of an element that is a metal interact with atoms of an element that is a non-metal, a small number of electrons transfer from the surface of the metal atom to the surface of the non-metal atom. Thi ...
... Ionic Compounds In nature, atoms will interact in such a way that they become more stable. When atoms of an element that is a metal interact with atoms of an element that is a non-metal, a small number of electrons transfer from the surface of the metal atom to the surface of the non-metal atom. Thi ...
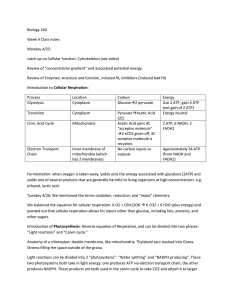
Week 4:
... We balanced the equation for cellular respiration: 6 O2 + C6H12O6 6 CO2 + 6 H2O (plus energy) and pointed out that cellular respiration allows for inputs other than glucose, including fats, proteins, and other sugars. Introduction of Photosynthesis: Reverse equation of Respiration, and can be divi ...
... We balanced the equation for cellular respiration: 6 O2 + C6H12O6 6 CO2 + 6 H2O (plus energy) and pointed out that cellular respiration allows for inputs other than glucose, including fats, proteins, and other sugars. Introduction of Photosynthesis: Reverse equation of Respiration, and can be divi ...
HL Multiple choice
... What mass, in g, of hydrogen is formed when 3 mol of aluminium react with excess hydrochloric acid according to the following equation? 2Al(s) + 6HCl(aq) → 2AlCl3(aq) + 3H2(g) A. ...
... What mass, in g, of hydrogen is formed when 3 mol of aluminium react with excess hydrochloric acid according to the following equation? 2Al(s) + 6HCl(aq) → 2AlCl3(aq) + 3H2(g) A. ...
Transition Metals
... in space than are the 3d orbitals. They have a higher quantum number n and the have fewer nodes (0 or 1) versus 2 for the d orbitals. ...
... in space than are the 3d orbitals. They have a higher quantum number n and the have fewer nodes (0 or 1) versus 2 for the d orbitals. ...
Catalytic Nitrene Transfer onto Isocyanide by a Redox
... In an effort to bridge the gap between late- and early-metal reactivity, we have used redox-active ligands that are capable of multielectron valence changes. These ligands on formally d0 metal centers have been shown to facilitate “oxidative addition” of halogens and reductive coupling of C-C and N= ...
... In an effort to bridge the gap between late- and early-metal reactivity, we have used redox-active ligands that are capable of multielectron valence changes. These ligands on formally d0 metal centers have been shown to facilitate “oxidative addition” of halogens and reductive coupling of C-C and N= ...
Lactic Acid and Energy from Fats and Proteins
... More generally it is used in chronic conditions when glycogen stores have been significantly diminished In the absence of other energy sources the body breaks down protein as a backup ...
... More generally it is used in chronic conditions when glycogen stores have been significantly diminished In the absence of other energy sources the body breaks down protein as a backup ...
Nucleic Acids - cpprashanths Chemistry
... transfers information from the DNA to the ribosomes - carries a protein recipe to the ribosome -ribosomes are structures in a cell ...
... transfers information from the DNA to the ribosomes - carries a protein recipe to the ribosome -ribosomes are structures in a cell ...
Metalloprotein

Metalloprotein is a generic term for a protein that contains a metal ion cofactor. A large number of all proteins are part of this category.