Packet 2 - w/answers
... 9. Which pair of terms is not correctly matched? a. Deoxyribose: RNA. b. Polypeptide: protein. c. Nitrogenous base; DNA. d. Amino acid: polypeptide. 10. Which does not describe a function of proteins? a. They encode genetic information b. They allow muscle cells to contract. c. They help to carry ou ...
... 9. Which pair of terms is not correctly matched? a. Deoxyribose: RNA. b. Polypeptide: protein. c. Nitrogenous base; DNA. d. Amino acid: polypeptide. 10. Which does not describe a function of proteins? a. They encode genetic information b. They allow muscle cells to contract. c. They help to carry ou ...
Biology: Exploring Life Resource Pro
... Concept 5.4 Proteins perform most functions in cells. (pp. 100–102) A protein is a polymer made from a set of 20 kinds of monomers called amino acids. An amino acid has a central carbon atom bonded to a hydrogen atom, a carboxyl group, an amino group, and a side group. The side group is different fo ...
... Concept 5.4 Proteins perform most functions in cells. (pp. 100–102) A protein is a polymer made from a set of 20 kinds of monomers called amino acids. An amino acid has a central carbon atom bonded to a hydrogen atom, a carboxyl group, an amino group, and a side group. The side group is different fo ...
chapter 2 - Lisle CUSD 202
... Account for over half of the body’s organic matter Provide for construction materials for body tissues Play a vital role in cell function Act as enzymes, hormones, and antibodies ...
... Account for over half of the body’s organic matter Provide for construction materials for body tissues Play a vital role in cell function Act as enzymes, hormones, and antibodies ...
Unit 10 PRACTICE Test with Answers
... 17. Samples of acid rain are brought to a laboratory for analysis. Several titrations are performed and it is determined that a 20.0-milliliter sample of acid rain is neutralized with 6.50 milliliters of 0.010 M NaOH. What is the molarity of the H+ ions in the acid rain? Your response must include b ...
... 17. Samples of acid rain are brought to a laboratory for analysis. Several titrations are performed and it is determined that a 20.0-milliliter sample of acid rain is neutralized with 6.50 milliliters of 0.010 M NaOH. What is the molarity of the H+ ions in the acid rain? Your response must include b ...
SCH3U - Norbraten
... Practice Writing Chemical Equations from Word Equations Write the word and skeletal equation for the following reactions. Be sure to include the proper states of matter by using the appropriate subscripts. You do not need to balance the equation. If the reaction does not occur write NO REACTION (NR) ...
... Practice Writing Chemical Equations from Word Equations Write the word and skeletal equation for the following reactions. Be sure to include the proper states of matter by using the appropriate subscripts. You do not need to balance the equation. If the reaction does not occur write NO REACTION (NR) ...
Food - cbbiology
... Triglyceride: The smallest lipid it has one molecule of glycerol linked to three fatty acid Phospholipid: a lipid where one of the fatty acids have been replaced with a phosphate group or has a phosphate group added to it Sources of lipids: butter, oils, margarine, cream ...
... Triglyceride: The smallest lipid it has one molecule of glycerol linked to three fatty acid Phospholipid: a lipid where one of the fatty acids have been replaced with a phosphate group or has a phosphate group added to it Sources of lipids: butter, oils, margarine, cream ...
Assignment
... fatty acids in smears and tissues. Fresh smears or cryostat sections of tissue are necessary because fixatives containing alcohols, or routine tissue processing with clearing, will remove lipids. The ORO is a rapid and simple stain. It can be useful in identifying fat emboli in lung tissue or clot s ...
... fatty acids in smears and tissues. Fresh smears or cryostat sections of tissue are necessary because fixatives containing alcohols, or routine tissue processing with clearing, will remove lipids. The ORO is a rapid and simple stain. It can be useful in identifying fat emboli in lung tissue or clot s ...
- Catalyst
... – acid donates a proton to a base, forming a molecule (water or another weak acid) and an aqueous salt – Acid: proton-donor; Base: proton-acceptor • Oxidation-Reduction: electron transfer reactions – electron transfer from one species to another, causing a change in the oxidation state of the two sp ...
... – acid donates a proton to a base, forming a molecule (water or another weak acid) and an aqueous salt – Acid: proton-donor; Base: proton-acceptor • Oxidation-Reduction: electron transfer reactions – electron transfer from one species to another, causing a change in the oxidation state of the two sp ...
Chapter 2: Matter
... Ex. Hydrogen, oxygen, and nitrogen occur naturally as colorless gases but when combined they form Nylon which is a flexible solid. ...
... Ex. Hydrogen, oxygen, and nitrogen occur naturally as colorless gases but when combined they form Nylon which is a flexible solid. ...
Provedení, principy činnosti a základy výpočtu pro výměníky tepla
... NaCl sodium chloride MgO magnesium oxide MgBr2 magnesium bromide (and not dibromide, oxidation number of Mg is always 2) Al2O3 aluminium oxide (without prefix, because oxidation numbers are unique) CuO copper(II) oxide (this is the case, when oxidation number of metal is variable and must ...
... NaCl sodium chloride MgO magnesium oxide MgBr2 magnesium bromide (and not dibromide, oxidation number of Mg is always 2) Al2O3 aluminium oxide (without prefix, because oxidation numbers are unique) CuO copper(II) oxide (this is the case, when oxidation number of metal is variable and must ...
Chapter 17 (part 2) - University of Nevada, Reno
... Degraded by the 26S Proteosome • The 26S proteosome is a large protease complex that specifically degrades ubiquinated proteins • 2 major components – 20S proteosome core, 19S cap. • Proteolysis occurs in 20S domain • Ubiquitin recognition occurs at 19S domain ...
... Degraded by the 26S Proteosome • The 26S proteosome is a large protease complex that specifically degrades ubiquinated proteins • 2 major components – 20S proteosome core, 19S cap. • Proteolysis occurs in 20S domain • Ubiquitin recognition occurs at 19S domain ...
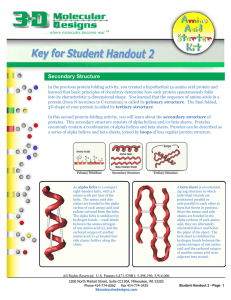
Secondary Structure - 3D Molecular Designs
... In the previous protein folding activity, you created a hypothetical 15-amino acid protein and learned that basic principles of chemistry determine how each protein spontaneously folds into its characteristic 3-dimensional shape. You learned that the sequence of amino acids in a protein (from N-term ...
... In the previous protein folding activity, you created a hypothetical 15-amino acid protein and learned that basic principles of chemistry determine how each protein spontaneously folds into its characteristic 3-dimensional shape. You learned that the sequence of amino acids in a protein (from N-term ...
AS 2.1.1 Protein Structure
... • We can look at proteins in various levels of detail. The first is their primary structure, this is followed by the secondary, tertiary and quaternary structures • Task: Using Cambridge Biology p110- 113, and a two page spread in your book, summarise the 4 levels of protein structure (including the ...
... • We can look at proteins in various levels of detail. The first is their primary structure, this is followed by the secondary, tertiary and quaternary structures • Task: Using Cambridge Biology p110- 113, and a two page spread in your book, summarise the 4 levels of protein structure (including the ...
The production and use of metals
... positively charged electrode (the anode). Here they have their excess electrons removed turning ions back into molecules. 2O2- - 4e ...
... positively charged electrode (the anode). Here they have their excess electrons removed turning ions back into molecules. 2O2- - 4e ...
Atom, etc
... Written formula-The smallest unit of a single molecule. Ex. CH3CH2OH ethanol, CO2 carbon dioxide, H2O water, O2 oxygen (same atoms) Covalent bond-Strong electrostatic attraction that joins two atoms that share electrons to create a full, stable shell. Organic-A chemical that exhibits the normal oxid ...
... Written formula-The smallest unit of a single molecule. Ex. CH3CH2OH ethanol, CO2 carbon dioxide, H2O water, O2 oxygen (same atoms) Covalent bond-Strong electrostatic attraction that joins two atoms that share electrons to create a full, stable shell. Organic-A chemical that exhibits the normal oxid ...
Chapter 3 An Introduction to Organic Compounds - Linn
... Blanching, pickling, cheesecheese-making, acid, pressure-canning, pasteurizing pressure- ...
... Blanching, pickling, cheesecheese-making, acid, pressure-canning, pasteurizing pressure- ...
Chemistry I – Fall 2004
... (B) NH4Cl (C) CCl4 (D) CO2 14. Covalent bonds are most likely to be found in the compound represented by the formula (A) NaCl (B) KBr (C) CH4 (D) HI E) CaF2 15. A pure substance melts at 113 °C and does not conduct electricity in either the solid or liquid state. What conclusions can be drawn concer ...
... (B) NH4Cl (C) CCl4 (D) CO2 14. Covalent bonds are most likely to be found in the compound represented by the formula (A) NaCl (B) KBr (C) CH4 (D) HI E) CaF2 15. A pure substance melts at 113 °C and does not conduct electricity in either the solid or liquid state. What conclusions can be drawn concer ...
Notes ch 2 the nature of matter
... Symbols and subscripts are used to show compounds. H2O – Symbols are used to represent the ...
... Symbols and subscripts are used to show compounds. H2O – Symbols are used to represent the ...
Key concepts for Essay #1
... a. Describe the various characteristics of the carbon atom that makes possible the building of a variety of biological molecules. b. Explain how reactions involving carbon-containing compounds can contribute to the greenhouse effect. c. The following structures are examples of two different categori ...
... a. Describe the various characteristics of the carbon atom that makes possible the building of a variety of biological molecules. b. Explain how reactions involving carbon-containing compounds can contribute to the greenhouse effect. c. The following structures are examples of two different categori ...
video slide
... • Protein shape can also be affected by temperature and pH changes. • When a protein loses its normal shape, this is called denaturing. • A denatured protein is biologically inactive. o Denaturing is usually permanent and not reversible. ...
... • Protein shape can also be affected by temperature and pH changes. • When a protein loses its normal shape, this is called denaturing. • A denatured protein is biologically inactive. o Denaturing is usually permanent and not reversible. ...
Lh6Ch04aProt
... • This structure is able to fulfill a specific biological function • This structure is called the native fold • The native fold has a large number of favorable interactions within the protein • There is a cost in conformational entropy of folding the protein into one specific native fold ...
... • This structure is able to fulfill a specific biological function • This structure is called the native fold • The native fold has a large number of favorable interactions within the protein • There is a cost in conformational entropy of folding the protein into one specific native fold ...
Metalloprotein

Metalloprotein is a generic term for a protein that contains a metal ion cofactor. A large number of all proteins are part of this category.