Protein Synthesis and Function: Chapter 3
... specifically attach amino acids to tRNAs. amino acid + ATP aminoacyl-AMP + PPi aminoacyl-AMP + tRNA aminoacyltRNA + AMP ...
... specifically attach amino acids to tRNAs. amino acid + ATP aminoacyl-AMP + PPi aminoacyl-AMP + tRNA aminoacyltRNA + AMP ...
Chapter 2 - SCHOOLinSITES
... • Made of structural units called amino acids (there are 20 AAs) • Two amino acids combine by dehydration synthesis to form a dipeptide. These are joined by a peptide bond. ...
... • Made of structural units called amino acids (there are 20 AAs) • Two amino acids combine by dehydration synthesis to form a dipeptide. These are joined by a peptide bond. ...
The Elements of Group 15 (5A, V, VA) The Nitrogen Group
... Phosphine (PH3) is a highly toxic, volatile gas. Its melting and boiling points are lower than for NH3 due to lack of H-bonding. ...
... Phosphine (PH3) is a highly toxic, volatile gas. Its melting and boiling points are lower than for NH3 due to lack of H-bonding. ...
Chapter 22-Newest-CD
... Color and Magnetism Magnetism • Many transition metal complexes are paramagnetic (i.e. they have unpaired electrons). • There are some interesting observations. Consider a d6 metal ion: – [Co(NH3)6]3+ has no unpaired electrons, but [CoF6]3has four unpaired electrons per ion. ...
... Color and Magnetism Magnetism • Many transition metal complexes are paramagnetic (i.e. they have unpaired electrons). • There are some interesting observations. Consider a d6 metal ion: – [Co(NH3)6]3+ has no unpaired electrons, but [CoF6]3has four unpaired electrons per ion. ...
Year 13 Winter Revision Guide
... Understand the relationship between enzyme structure and function: catalysts that lower the activation energy through the formation of enzyme – substrate complexes; the Lock and Key hypothesis and Induced-fit hypothesis; effect of temperature, pH, substrate and enzyme concentrations on activity; enz ...
... Understand the relationship between enzyme structure and function: catalysts that lower the activation energy through the formation of enzyme – substrate complexes; the Lock and Key hypothesis and Induced-fit hypothesis; effect of temperature, pH, substrate and enzyme concentrations on activity; enz ...
L3_bacterial growth
... Why can some organisms grow in the presence of oxygen? • Toxic forms of oxygen need to be neutralized by enzymes – Superoxide dismutase – Catalase – Peroxidase ...
... Why can some organisms grow in the presence of oxygen? • Toxic forms of oxygen need to be neutralized by enzymes – Superoxide dismutase – Catalase – Peroxidase ...
Topic 13 – The periodic table: the transition metals (AHL)
... 7. D; both phosphane (PH3) and water (H2O) contain at least one lone pair of electron on the central atom, enabling them to act as a ligand; the nitrite ion (NO2-) can form coordination complexes in a number of ways; 8. D; the color of transition metal ions is associated with partially filled d or ...
... 7. D; both phosphane (PH3) and water (H2O) contain at least one lone pair of electron on the central atom, enabling them to act as a ligand; the nitrite ion (NO2-) can form coordination complexes in a number of ways; 8. D; the color of transition metal ions is associated with partially filled d or ...
Glossary (PDF file)
... substances that can be separated by physical means. Bird seed is a mixture. You can separate the mixture into the different types of seeds it contains. A saltwater solution is a mixture, too. The salt can be separated from the water by evaporating the water. Both these methods of separation are phys ...
... substances that can be separated by physical means. Bird seed is a mixture. You can separate the mixture into the different types of seeds it contains. A saltwater solution is a mixture, too. The salt can be separated from the water by evaporating the water. Both these methods of separation are phys ...
Kofaktörler - mustafaaltinisik.org.uk
... Essential Ion Cofactors • Activator ions – bind reversibly to enzyme and often participate in substrate binding. • Metal ions of metalloenzymes – cations that are tightly bound to enzyme and participate directly in catalysis (Fe, Zn, Cu, Co). • Metal activated enzymes – require or are stimulated by ...
... Essential Ion Cofactors • Activator ions – bind reversibly to enzyme and often participate in substrate binding. • Metal ions of metalloenzymes – cations that are tightly bound to enzyme and participate directly in catalysis (Fe, Zn, Cu, Co). • Metal activated enzymes – require or are stimulated by ...
2. Where does translation take place
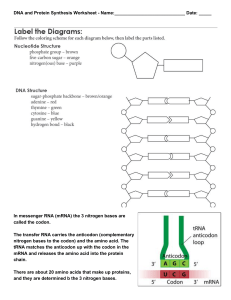
... 5. What is the role of ribosomes in protein production? 6. Below you’ll be given an mRNA codon. Write down the tRNA anticodon and the corresponding amino acid that the codon codes for. You will need the handout Genetic Code. mRNA codon tRNA anticodon Amino acid (AA) UAC CGU AUG UUC AAA AUU AAC CCA ...
... 5. What is the role of ribosomes in protein production? 6. Below you’ll be given an mRNA codon. Write down the tRNA anticodon and the corresponding amino acid that the codon codes for. You will need the handout Genetic Code. mRNA codon tRNA anticodon Amino acid (AA) UAC CGU AUG UUC AAA AUU AAC CCA ...
Macromolecule Expert Sheets
... 3. What kinds of atoms are found in lipids? Carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen (also phosphorous and sometimes nitrogen in phospholipids) 4. Explain why oils don’t dissolve in water. Their fatty acid components have long hydrocarbon tails that are hydrophobic. 5. What smaller molecules make up a fat molec ...
... 3. What kinds of atoms are found in lipids? Carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen (also phosphorous and sometimes nitrogen in phospholipids) 4. Explain why oils don’t dissolve in water. Their fatty acid components have long hydrocarbon tails that are hydrophobic. 5. What smaller molecules make up a fat molec ...
Atomic Structure
... 5. Are nutritious and found in eggs and seeds 6. Hormones are proteins that signal changes in cell activities ...
... 5. Are nutritious and found in eggs and seeds 6. Hormones are proteins that signal changes in cell activities ...
DNA and RNA review
... How do the purines and pyrimidines differ structurally? What type of bond holds the 2 strands of DNA together? Describe this type of bond. Explain the complementary base pairing of the nitrogen bases in DNA. What is produced in DNA replication? Why is DNA replication necessary? What important roles ...
... How do the purines and pyrimidines differ structurally? What type of bond holds the 2 strands of DNA together? Describe this type of bond. Explain the complementary base pairing of the nitrogen bases in DNA. What is produced in DNA replication? Why is DNA replication necessary? What important roles ...
Name:______________________________ Biochemistry I-First Exam
... 4. Which pair of amino acids absorbs the most UV light at 280 nm? a) Threonine & Histidine b) Tryptophan & Tyrosine c) Cystine & Aspartate d) Glycine & Tryptophan 5. Which of the following is not a sensible grouping of amino acids based on their polarity ...
... 4. Which pair of amino acids absorbs the most UV light at 280 nm? a) Threonine & Histidine b) Tryptophan & Tyrosine c) Cystine & Aspartate d) Glycine & Tryptophan 5. Which of the following is not a sensible grouping of amino acids based on their polarity ...
Chapter 2
... functional domain such as a barrel or pocket. In this example, the coils of a globin chain form a pocket. 4) Some proteins have quaternary structure, in which two or more polypeptide chains associate as one molecule. Hemoglobin, shown here, consists of four globin chains (green and blue). Each globi ...
... functional domain such as a barrel or pocket. In this example, the coils of a globin chain form a pocket. 4) Some proteins have quaternary structure, in which two or more polypeptide chains associate as one molecule. Hemoglobin, shown here, consists of four globin chains (green and blue). Each globi ...
Instructions for AP/IB 2 Chem Summer Assignment Note
... iii) Compounds of calcium, barium, strontium and transition metals are insoluble except halides (and those trumped by rule i) These three rules don't cover every possible compound, but they include most compounds that appear on the AP or IB test. So write soluble compounds as separated ions. Insolub ...
... iii) Compounds of calcium, barium, strontium and transition metals are insoluble except halides (and those trumped by rule i) These three rules don't cover every possible compound, but they include most compounds that appear on the AP or IB test. So write soluble compounds as separated ions. Insolub ...
Protein degradation in mouse brain slices
... a role for neurotoxic and unusual neuroexitatory amino acids in the aetiology of certain neurodegenerative disordcrs (Spencer er ul., 1987). This has led us to speculate whether those amino acids that are implicated as possible causativc o r contributory agents in these diseases, might also be invol ...
... a role for neurotoxic and unusual neuroexitatory amino acids in the aetiology of certain neurodegenerative disordcrs (Spencer er ul., 1987). This has led us to speculate whether those amino acids that are implicated as possible causativc o r contributory agents in these diseases, might also be invol ...
Proteins - Westgate Mennonite Collegiate
... 2. secondary structure (2) of a protein results from hydrogen bonds involving the backbone, where the peptide chain is held in structures, either a coiled α-helix or folded β-pleated sheet; proteins often have both types of secondary structure in different regions of the chain ...
... 2. secondary structure (2) of a protein results from hydrogen bonds involving the backbone, where the peptide chain is held in structures, either a coiled α-helix or folded β-pleated sheet; proteins often have both types of secondary structure in different regions of the chain ...
Heme Redox State Triggers Conformational Changes in the Ec DOS
... protein responsible for phosphodiesterase (PDE) activity. The Ec DOS is composed of two domains, an N-terminal sensor domain and a C-terminal PDE catalytic domain. PDE activity is dependent on the redox state of Ec DOS. The enzyme is active only when the heme is in the reduced state. The crystal str ...
... protein responsible for phosphodiesterase (PDE) activity. The Ec DOS is composed of two domains, an N-terminal sensor domain and a C-terminal PDE catalytic domain. PDE activity is dependent on the redox state of Ec DOS. The enzyme is active only when the heme is in the reduced state. The crystal str ...
Metalloprotein

Metalloprotein is a generic term for a protein that contains a metal ion cofactor. A large number of all proteins are part of this category.