any molecule that is present in living organisms. Carbohydrates
... Unsaturated: at least 1 C = C double bond Triglyceride: 3 fatty acids + glycerol ...
... Unsaturated: at least 1 C = C double bond Triglyceride: 3 fatty acids + glycerol ...
Biomolecules - Pearland ISD
... Unsaturated: at least 1 C = C double bond Triglyceride: 3 fatty acids + glycerol ...
... Unsaturated: at least 1 C = C double bond Triglyceride: 3 fatty acids + glycerol ...
Lipids (lect 4))
... Acetyl CoA is the precursor of fatty acid synthesis. It is produced from oxidation of glucose (by oxidative decarboxylation of pyruvate), βoxidation of fatty acids and metabolism of ketogenic and mixed amino acids. Acetyl CoA is produced in mitochondria, and FA synthesis occurs in cytoplasm, so acet ...
... Acetyl CoA is the precursor of fatty acid synthesis. It is produced from oxidation of glucose (by oxidative decarboxylation of pyruvate), βoxidation of fatty acids and metabolism of ketogenic and mixed amino acids. Acetyl CoA is produced in mitochondria, and FA synthesis occurs in cytoplasm, so acet ...
Fatty acids
... • Control immune system, blood pressure, nervous system, inflammatory reactions, blood clotting and hormonal functions. • Regulate a large number of mechanisms including increasing the fluidity of cell membranes and improving the ability of selective permeability and help to keep toxin out and brin ...
... • Control immune system, blood pressure, nervous system, inflammatory reactions, blood clotting and hormonal functions. • Regulate a large number of mechanisms including increasing the fluidity of cell membranes and improving the ability of selective permeability and help to keep toxin out and brin ...
Lehninger Principles of Biochemistry
... puts an Asp side chain in position to cleave citroyl-CoA. ...
... puts an Asp side chain in position to cleave citroyl-CoA. ...
File - Mr. Shanks` Class
... Hydrogen bonding occurs between polar molecules containing hydrogen. The slightly negatove atom in one molecule (usually O or N) exerts a pull on a hydroogen atom in an adjacent molecule, creating a hydogen bond. The hydrogen bond is easily broken but acts to hold molecules together. ...
... Hydrogen bonding occurs between polar molecules containing hydrogen. The slightly negatove atom in one molecule (usually O or N) exerts a pull on a hydroogen atom in an adjacent molecule, creating a hydogen bond. The hydrogen bond is easily broken but acts to hold molecules together. ...
Lipids - AHSbogna
... all of the same properties of fat when it is used in cooking, but the body can not absorb it so it has no calories. At first glance, olestra sounds like the answer to the prayers of many dieters'. However, there are some serious pro's and con's that go with this story. Proctor and Gamble began devel ...
... all of the same properties of fat when it is used in cooking, but the body can not absorb it so it has no calories. At first glance, olestra sounds like the answer to the prayers of many dieters'. However, there are some serious pro's and con's that go with this story. Proctor and Gamble began devel ...
Lec 12: Fatty acid biosynthesis
... Fatty acid synthesis occurs through intermediates similar to those of fatty acid oxidation, but with differences in electron carriers, carboxyl group activation, stereochemistry, acyl‐carrier, and cellular location. • Electron carrier: NADPH instead of NADH and FADH2 • Carboxyl group activation: mal ...
... Fatty acid synthesis occurs through intermediates similar to those of fatty acid oxidation, but with differences in electron carriers, carboxyl group activation, stereochemistry, acyl‐carrier, and cellular location. • Electron carrier: NADPH instead of NADH and FADH2 • Carboxyl group activation: mal ...
Chapter 3
... • The shape of a protein determines its function 1.Primary structure – sequence of amino acids 2.Secondary structure – interaction of groups in the peptide backbone ...
... • The shape of a protein determines its function 1.Primary structure – sequence of amino acids 2.Secondary structure – interaction of groups in the peptide backbone ...
Traffic Lights Biological Cpds
... forming microfibrils (being laid down in different directions). In chitin second carbon –OH groups are replaced by amino groups. 16. The elements which make up lipid molecules are carbon, hydrogen and oxygen plus phosphorus as phosphate in phospholipids. 17. The main types of lipids are described as ...
... forming microfibrils (being laid down in different directions). In chitin second carbon –OH groups are replaced by amino groups. 16. The elements which make up lipid molecules are carbon, hydrogen and oxygen plus phosphorus as phosphate in phospholipids. 17. The main types of lipids are described as ...
Macromolecules Worksheet
... pH scale_ 1. This measures the hydrogen ion level of a solution. acid_ 2. What kind of solution contains more hydrogen ions than hydroxide ions? carbohydrate or polysaccharide_ 3. This is the name for a compound with many sugar subunits linked together. protons_ 4. What are the positively charged pa ...
... pH scale_ 1. This measures the hydrogen ion level of a solution. acid_ 2. What kind of solution contains more hydrogen ions than hydroxide ions? carbohydrate or polysaccharide_ 3. This is the name for a compound with many sugar subunits linked together. protons_ 4. What are the positively charged pa ...
Worksheet Answer Key
... cellulose (major component in cell walls) chitin (major component in fungus cell walls and exoskeletons of insects). ...
... cellulose (major component in cell walls) chitin (major component in fungus cell walls and exoskeletons of insects). ...
Basic Chemistry and Biochemistry Unit Review Sheet File
... 11. Measurement of the hydrogen ion concentration of a solution may be given in terms of _________________. 12. Glucose is a __________________________________, maltose is a __________________________, and starch is a _________________________________. 13. The type of reaction by which proteins are ...
... 11. Measurement of the hydrogen ion concentration of a solution may be given in terms of _________________. 12. Glucose is a __________________________________, maltose is a __________________________, and starch is a _________________________________. 13. The type of reaction by which proteins are ...
File
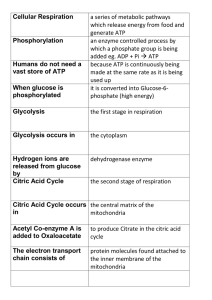
... because ATP is continuously being made at the same rate as it is being used up it is converted into Glucose-6phosphate (high energy) ...
... because ATP is continuously being made at the same rate as it is being used up it is converted into Glucose-6phosphate (high energy) ...
video slide - SP New Moodle
... omega 3 and omega 6 comes from which numbered carbon has the double bond. ...
... omega 3 and omega 6 comes from which numbered carbon has the double bond. ...
LECTURE #1 STUDY GUIDE
... Complete the following chemical equation: NADH + H+ + 3ADP + 3 P + 1/2 O2 –––––––> ...
... Complete the following chemical equation: NADH + H+ + 3ADP + 3 P + 1/2 O2 –––––––> ...
1 - Medical Mastermind Community
... had not eaten for the last two days, due to a mild infection. Blood glucose and ketone body levels were found to be abnormally low, while circulating non-esterified fatty acids were greatly elevated. An abnormality in which one of the following enzymes is most ...
... had not eaten for the last two days, due to a mild infection. Blood glucose and ketone body levels were found to be abnormally low, while circulating non-esterified fatty acids were greatly elevated. An abnormality in which one of the following enzymes is most ...
video slide - Blue Valley Schools
... Chitin, another structural polysaccharide, is found in the exoskeleton of arthropods. Chitin also provides structural support for the cell walls of many fungi. Chitin can be used as surgical thread. ...
... Chitin, another structural polysaccharide, is found in the exoskeleton of arthropods. Chitin also provides structural support for the cell walls of many fungi. Chitin can be used as surgical thread. ...
Second test - rci.rutgers.edu
... CO2 in respiring mitochondria is A. 2 D. 12.5 B. 5 E. 30 C. 10 Compared with cytochromes, iron sulfur clusters are A. higher in energy, evolutionarily older B. higher in energy, evolutionarily younger C. lower in energy, evolutionarily older D. lower in energy, evolutionarily younger E. none of the ...
... CO2 in respiring mitochondria is A. 2 D. 12.5 B. 5 E. 30 C. 10 Compared with cytochromes, iron sulfur clusters are A. higher in energy, evolutionarily older B. higher in energy, evolutionarily younger C. lower in energy, evolutionarily older D. lower in energy, evolutionarily younger E. none of the ...
Biology 2.3 Carbon Compounds
... bones and muscles. Other proteins transport substances into or out of cells or help to fight disease. ...
... bones and muscles. Other proteins transport substances into or out of cells or help to fight disease. ...
Download PDF
... capture, proton and ion gradients, and conversion to mechanical energy. In addition, we will explore the thermodynamics of electron transport, proton pumping, and ATP biosynthesis. 3. Molecular biosynthesis. Most organisms can biosynthesize amino acids, lipids, nucleotides, vitamins, and cofactors u ...
... capture, proton and ion gradients, and conversion to mechanical energy. In addition, we will explore the thermodynamics of electron transport, proton pumping, and ATP biosynthesis. 3. Molecular biosynthesis. Most organisms can biosynthesize amino acids, lipids, nucleotides, vitamins, and cofactors u ...
Biochemistry Test Review
... List the five natural elements which make up 96% of the human body. What is an organic compound vs. inorganic? List the total number of atoms in the following compound: C18H36O2 Elements with a different number of neutrons that protons such as Carbon-13 and Carbon-14 are considered______________. Ex ...
... List the five natural elements which make up 96% of the human body. What is an organic compound vs. inorganic? List the total number of atoms in the following compound: C18H36O2 Elements with a different number of neutrons that protons such as Carbon-13 and Carbon-14 are considered______________. Ex ...
Name: Correctly complete the following statements with a term that
... 28. At a conference, the speaker's grand finale was sautéing mealworms (insect larvae) in butter and serving them to the audience. They were crunchy (like popcorn) because their exoskeletons contain the polysaccharide (a) linolenic acid (b) cellulose (c) collagen (d) glycogen (e) chitin. 29. ______ ...
... 28. At a conference, the speaker's grand finale was sautéing mealworms (insect larvae) in butter and serving them to the audience. They were crunchy (like popcorn) because their exoskeletons contain the polysaccharide (a) linolenic acid (b) cellulose (c) collagen (d) glycogen (e) chitin. 29. ______ ...
Biochemistry Quiz
... 22. The main difference between the secondary and quaternary structure of a protein is (a) bond angles between amino acids (b) sequence of amino acids (c) number of polypeptides in the molecule (d) the folding pattern of the molecule (e) The disulphide bridges 23. The 'primary structure' of a protei ...
... 22. The main difference between the secondary and quaternary structure of a protein is (a) bond angles between amino acids (b) sequence of amino acids (c) number of polypeptides in the molecule (d) the folding pattern of the molecule (e) The disulphide bridges 23. The 'primary structure' of a protei ...
Fatty acid synthesis

Fatty acid synthesis is the creation of fatty acids from acetyl-CoA and malonyl-CoA precursors through action of enzymes called fatty acid synthases. It is an important part of the lipogenesis process, which – together with glycolysis – functions to create fats from blood sugar in living organisms.