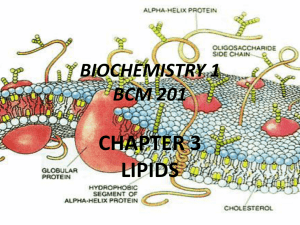
Biochemistry - Fort Thomas Independent Schools
... Enzymes special proteins that are biological catalyst lock & key fit with enzyme & substrate substrate – is the substance that binds to enzyme substrate changes enzyme does not ...
... Enzymes special proteins that are biological catalyst lock & key fit with enzyme & substrate substrate – is the substance that binds to enzyme substrate changes enzyme does not ...
Metabolism Fact Sheet - Barth Syndrome Foundation
... production. Summarizing: a gene named TAZ encodes a protein called tafazzin that probably functions as an enzyme to help make mature cardiolipin. Cardiolipin is made first with one kind of fatty acids attached to it which are mostly saturated, then the original fatty acids are removed and other fatt ...
... production. Summarizing: a gene named TAZ encodes a protein called tafazzin that probably functions as an enzyme to help make mature cardiolipin. Cardiolipin is made first with one kind of fatty acids attached to it which are mostly saturated, then the original fatty acids are removed and other fatt ...
The Chemistry of Life
... 3.2.6 State three functions of lipids. 3.2.7 Compare the use of carbohydrates and lipids in energy storage. ...
... 3.2.6 State three functions of lipids. 3.2.7 Compare the use of carbohydrates and lipids in energy storage. ...
Amino Acids Worksheet - Newcastle University
... 2. A proton has been removed from carboxylic acid and the amine has been protonated causing each end to become charged. This is called a Zwitterion. Due to the positive and negative ends of each zwitterion strong intermolecular are formed which require more energy to break raising the melting point. ...
... 2. A proton has been removed from carboxylic acid and the amine has been protonated causing each end to become charged. This is called a Zwitterion. Due to the positive and negative ends of each zwitterion strong intermolecular are formed which require more energy to break raising the melting point. ...
Organic Molecule
... 2 Types of Fatty Acids Saturated: If each carbon atom in a lipid’s fatty acid has single covalent bonds. - Results in straight chains(Solid at room ...
... 2 Types of Fatty Acids Saturated: If each carbon atom in a lipid’s fatty acid has single covalent bonds. - Results in straight chains(Solid at room ...
Notes Guide Part 2
... Protein- Amino acids join by _________________________________ rxn to form dipeptides and polypeptides. ...
... Protein- Amino acids join by _________________________________ rxn to form dipeptides and polypeptides. ...
Structure, Mechanism, and Disease Implications of Acetyl CoA
... include their attachment to proteins to direct them to the right locations within the cell as well as their ability to serve as hormones and other intracellular messengers. It is easy to see that the needs for these long hydrocarbon chains with their terminal carboxylate group, coined fatty acids, a ...
... include their attachment to proteins to direct them to the right locations within the cell as well as their ability to serve as hormones and other intracellular messengers. It is easy to see that the needs for these long hydrocarbon chains with their terminal carboxylate group, coined fatty acids, a ...
PASS MOCK EXAM
... a. The control enzyme is acetyl CoA carboxylase b. The enzyme is activated by protein phosphatase c. Protein phosphatase is activated as a result of glucagon binding to liver cells d. The control enzyme converts ATP, CO2, and acetyl CoA into malonyl CoA, ADP, and Pi e. The concentrations of ...
... a. The control enzyme is acetyl CoA carboxylase b. The enzyme is activated by protein phosphatase c. Protein phosphatase is activated as a result of glucagon binding to liver cells d. The control enzyme converts ATP, CO2, and acetyl CoA into malonyl CoA, ADP, and Pi e. The concentrations of ...
Acid-Base Principles to Organic Acids
... Objective 11. Apply acid-base principles to organic acids. Skills: Draw structure ID structural features and reactive sites (alpha C, beta C, LG, etc.) ID Nu- and E+ use curved arrows to show bonds breaking and forming show delocalized electrons with resonance structures. Key ideas: Organic acids ar ...
... Objective 11. Apply acid-base principles to organic acids. Skills: Draw structure ID structural features and reactive sites (alpha C, beta C, LG, etc.) ID Nu- and E+ use curved arrows to show bonds breaking and forming show delocalized electrons with resonance structures. Key ideas: Organic acids ar ...
Document
... More than 20 different amino acids are found in nature. This variety results in proteins being among the most diverse macromolecules. Levels of Organization Proteins have four levels of structure. A protein’s primary structure is the sequence of its amino acids. Secondary structure is the folding or ...
... More than 20 different amino acids are found in nature. This variety results in proteins being among the most diverse macromolecules. Levels of Organization Proteins have four levels of structure. A protein’s primary structure is the sequence of its amino acids. Secondary structure is the folding or ...
AP Biology 042 – Biological Molecules Video
... monomers together in a certain sequence/order they have a. The process of “putting monomers together” is called b. What is lost during the process of #11? c. What kind of bond is formed generally? Specifically between amino acids of a protein? d. What must be added to break the bonds? e. What is the ...
... monomers together in a certain sequence/order they have a. The process of “putting monomers together” is called b. What is lost during the process of #11? c. What kind of bond is formed generally? Specifically between amino acids of a protein? d. What must be added to break the bonds? e. What is the ...
chapter_6_ppt
... • One double bond • Oleic acid (Omega 9) • Olive oil, canola oil, nuts • Rate of CHD low in Mediterranean countries where diet is rich in olive oil • Diet high in MUFA equivalent to low-fat diet in ↓ LDL-C, but does not ↓ HDL-C ...
... • One double bond • Oleic acid (Omega 9) • Olive oil, canola oil, nuts • Rate of CHD low in Mediterranean countries where diet is rich in olive oil • Diet high in MUFA equivalent to low-fat diet in ↓ LDL-C, but does not ↓ HDL-C ...
DISEASES OF LIPID METABOLISM
... protein Apicks-up@ the fatty acids and holds them within the hepatocyte. Presumably, other peripheral tissues, such as skeletal muscle have a similar binding protein. 2. FA Activation a. Hepatic degradation of fatty acids requires that they be Aactivated@ as acyl~SCoA. This reaction is catalyzed by ...
... protein Apicks-up@ the fatty acids and holds them within the hepatocyte. Presumably, other peripheral tissues, such as skeletal muscle have a similar binding protein. 2. FA Activation a. Hepatic degradation of fatty acids requires that they be Aactivated@ as acyl~SCoA. This reaction is catalyzed by ...
The Organic Macromolecules of Life
... When people speak about nutrition and health, they often refer to saturated vs. unsaturated fats. Lipids can be saturated or unsaturated molecules. Remember that fatty acids are made of several carbon atoms connected together in a chain. If every carbon atom in a fatty acid is joined to another carb ...
... When people speak about nutrition and health, they often refer to saturated vs. unsaturated fats. Lipids can be saturated or unsaturated molecules. Remember that fatty acids are made of several carbon atoms connected together in a chain. If every carbon atom in a fatty acid is joined to another carb ...
Review F14
... 14. Draw the process of exocytosis. 15. What is the difference between and permeable and semi permeable membrane? What kind is a cell membrane? 16. Why is it dangerous to have a really high fever? 17. What do plants need to accomplish photosynthesis? Draw a diagram showing how plants get the needed ...
... 14. Draw the process of exocytosis. 15. What is the difference between and permeable and semi permeable membrane? What kind is a cell membrane? 16. Why is it dangerous to have a really high fever? 17. What do plants need to accomplish photosynthesis? Draw a diagram showing how plants get the needed ...
Macromolecules Notes File
... ____________________ - molecules used to store energy in organisms as well as structural materials. Made of C,H,O,. Less oxygen than in carbohydrates. Twice the amount of energy storage. Soluble in nonpolar solvents. ...
... ____________________ - molecules used to store energy in organisms as well as structural materials. Made of C,H,O,. Less oxygen than in carbohydrates. Twice the amount of energy storage. Soluble in nonpolar solvents. ...
lipids - LSU School of Medicine
... The carbons at positions 10 and 13 and the alkyl group at position 17 are nearly always oriented on the same side of the steroid nucleus, the betaorientation. Alkyl groups that extend from the other side of the steroid backbone are in an alpha-orientation. ...
... The carbons at positions 10 and 13 and the alkyl group at position 17 are nearly always oriented on the same side of the steroid nucleus, the betaorientation. Alkyl groups that extend from the other side of the steroid backbone are in an alpha-orientation. ...
Lipids
... it is also called the plasma membrane or, in a more general sense, a unit membrane. This is a very thin, semifluid, sheet like structure made of four continuous monolayers of molecules. • The plasma membrane and the membranes making up all the intracellular membranous organelles display a common mol ...
... it is also called the plasma membrane or, in a more general sense, a unit membrane. This is a very thin, semifluid, sheet like structure made of four continuous monolayers of molecules. • The plasma membrane and the membranes making up all the intracellular membranous organelles display a common mol ...
Chapter 5 - SchoolRack
... Made of glycerol and 3 fatty acids Fatty acid has a long carbon skeleton and a carboxyl group C-H bonds responsible for hydrophobia of fats ...
... Made of glycerol and 3 fatty acids Fatty acid has a long carbon skeleton and a carboxyl group C-H bonds responsible for hydrophobia of fats ...
Final Review - Chemistry Courses: About: Department of
... 16. energetics of FA synthesis and degradation 17. nitrogen processing, catabolism of AA 18. medical applications of nucleotide metabolism 19. nucleic acid structure on atomic level ...
... 16. energetics of FA synthesis and degradation 17. nitrogen processing, catabolism of AA 18. medical applications of nucleotide metabolism 19. nucleic acid structure on atomic level ...
Biology Content Standards
... of very few elements. The six most common are C, H, #, O, P, S. 1.2 Describe the basic molecular structures and primary functions of the four major categories of organic molecules (carbohydrates, lipids, proteins, and nucleic acids). 1.3 Explain the role of enzymes as catalysts that lower the activa ...
... of very few elements. The six most common are C, H, #, O, P, S. 1.2 Describe the basic molecular structures and primary functions of the four major categories of organic molecules (carbohydrates, lipids, proteins, and nucleic acids). 1.3 Explain the role of enzymes as catalysts that lower the activa ...
Chapter 5
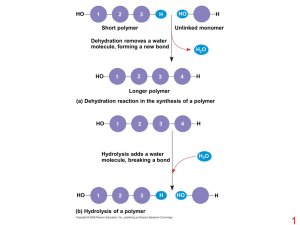
... Dehydration reaction - a reaction in which two molecules are covalently bonded to each other through loss of a water molecule (Fig 5.2) Hydrolysis - a reaction in which polymers are disassembled. The reverse of a dehydration reaction Carbohydrates Monosaccharide - single sugar (Fig 5.3 & 5.4) Disacc ...
... Dehydration reaction - a reaction in which two molecules are covalently bonded to each other through loss of a water molecule (Fig 5.2) Hydrolysis - a reaction in which polymers are disassembled. The reverse of a dehydration reaction Carbohydrates Monosaccharide - single sugar (Fig 5.3 & 5.4) Disacc ...
service request form
... Questions please contact: Terri Pietka (362-8469; [email protected]) or Nada Abumrad (747-0348; [email protected]) Enter the approximate number of analyses needed for each service below. a. Cells for Culture: 3T3-L1 ____ 3T3-F442A ____ OP9 ____ HIB1B _____ LS14 _____ LiSa-2 _____ SBGS _____ ...
... Questions please contact: Terri Pietka (362-8469; [email protected]) or Nada Abumrad (747-0348; [email protected]) Enter the approximate number of analyses needed for each service below. a. Cells for Culture: 3T3-L1 ____ 3T3-F442A ____ OP9 ____ HIB1B _____ LS14 _____ LiSa-2 _____ SBGS _____ ...
Fatty acid synthesis

Fatty acid synthesis is the creation of fatty acids from acetyl-CoA and malonyl-CoA precursors through action of enzymes called fatty acid synthases. It is an important part of the lipogenesis process, which – together with glycolysis – functions to create fats from blood sugar in living organisms.