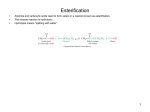
* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Ch. 5 - LIPIDS
Ethanol-induced non-lamellar phases in phospholipids wikipedia , lookup
15-Hydroxyeicosatetraenoic acid wikipedia , lookup
Epoxyeicosatrienoic acid wikipedia , lookup
Cholesterol wikipedia , lookup
Low-density lipoprotein wikipedia , lookup
High-density lipoprotein wikipedia , lookup
Phospholipid-derived fatty acids wikipedia , lookup
Saturated fat and cardiovascular disease wikipedia , lookup
Nutrition 101 Ch. 5 - LIPIDS Vocabulary Fatty Acid: Saturated Fatty Acid: Unsaturated Fatty Acid: Trans Fatty Acid: Eicosanoid: Lipase: Bile: Micelle: Chylomicron: HDL: LDL: WHAT ARE LIPIDS? Organic compounds that contain _____________________, hydrogen, and oxygen Different arrangement from carbohydrates Hydrophobic – Lipophilic – 3 CLASSES of LIPIDS 1. Triglycerides 2. _____________________________________ 3. Sterols Building Blocks: FATTY ACIDS Key building blocks for ________________/___________________________ (and phosopholipids) Chains of carbon atoms: Methyl (CH3) group at one (_____________________ end) 1 __________________________ (COOH) group at the other end (alpha end) o Also known as carboxylic acid end Draw basic fatty acid here CHEMISTRY OF FATTY ACIDS Influences the _______________________________ of fats in foods & health effects in our ______________ Solid or liquid at _____________ _________________________________ Spoilage factors (oxidation) You will find fatty acids either “______________” or ___________________________ to another compound 3 Characteristics of fatty acids that affect how they act in foods and in the body: Degrees of ___________________________ (double bonds) If any double bonds, where the __________________ double bond is located CHAIN LENGTH Naturally occurring fatty acids contain ___________________ numbers of carbons Short chain = o Foods: Medium chain = o Foods: Long chain = o Most common in the diet o Foods: DEGREES OF SATURATION 2 Classifications: 2 ___________________________ FATTY ACID = Fully loaded with hydrogen atoms and contains only ____________________ bonds between its carbon atoms _________________________________ FATTY ACID = Lacks ____________________________ hydrogen atoms and has at least one __________________________ bond between carbons Classifications of Unsaturated Fatty Acids One double bond = _________________unsaturated fatty acid (MUFA) Two or more double bonds = ________________unsaturated fatty acid (PUFA) Unsaturated Fatty Acid Food Sources Monounsaturated Fats: Olive oil, ___________________ oil, _____________________ oil, avocados Polyunsaturated Fats: Vegetable oils: safflower, ____________________, _____________, corn, _____________________ Nuts, ____________________ FATTY ACID CONSISTENCY Long-chain ___________________________ fatty acids stack tightly o Form _____________________ at room temperature o Examples: Monounsaturated & ___________________unsaturated fatty acids don’t stack compactly o ____________________________ at room temperature o Examples: ______________________ saturated fatty acids are _____________ or ____________________at room temperature o Examples: 3 TWO TYPES OF BOND FORMATION for Unsaturated Fatty Acids: ______________ - hydrogens on the carbons joined by a double bond are on the _____________ side o Carbon chain is _________________ ______________ - hydrogens on the carbons joined by a double bond are on the __________________________ side o Carbon chain is _____________________________ Figure 5-7: Cis- and Trans-Fatty Acids Compared TRANS-FATTY ACIDS _____________________________________ - chemical process where hydrogens are added to mono or polyunsaturated fats to reduce the number of ________________________ bonds Liquid fats are changed to _________________ fats (become more _________________________) Resistant to _______________________ (avoid rancidity) The downside is that this process produces ______________ fatty acids Figure 5-6: Hydrogenation Takes a _____________________ oil through a process that adds hydrogen and changes it to a __________________ fat at room temperature Figure 5-5: Comparison of Dietary Fats ESSENTIAL FATTY ACIDS Our bodies cannot make C-C double bonds before the 9th carbon from the methyl (CH3) end o Omega 3’s and Omega 6’s We must get these fatty acids from our _______________ o Examples: Figure 5-1: Omega-3 and Omega-6 Fatty Acids Compared 4 Omega-3 Fatty Acids – first double bond at carbon ________: ALA - Alpha-Linolenic Acid EPA - Eicosapentaenoic Acid DHA - Docosahexaenoic Acid Omega-6 Fatty Acids – first double bond at carbon ________: Linoleic Acid Arachidonic Acid Food Sources of Omega-3 Fatty Acids Linolenic acid: o Flaxseeds & its oil o _______________ seeds o _______________ seeds and its oil o ____________________ o Small amounts: soybean and canola oils EPA & DHA: o Fatty fish - _____________________, sardines, _________________________ o Fish oils Food Sources of Omega-6 Fatty Acids Linoleic: o Nuts and _________________ o Common __________________________ oils - ___________, safflower, ______________________, soybean Arachidonic acid: o ______________ EICOSANOIDS Made from _____________________________ (Omega 6) and __________ & _________ (Omega 3’s) 5 Hormone-like compounds – have a more localized effect, have different effects on different cells Important in: The ______________________________ process __________________________________ dilation and constriction Blood ___________________ Omega-6 Eicosanoids Linoleic acid arachidonic acid Omega-6 eicosanoids are formed Overall effect: o __________________ blood vessels, promote __________________ clotting and __________________ inflammation Omega-3 Eicosanoids Alpha-linolenic acid EPA and DHA Omega-3 eicosanoids are formed Overall effect: o ________________ blood vessels, discourage blood clotting, _________________ inflammation o Supports ________________ ___________________ Major Sources of Various Fatty Acids 3 CLASSES of LIPIDS 1. Triglycerides Made up of 3 __________________ _______________ bound to a glycerol 2. _____________________________________ Made up of 2 fatty acids and a _______________________ bound to a glycerol Act as ______________________________ 6 Make up __________________ membranes 3. Sterols ____________________________ ring structures Examples: 1st Class of Lipids: TRIGLYCERIDES TRIGLYCERIDE STRUCTURE ________glyceride = ________ fatty acids attached to a glycerol backbone _______glyceride = _______ fatty acids + glycerol ___________glyceride = _______ fatty acid + glycerol _______________________________ reactions occur to make a triglyceride o Loss of ________________ to make a bond Figure 5-3: Condensation Reactions Form Triglycerides Triglycerides are the main form of fat consumed in the _____________ (95% as fats and oils) Triglycerides are the main form of fat stored in the _______________ (99%) FUNCTIONS OF TRIGLYCERIDES Stored fat provides much of the body’s _______________ needs during rest – compactly! ____________________ the body and keeps it warm Protection of _____________ and organs as a natural ____________________________________ Sensory qualities – provides __________________ and _______________________ 2nd Class of Lipids: PHOSPHOLIPIDS Glycerol bonded to ________ fatty acids and a _____________________ group o Phosphate group is hydrophilic – attracted to and dissolves in ___________________ o Fatty acid groups are lipophilic – attracted to and soluble in _____________ 7 Because of this structure, phospholipids are ideal __________________________ to mix or transport fats in water, and to create barriers Figure 5-9: Phospholipids of a Cell Membrane FUNCTIONS OF PHOSPHOLIPIDS Cell Membranes Phospholipids are the major component of ___________ __________________ Lipid Transport and Emulsifiers In the stomach, intestines, _____________________and the ____________________ system PHOSPHOLIPIDS in FOOD Phospholipids as Emulsifiers in Foods Combine __________ that wouldn’t normally mix Increase dispersion and reduce ________ Increase _____________________ Prolong flavor release ______________________ Natural Phospholipids in Food Lecithin (phosphatidylcholine) is the major ___________________________ in foods o Naturally present in liver, ___________, soybeans, _________________, wheat germ Liver produces what the body needs….lecithin is not an _________________ nutrient 3rd Class of Lipids: STEROLS Compounds (hydrocarbons) with a _____________________-ring structure Contain no _________________ _______________ _________________________ is the best-known sterol, found ONLY in ______________________ food products 8 CHOLESTEROL: Functions Major component of ____________ ______________________ (especially abundant in nerve and _______________ tissue) Precursor molecule to: Examples - Vitamin ______, testosterone, cortisol (adrenaline hormone) Important in the synthesis of ____________ acids (for fat digestion) Figure 5-10: Cholesterol CHOLESTEROL: Synthesis ______________ manufactures most of the cholesterol in our bodies = 800-1500 mg per day ________% of all the body’s cholesterol is found in the ______________ PLANT STEROLS Similar in structure to __________________________ Interfere with cholesterol __________________________ Diets rich in plant sterols ________________ blood cholesterol levels Plant sterols & stanols are found naturally in small amounts in: o Grains, ___________________________, fruits, ____________________, nuts & _______________ Table 5-2: The Lipid Family LIPID DIGESTION Mouth Some hard fats melt ________________________ mixes fats with _____________________ Lingual ______________________ found in saliva Minimal fat digestion occurs here (except in infants – lingual lipase plays active role) Stomach Muscular actions mix __________ with watery _________________ Exposes food to gastric ________________: works in _________________ conditions Little digestion of fats occurs here, however 9 Small Intestine Fat signals release of _________ (hormone), which stimulates the _____________________ to release ___________ Acidic chyme signals release of _______________________ (hormone), which travels to the ______________________ and signals the release of its bicarbonate-rich pancreatic juices – contains pancreatic __________________ Released from villi are ____________________________ ___________________ All lipases break down triglycerides & phospholipids to mostly ____________glycerides & free ________________________ (depends on length of carbon chain in fatty acids) Figure 5-12: The Importance of Bile Figure 5-13: Digestion (Hydrolysis) of a Large Triglyceride LIPID ABSORPTION Small Intestine Most absorption takes place in the duodenum or jejunum _________________ lipid molecules __________________ into enterocytes (intestinal cells) ______________________: tiny emulsified fat packets that carry monoglycerides & _________________________ free fatty acids to the brush border → ________________ into enterocytes In the enterocytes, monoglycerides & free fatty acids are reformed into _________________ The newly reformed triglycerides, ________________________, phospholipids, and _____________________ carriers form _____________________________ (lipoprotein) o Chylomicrons enter the _______________________ system, which bypasses the ______________ and continues onto the rest of the body (unlike nutrients that enter the bloodstream directly from the small intestine) Smaller lipids: o Medium-chain & short-chain fatty acids and glycerol are absorbed directly into ___________________________ and travel first to the __________ . o They do not enter the lymph system. 10 Figure 5-15: Absorption of Fat LIPOPROTEINS Lipids in the Bloodstream – Transported as lipoproteins, which solves the body’s problem of transporting fat-soluble mocules in the watery fluids of our body Chylomicrons ________________________, least dense of lipoproteins Transport ______________________________ lipids (mostly TGs) from SI to rest of body As cells remove TG’s, chylomicrons become _______________________ Become chylomicron __________________________ ________________ collects remnants & recycles what’s left VLDL (Very Low-Denstiy Lipoprotein) Lipids made in ______________ + chylomicron remnants make ___________ Shipped to rest of ____________ TG’s are removed by body’s _____________ VLDL becomes smaller and more _________________ → become LDL LDL (Low-Density Lipoprotein) Contain mostly _________________________ Distributes contents to _____________ o Make new ___________ _________________________ o Make ___________________ or other compounds o ___________________ for later use LDL receptors on the _______________ control amount of blood cholesterol by removing ___________ from circulation for recycling 11 HDL (High-Density Lipoprotein) Made by _______________ ______________________ cholesterol from cells Delivers it back to the __________________ for recycling or disposal Has _______________________________________________ properties o Prevents atherosclerotic plaques from breaking apart & causing ________________ _______________ Figure 5-16: Sizes and Compositions of the Lipoproteins Figure 5-17: Lipid Transport via Lipoproteins CHOLESTEROL IN THE BODY “Good” vs. “bad” cholesterol o ___________ LDL - increased risk of _____________ ______________ & strokes o ___________ HDL – __________________________ against heart attacks There is only one type of cholesterol; in and of itself, cholesterol is not bad (we need it to survive!) Differences between LDL & HDL reflect proportions (amounts) & direction of movement of cholesterol, not “type” of cholesterol DIETARY CHOLESTEROL Overall diet can affect amount ___________________ Dietary long-chain ____________________ fat increases ___________________ absorption Fiber (especially soluble fiber) ___________________ cholesterol absorption HEART DISEASE 12 Nearly _______________________ people die each ____________ in the United States due to CVD (Cardiovascular Disease) Myocardial Infarction or _________________________ is the leading cause of death in American men and women ATHEROSCLEROSIS “__________________________ and narrowing of the arteries” Starts with accumulation of soft, _____________ __________________ along inner arterial walls Most people have well-developed plaques by age ___________ Slow, progressive disease - takes _______________________ to advance. _________________________ forms in response to injuries on the artery wall Injury can be caused by: High blood ____________________________ levels _________________________________ ________________________ ________________________ High homocysteine levels Diets high in ____________________ (?) or ______________ fat Infections What Are Risk Factors For CVD? Potentially: High ___________ Cholesterol Low ___________ Cholesterol 13 An ______________________ diet: high in…. o Highly _____________________ foods o ______________ fatty acids o Too many ________________ carbohydrates (refined grains and sugars) o Low in veggies, fruits, whole ________________ foods Figure H5-1: Two Meals Compared: Replacing Saturated Fat with Unsaturated Fat Table 5-3: Replacing Saturated Fat with Unsaturated Fat Table 5-20: Cutting Fat Cuts kCalories – and Saturated Fat Other Risk Factors for CVD ___________ & ____________________ o Men have an increased risk by age ________, women by age _________ o More ___________________ will die from heart disease Family history o History of ______________ CVD is an independent risk factor o The more members of your family and earlier age of onset equates to a higher risk _____________________ o The ______________ you smoke, the greater your risk o Damages the __________________, makes it work harder, increases blood pressure o Damages platelets – increases risk of _______________ clots o Toxins and increased blood pressure damage blood _______________________, leading to greater atherosclerosis ___________________________ o Tiny blood vessels become ___________________, decreases circulation o Greater risk for ________________________, leading to rapid atherosclerosis 14 o Diabetics have a much greater risk of ______________ from CVD than non-diabetics Physical _____________________________ Obesity… especially _____________________________ obesity o Contributes to high ___________, low HDL, hypertension, and _________________ o Exercising and ___________________ loss promotes low LDL, high ____________, lower blood pressure, and improves ___________________ sensitivity Metabolic Syndrome o Includes 3 of the following 5 factors indicating metabolic disorders within the body 1. Abdominal obesity, 2. High triglycerides, 3. Low HDL, 4. High blood pressure, 5. High fasting blood glucose o Associated with many ____________________ diseases o _____________________________ and physical inactivity contribute to this Table 18-3: Risk Factors for CHD Table 18-4: Standards for CHD Risk Factors Desirable Blood Lipid Profile: Factors that Lower LDL and/or Increase HDL…. _______________________ control Healthy mono & polyunsaturated fats – whole plant foods; unrefined, extra virgin oils Healthy _____________________ fats (like from coconut oil; raw, organic dairy products) ___________________________ dietary fibers (lowers LDL specifically) Phytochemicals (__________________ - _____________ plants) _______________________ alcohol consumption o No more than _____ drink per day for women of legal age o No more than _____ drinks per day for men of legal age o Have to be careful of what constitutes “1 drink” PHYSICAL ___________________________ (increases HDL separate from diet) TRANS FATTY ACIDS Tend to ____________________ total blood cholesterol 15 Tend to raise __________ cholesterol and lower __________ cholesterol FDA mandates grams of ______________ fats in a food must be included on the Nutrition Facts panel as of _____________ - however, the serving size can contain up to 0.49 grams of trans fat and the food label can still legally list 0g of trans fat per serving Food Sources: The only way to make sure the food contains no trans fat is to read the ingredients label! o Look for anything containing “partially _______________________________ oil” – that means it contains trans fats o Foods with fully hydrogenated oils should be avoided as well, since those contain artificial fats. IMPORTANT DIETARY FACTORS for CVD Homocysteine levels in the blood o amino acid, acquired mostly from eating meat o High levels of this amino acid may promote ________________________________, excessive blood clotting, and blood vessel _________________________ → Increases risk of heart disease Omega-3 Fatty Acids o Support _________________ health! o Reduce inflammation, relax blood vessels, and reduce blood clotting o Ratio of omega 6’s to omega 3’s is important – aim for 4:1 (the Standard American Diet is close to 15:1 or higher) o Eat more ________________ and other fatty fish, flaxseeds, hemp seeds, chia seeds, walnuts; limit meat and use unrefined/extra virgin oils that are low in omega 6’s (olive, avocado, coconut, macadamia nut, etc.) ______________________ fiber o Helps __________________ blood cholesterol levels o Binds bile salts and cholesterol from food and causes their excretion – forces liver to make new lipids, lowering LDL 16 Antioxidants o clean up free-radicals that increase plaque build-up in the arteries o Examples: Vitamin E, Vitamin C, beta carotene, etc. COCONUT OIL Just because it is high in saturated fat, this does not mean that unrefined EV coconut oil is bad for you. It contains different types of saturated fats than most animal sources. Composed mostly of medium-chain triglycerides (MCTs; medium-chain fatty acids (MCFAs)) MCTs may help protect against _______________________________________ Some of the other health benefits of unrefined, extra virgin coconut oil: Antimicrobial: Kills ______________________, viruses, fungi, yeast, parasites Improves ______________________/________________________ of vitamins & minerals Reduces _________________________________ Aids _____________________ __________________ function May aid in ____________________________________ Keeps ______________, hair, mouth healthier Check out coconutresearchcenter.org for more great info! Table 18-5: Strategies to Reduce Risk of CHD RECOMMENDED INTAKES OF FAT Lipid Recommendations: DRI and 2010 Dietary Guidelines recommend fat at _______ to _______ % of energy intake (400 - 700 calories of a 2,000-kcalorie diet) FDA: ______ % of energy intake from saturated fat and _______% of energy intake total fat Reduce __________ fats and other artificial fats Reduced refined polyunsaturated vegetable oils (i.e. soybean, canola, corn oils, etc.) Increase ______________-food plant sources of fats (i.e. nuts, seeds, avocados, etc.) Consume healthy _____________________ fats (i.e. coconut, macadamia nut oils, butter from grass-fed beef, etc.) Consume unrefined, extra-virgin monounsaturated oils (olive, avocado) 17 Focus on _____________________-rich foods (see previous lists) See previous slides/handouts for more details about what foods/fats/oils to consume. Figure 5-H2: Mediterranean Diet Pyramid Promotes a healthy eating plan that is more balanced in all food groups/nutrients, including the types of fats consumed, than the Standard American Diet (SAD) 18