Modern Biology (I) First Midterm (10/24/2007)
... c. DNA is a very long helix composed of two strands d. genes are associated with chromosomes 35. During DNA synthesis, one strand is synthesized ______ and the complementary strand is synthesized ______. a. 3’ to 5’; 5’ to 3’ b. 3’ to 5’; 3’ to 5’ c. 5’ to 3’; 3’ to 5’ d. 5’ to 3’; 5’ to 3’ 36. When ...
... c. DNA is a very long helix composed of two strands d. genes are associated with chromosomes 35. During DNA synthesis, one strand is synthesized ______ and the complementary strand is synthesized ______. a. 3’ to 5’; 5’ to 3’ b. 3’ to 5’; 3’ to 5’ c. 5’ to 3’; 3’ to 5’ d. 5’ to 3’; 5’ to 3’ 36. When ...
the chemistry of organic molecules
... 3. Maltose 3. Polysaccharides-sugars that are composed of more than 2 monosaccharides that are covalently bonded together. These are often very large molecules. a. What types of reactions are these formed by? b. Types of Polysaccharides 1. Starch-a stored form of glucose in plant cells. Plants can u ...
... 3. Maltose 3. Polysaccharides-sugars that are composed of more than 2 monosaccharides that are covalently bonded together. These are often very large molecules. a. What types of reactions are these formed by? b. Types of Polysaccharides 1. Starch-a stored form of glucose in plant cells. Plants can u ...
THE CHEMISTRY OF LIFE – CH
... capillary action – creep up small tubes (plants) Hydrogen bonds are important to organisms because they hold many biomolecules (proteins, carbohydrates) together. Organic Compounds (compounds made with carbon): are macromolecules (or polymers) – large molecules made when smaller molecules bo ...
... capillary action – creep up small tubes (plants) Hydrogen bonds are important to organisms because they hold many biomolecules (proteins, carbohydrates) together. Organic Compounds (compounds made with carbon): are macromolecules (or polymers) – large molecules made when smaller molecules bo ...
- Circle of Docs
... 4. The formation of glucose from non- carbohydrate sources such as amino acids is referred to as? a. Glycolysis b. Gluconeogenesis c. Glycogenolysis d. Glycogenesis 5. Exogenous fat is transported via which class of lipoproteins? a. Very low density lipoproteins b. Low density lipoproteins c. High d ...
... 4. The formation of glucose from non- carbohydrate sources such as amino acids is referred to as? a. Glycolysis b. Gluconeogenesis c. Glycogenolysis d. Glycogenesis 5. Exogenous fat is transported via which class of lipoproteins? a. Very low density lipoproteins b. Low density lipoproteins c. High d ...
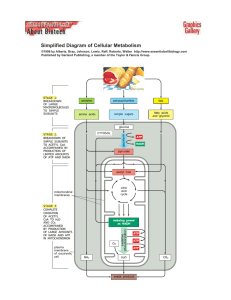
Simplified Diagram of Cellular Metabolism
... . http://www.essentialcellbiology.com Published by Garland Publishing, a member of the Taylor & Francis Group. ...
... . http://www.essentialcellbiology.com Published by Garland Publishing, a member of the Taylor & Francis Group. ...
Chapter 3
... – Cystic fibrosis is a hereditary disorder • In some individuals, protein appears to have correct amino acid sequence but fails to fold ...
... – Cystic fibrosis is a hereditary disorder • In some individuals, protein appears to have correct amino acid sequence but fails to fold ...
BIOCHEMISTRY I Spring 2013 (General medicine, Dental
... - to write a brief synopsis emphasizing the main ideas - to draw metabolic pathways in structural formulas with a short comment - where appropriate, to draw a picture (e.g. membranes, respiratory chain etc.) A good and concise preparation reflects the students’ knowledge and understanding the bioche ...
... - to write a brief synopsis emphasizing the main ideas - to draw metabolic pathways in structural formulas with a short comment - where appropriate, to draw a picture (e.g. membranes, respiratory chain etc.) A good and concise preparation reflects the students’ knowledge and understanding the bioche ...
Examination questions
... - to write a brief synopsis emphasizing the main ideas - to draw metabolic pathways in structural formulas with a short comment - where appropriate, to draw a picture (e.g. membranes, respiratory chain etc.) A good and concise preparation reflects the students’ knowledge and understanding the bioche ...
... - to write a brief synopsis emphasizing the main ideas - to draw metabolic pathways in structural formulas with a short comment - where appropriate, to draw a picture (e.g. membranes, respiratory chain etc.) A good and concise preparation reflects the students’ knowledge and understanding the bioche ...
Lecture: Biochemistry
... a. composed of glycerol and 3 fatty acid chains i. non-polar fatty acid side chains make them insoluable in water b. different fats = different fatty acid chains c. saturated fats - all single bonds for carbons i. generally solid at room temperature d. unsaturated fats - one/more double bonds ii. ge ...
... a. composed of glycerol and 3 fatty acid chains i. non-polar fatty acid side chains make them insoluable in water b. different fats = different fatty acid chains c. saturated fats - all single bonds for carbons i. generally solid at room temperature d. unsaturated fats - one/more double bonds ii. ge ...
Ativity 30
... Enzymes • …are proteins – biological catalysts that lower the activation energy of a reaction. • …are highly specific; they only act only on a small number of substrates (often just one.) • …increase the rate of a chemical reaction. • …are re-used; they are not consumed in the reaction. E + S ES ...
... Enzymes • …are proteins – biological catalysts that lower the activation energy of a reaction. • …are highly specific; they only act only on a small number of substrates (often just one.) • …increase the rate of a chemical reaction. • …are re-used; they are not consumed in the reaction. E + S ES ...
Organic Chemistry
... 2. Carbohydrates are a class of organic molecule that contain Carbon , Hydrogen, and Oxygen molecules in a 1:2:1 ratio. They are often in structured into 5 or 6 carbon rings. They are also called saccharides or sugars and provide living organisms with energy. Examples: glucose, fructose (Monosacchar ...
... 2. Carbohydrates are a class of organic molecule that contain Carbon , Hydrogen, and Oxygen molecules in a 1:2:1 ratio. They are often in structured into 5 or 6 carbon rings. They are also called saccharides or sugars and provide living organisms with energy. Examples: glucose, fructose (Monosacchar ...
Document
... • Fatty acid composed of a long hydrocarbon chain with a carboxyl group at one end • Saturated—single bonds; unsaturated—one or more double bonds • Acetyl-CoA carboxylase and fatty acid synthase: make saturated fatty acids with 14 or 16 carbons. • Desaturase enzymes located in ER introduce double bo ...
... • Fatty acid composed of a long hydrocarbon chain with a carboxyl group at one end • Saturated—single bonds; unsaturated—one or more double bonds • Acetyl-CoA carboxylase and fatty acid synthase: make saturated fatty acids with 14 or 16 carbons. • Desaturase enzymes located in ER introduce double bo ...
Title: Molecular recognition of amino acids by using pseudopeptidic
... amination reaction is described. They differ in the linking positions of the central benzene ring (meta or para). In both cases, the use of anionic templates is necessary to favor the formation of the desired product. To ensure the formation of the products, they were characterized by NMR and ESI-MS ...
... amination reaction is described. They differ in the linking positions of the central benzene ring (meta or para). In both cases, the use of anionic templates is necessary to favor the formation of the desired product. To ensure the formation of the products, they were characterized by NMR and ESI-MS ...
Download PDF
... capture, proton and ion gradients, and conversion to mechanical energy. In addition, we will explore the thermodynamics of electron transport, proton pumping, and ATP biosynthesis. 3. Molecular biosynthesis. Most organisms can biosynthesize amino acids, lipids, nucleotides, vitamins, and cofactors u ...
... capture, proton and ion gradients, and conversion to mechanical energy. In addition, we will explore the thermodynamics of electron transport, proton pumping, and ATP biosynthesis. 3. Molecular biosynthesis. Most organisms can biosynthesize amino acids, lipids, nucleotides, vitamins, and cofactors u ...
Most common elements in living things are carbon, hydrogen
... Lipids are large, nonpolar (won't dissolve in water) molecules. Phospholipids make up cell membranes. Lipids also serve as waxy coverings (cuticle) on plants, pigments (chlorophyll), and steroids. Lipids have more carbon and hydrogen atoms than oxygen atoms. Fats are made of a glycerol (alcohol) an ...
... Lipids are large, nonpolar (won't dissolve in water) molecules. Phospholipids make up cell membranes. Lipids also serve as waxy coverings (cuticle) on plants, pigments (chlorophyll), and steroids. Lipids have more carbon and hydrogen atoms than oxygen atoms. Fats are made of a glycerol (alcohol) an ...
HW Questions on Lipids and Proteins
... 16 & 17. What are the two main chemical components (monomers) of a fat molecule called? How many of each of the components mentioned above do you need to make one fat molecule? 1 Glycerol & 3 fatty acids 18. What is the process called by which you form a triglyceride (fat molecule)? Dehydration synt ...
... 16 & 17. What are the two main chemical components (monomers) of a fat molecule called? How many of each of the components mentioned above do you need to make one fat molecule? 1 Glycerol & 3 fatty acids 18. What is the process called by which you form a triglyceride (fat molecule)? Dehydration synt ...
Lipids
... C. sphingolipids and glycerophospholipids D. glycerophospholipids and waxes Answer is B. Triacylglycerols and glycerophospholipids contain the alcohol glycerol. ...
... C. sphingolipids and glycerophospholipids D. glycerophospholipids and waxes Answer is B. Triacylglycerols and glycerophospholipids contain the alcohol glycerol. ...
Cellular Respiration - Chapter 8 (new book).
... C2H3O + CO2 + NADH leave the reaction D. Kreb’s cycle or Citric Acid cycle 1. a series of enzyme mediated reactions linked to each other in which several carbon chain intermediates are produces (C6, C5, C4) 2. First intermediate formed is Citrate (Citric acid cycle) 3. Acetyl Co-A enters the cycle a ...
... C2H3O + CO2 + NADH leave the reaction D. Kreb’s cycle or Citric Acid cycle 1. a series of enzyme mediated reactions linked to each other in which several carbon chain intermediates are produces (C6, C5, C4) 2. First intermediate formed is Citrate (Citric acid cycle) 3. Acetyl Co-A enters the cycle a ...
Chemistry of Life
... Hydrocarbons undergo reactions that release relatively large amounts of energy Replace a H with a C and the backbone grows, keep going and you get long chains, branched chains, and ring structures No polarity to bonds, not soluble in water ...
... Hydrocarbons undergo reactions that release relatively large amounts of energy Replace a H with a C and the backbone grows, keep going and you get long chains, branched chains, and ring structures No polarity to bonds, not soluble in water ...
Chapter 24_CHEM 131
... • After urea is formed, it diffuses out of liver cells into the blood, the kidneys filter it out, and it is excreted in the urine. • Normal urine from an adult contains 25-30 g of urea daily, but exact amount varies with protein content of the diet. • The direct excretion of NH4+ accounts for a smal ...
... • After urea is formed, it diffuses out of liver cells into the blood, the kidneys filter it out, and it is excreted in the urine. • Normal urine from an adult contains 25-30 g of urea daily, but exact amount varies with protein content of the diet. • The direct excretion of NH4+ accounts for a smal ...
1 - Rosshall Academy
... State that photosynthesis is the process by which plants make carbohydrates from carbon dioxide and water using light energy in the presence of chlorophyll; oxygen is released in the process. ...
... State that photosynthesis is the process by which plants make carbohydrates from carbon dioxide and water using light energy in the presence of chlorophyll; oxygen is released in the process. ...
Enzymes - WordPress.com
... 5. A scientist is analyzing a sample of tissue from a plant. Which of the following elements will be most abundant in the sample? A. zinc and copper B. sodium and chlorine C. carbon and hydrogen D. magnesium and calcium 6. Resistance to antibiotics results from variations in the genes of Streptococ ...
... 5. A scientist is analyzing a sample of tissue from a plant. Which of the following elements will be most abundant in the sample? A. zinc and copper B. sodium and chlorine C. carbon and hydrogen D. magnesium and calcium 6. Resistance to antibiotics results from variations in the genes of Streptococ ...
18 April 2007 - Santa Fe Institute
... Accidents can matter “Any replay of the tape would lead evolution down a pathway radically different from the road actually taken.” ...
... Accidents can matter “Any replay of the tape would lead evolution down a pathway radically different from the road actually taken.” ...
Fatty acid synthesis

Fatty acid synthesis is the creation of fatty acids from acetyl-CoA and malonyl-CoA precursors through action of enzymes called fatty acid synthases. It is an important part of the lipogenesis process, which – together with glycolysis – functions to create fats from blood sugar in living organisms.