LOYOLA COLLEGE (AUTONOMOUS), CHENNAI – 600 034
... Answer any two of the following, each within 1500 words; Draw diagrams wherever necessary: (2x20= 40 marks) 26. Elaborate on pH scale and pH meter. Add a note on Henderson Hasselbalch equation. 27. Write in detail about the steps involved in synthesis and degradation of fatty acids. 28. Analyze biom ...
... Answer any two of the following, each within 1500 words; Draw diagrams wherever necessary: (2x20= 40 marks) 26. Elaborate on pH scale and pH meter. Add a note on Henderson Hasselbalch equation. 27. Write in detail about the steps involved in synthesis and degradation of fatty acids. 28. Analyze biom ...
Macromolecules
... acids together toAmino Side make proteins The process is called dehydration synthesis Peptide bonds form to hold the amino acids together ...
... acids together toAmino Side make proteins The process is called dehydration synthesis Peptide bonds form to hold the amino acids together ...
Lab Time
... nonfunctional by excessive heat. All biological enzymes are proteins and their destruction is lethal because many key enzymatic reactions for life would be stopped. ...
... nonfunctional by excessive heat. All biological enzymes are proteins and their destruction is lethal because many key enzymatic reactions for life would be stopped. ...
File
... Elements & Macromolecules in Organisms Most common elements in living things are carbon, hydrogen, nitrogen, and oxygen. These four elements constitute about 95% of your body weight. All compounds can be classified in two broad categories --- organic and inorganic compounds. Organic compounds are ma ...
... Elements & Macromolecules in Organisms Most common elements in living things are carbon, hydrogen, nitrogen, and oxygen. These four elements constitute about 95% of your body weight. All compounds can be classified in two broad categories --- organic and inorganic compounds. Organic compounds are ma ...
Macromolecule Jeopardy
... 100- What elements have to be in a molecule for it to be considered organic? Carbon and hydrogen 200- Is a saturated fat solid or liquid at room temperature? solid 300- What are is the difference between a saturated and an unsaturated fat?? Saturated fats have all single bonds and unsaturated fats h ...
... 100- What elements have to be in a molecule for it to be considered organic? Carbon and hydrogen 200- Is a saturated fat solid or liquid at room temperature? solid 300- What are is the difference between a saturated and an unsaturated fat?? Saturated fats have all single bonds and unsaturated fats h ...
Perspectives in Nutrition, 8th Edition
... Chapter 9 Outline: Energy Metabolism After studying this chapter, you will be able to: 1. Explain the differences among metabolism, catabolism, and anabolism. 2. Describe aerobic and anaerobic metabolism of glucose. 3. Illustrate how energy is extracted from glucose, fatty acids, amino acids, and al ...
... Chapter 9 Outline: Energy Metabolism After studying this chapter, you will be able to: 1. Explain the differences among metabolism, catabolism, and anabolism. 2. Describe aerobic and anaerobic metabolism of glucose. 3. Illustrate how energy is extracted from glucose, fatty acids, amino acids, and al ...
general biology syllabus
... 2) Energy (ATP, high-energy electrons) C) Coupled channels: active transport followed by facilitated diffusion 1) Proton pump (proton = H+) a) In photosynthesis and cellular respiration, high-energy e– power first transport protein in active transport of H+ through membrane b) As H+ passes through s ...
... 2) Energy (ATP, high-energy electrons) C) Coupled channels: active transport followed by facilitated diffusion 1) Proton pump (proton = H+) a) In photosynthesis and cellular respiration, high-energy e– power first transport protein in active transport of H+ through membrane b) As H+ passes through s ...
Fatty Acid Metabolism - Weber State University
... triacyl-esters of glycerol in which each of its three alcohol groups is esterified to a fatty acid. Almost all fatty acids contain an even number of carbon atoms. We will see in this discussion that this is a result of the way they are synthesized, namely from acetyl-CoA (two carbon building blocks) ...
... triacyl-esters of glycerol in which each of its three alcohol groups is esterified to a fatty acid. Almost all fatty acids contain an even number of carbon atoms. We will see in this discussion that this is a result of the way they are synthesized, namely from acetyl-CoA (two carbon building blocks) ...
Regulation of gene expression by polyunsaturated fatty acids
... proaggregatory effects [9]. Thus understanding the mechanisms by which these fatty acids exert their effects will be key to understanding whether and how PUFAs can help promote optimal health and in establishing a much-needed healthy dietary n-3 : n-6 ratio. ...
... proaggregatory effects [9]. Thus understanding the mechanisms by which these fatty acids exert their effects will be key to understanding whether and how PUFAs can help promote optimal health and in establishing a much-needed healthy dietary n-3 : n-6 ratio. ...
BIS103-002 (Spring 2008) - UC Davis Plant Sciences
... to regenerate NAD+ for maintaining glycolysis. Why is this alternative not used in tissues or organs undergoing anaerobic glycolysis to regenerate NAD+? (2 pts) Tissues that undergo anaerobic glycolysis (e.g., skeletal muscles) are in desperate need of ATP (no or only very low ATP production by oxid ...
... to regenerate NAD+ for maintaining glycolysis. Why is this alternative not used in tissues or organs undergoing anaerobic glycolysis to regenerate NAD+? (2 pts) Tissues that undergo anaerobic glycolysis (e.g., skeletal muscles) are in desperate need of ATP (no or only very low ATP production by oxid ...
Lec. # 2
... ý Strong acids and bases completely dissociate or accept a proton in aqueous solution to produce their respective conjugate bases and acids. ý They undergo 100% dissociation in water with equilibrium shifted completely to the right side. ý Many different organic functional groups behave as acids or ...
... ý Strong acids and bases completely dissociate or accept a proton in aqueous solution to produce their respective conjugate bases and acids. ý They undergo 100% dissociation in water with equilibrium shifted completely to the right side. ý Many different organic functional groups behave as acids or ...
Fatty Acid Synthesis
... Thus some polyunsaturated fatty acids are dietary essentials, e.g., linoleic acid, 18:2 cis D9,12 (18 C atoms long, with cis double bonds at carbons 9-10 & 12-13). ...
... Thus some polyunsaturated fatty acids are dietary essentials, e.g., linoleic acid, 18:2 cis D9,12 (18 C atoms long, with cis double bonds at carbons 9-10 & 12-13). ...
Phytochemistry 1
... -Acetylenic compounds are basically alkyne compounds that have C-C triple bonds in their structures. -Polyacetylene term is often used interchangeably to describe this class of natural products, although they are not polymers and many precursors and metabolites contain only a single acetylenic bond. ...
... -Acetylenic compounds are basically alkyne compounds that have C-C triple bonds in their structures. -Polyacetylene term is often used interchangeably to describe this class of natural products, although they are not polymers and many precursors and metabolites contain only a single acetylenic bond. ...
24.8 Fates of the Carbon Atoms from Amino Acids
... Match each of the following citric acid intermediates with the amino acid that provides its carbon skeleton: 1) pyruvate 2) fumarate 3) α-ketoglutarate A. cysteine B. glutamine C. aspartate ...
... Match each of the following citric acid intermediates with the amino acid that provides its carbon skeleton: 1) pyruvate 2) fumarate 3) α-ketoglutarate A. cysteine B. glutamine C. aspartate ...
Overview of Fasting
... Increased fatty acid oxidation: • The oxidation of fatty acids derived from adipose tissue is the major source of energy in hepatic tissue in the postabsorptive state ③. • The fall in malonyl CoA due to phosphorylation (inactivation) of acetyl CoA carboxylase by activated protein kinase (AMPK) remo ...
... Increased fatty acid oxidation: • The oxidation of fatty acids derived from adipose tissue is the major source of energy in hepatic tissue in the postabsorptive state ③. • The fall in malonyl CoA due to phosphorylation (inactivation) of acetyl CoA carboxylase by activated protein kinase (AMPK) remo ...
Outline
... A) Oxidation and Reduction (Redox) reactions are always coupled C. Carbohydrate Metabolism 1. Glucose catabolism is the breakdown of CHO to release energy A) It is accomplished in four steps: ...
... A) Oxidation and Reduction (Redox) reactions are always coupled C. Carbohydrate Metabolism 1. Glucose catabolism is the breakdown of CHO to release energy A) It is accomplished in four steps: ...
Macromolecule Molecular Structure Carbohydrates
... drawing, except that in the complete glycogen molecule there are 12 layers whereas for simplicity only 5 are shown in the drawing: The essential features of this general structure are that each B-chain has two branch points, and all chains have the same length, as the experiments showed that the mat ...
... drawing, except that in the complete glycogen molecule there are 12 layers whereas for simplicity only 5 are shown in the drawing: The essential features of this general structure are that each B-chain has two branch points, and all chains have the same length, as the experiments showed that the mat ...
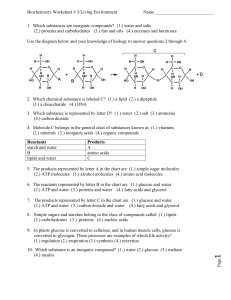
1. Which substances are inorganic compounds?
... 5. The products represented by letter A in the chart are (1.) simple sugar molecules (2.) ATP molecules (3.) alcohol molecules (4.) amino acid molecules 6. The reactants represented by letter B in the chart are (1.) glucose and water (2.) ATP and water (3.) proteins and water (4.) fatty acids and gl ...
... 5. The products represented by letter A in the chart are (1.) simple sugar molecules (2.) ATP molecules (3.) alcohol molecules (4.) amino acid molecules 6. The reactants represented by letter B in the chart are (1.) glucose and water (2.) ATP and water (3.) proteins and water (4.) fatty acids and gl ...
Citric Acid Cycle Overview of Cycle Fate of Acetyl CoA
... Net ATP Harvest from Glucose • Glycolysis = 5‐7 ATP – 3 or 5 ATP from cytosolic NADH – In humans, cytosolic NADH transport costs 2 ATP equivalents ...
... Net ATP Harvest from Glucose • Glycolysis = 5‐7 ATP – 3 or 5 ATP from cytosolic NADH – In humans, cytosolic NADH transport costs 2 ATP equivalents ...
lipid digestion - anslab.iastate.edu
... – Little synthesis of fatty acids in liver and lipoproteins from intestinal mucosa are not utilized by liver – Liver synthesis of triglycerides are dependent on the concentrations of circulating non-esterified fatty acids (NEFAS) and glycerol from glucose • If glucose is limiting glycerol synthesis ...
... – Little synthesis of fatty acids in liver and lipoproteins from intestinal mucosa are not utilized by liver – Liver synthesis of triglycerides are dependent on the concentrations of circulating non-esterified fatty acids (NEFAS) and glycerol from glucose • If glucose is limiting glycerol synthesis ...
Lipids
... phosphate (DHAP), a glycolytic intermediate. The free F.As produced are either reesterified to TAG in the adipose tissue or travel in the blood to be taken up by the cells for oxidation. ...
... phosphate (DHAP), a glycolytic intermediate. The free F.As produced are either reesterified to TAG in the adipose tissue or travel in the blood to be taken up by the cells for oxidation. ...
Detergents from renewable resources
... (caramellization and Maillard reaction) Dissolution in suitable medium Bleach with alkaline hydrogen peroxide, risk for oxidized by-products ...
... (caramellization and Maillard reaction) Dissolution in suitable medium Bleach with alkaline hydrogen peroxide, risk for oxidized by-products ...
Modern Biology (I) First Midterm (10/24/2007)
... c. DNA is a very long helix composed of two strands d. genes are associated with chromosomes 35. During DNA synthesis, one strand is synthesized ______ and the complementary strand is synthesized ______. a. 3’ to 5’; 5’ to 3’ b. 3’ to 5’; 3’ to 5’ c. 5’ to 3’; 3’ to 5’ d. 5’ to 3’; 5’ to 3’ 36. When ...
... c. DNA is a very long helix composed of two strands d. genes are associated with chromosomes 35. During DNA synthesis, one strand is synthesized ______ and the complementary strand is synthesized ______. a. 3’ to 5’; 5’ to 3’ b. 3’ to 5’; 3’ to 5’ c. 5’ to 3’; 3’ to 5’ d. 5’ to 3’; 5’ to 3’ 36. When ...
Fatty acid synthesis

Fatty acid synthesis is the creation of fatty acids from acetyl-CoA and malonyl-CoA precursors through action of enzymes called fatty acid synthases. It is an important part of the lipogenesis process, which – together with glycolysis – functions to create fats from blood sugar in living organisms.