* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Phytochemistry 1
Metalloprotein wikipedia , lookup
Amino acid synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Nucleic acid analogue wikipedia , lookup
Citric acid cycle wikipedia , lookup
Fatty acid metabolism wikipedia , lookup
15-Hydroxyeicosatetraenoic acid wikipedia , lookup
Biochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Biosynthesis wikipedia , lookup
Butyric acid wikipedia , lookup
Specialized pro-resolving mediators wikipedia , lookup
Phytochemistry 1
Lecture 11
Date: 15/3/2015
Natural Acetylenic compounds
Done by: Dalia Zakaria
You have to refer to the slides.
-Acetylenic compounds are basically alkyne compounds that have C-C triple bonds in their
structures.
-Polyacetylene term is often used interchangeably to describe this class of natural products,
although they are not polymers and many precursors and metabolites contain only a single
acetylenic bond.
-They are used as precursors for the synthesis of other naturally occurring compounds.
-Acetylenic compounds are derived from acetate polymalonate pathway.
-They are not restricted to plants, they can be found in moss, lichens, fungi, marine algae,
sponges, tunicates, insects, frogs and, in traces quantities, in humans.
-These compounds are unstable in human bodies due to the presence of certain enzymes
which are responsible for either formation or removal of the triple bonds.
-Generally Scientists don’t like to work on the acetylenic compounds due to their instability and
difficulties of its isolation and characterizations.
* History of Acetylenic Compounds:
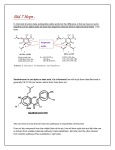
- Dehydromatricaria ester (1A) was the earliest isolated alkyne-bearing natural product. This
compound was found in chamomile (chamomile also contains volatile oils and flavonoids which
responsible for its action) and it has 3 triple bonds.
- Agrocybin, crepenynic acid, steariolic acid , and tariric acid are the most common acetylenic
compounds.
- Agrocybin contains three double bonds, While steariolic acid, crepenynic acid , and tariric acid
contain only one triple bond.
|Page1
Phytochemistry 1
* Biosynthesis of Acetylenic Acid in Plants:
- Major plant-derived polyacetylenes from Asteraceae (Compositae).
- Crepenynic acid plays a major role in biosynthesis of polyacetylenic compounds; accordingly
their biosynthesis pathway was called "Crepenynate Pathway".
- Mechanisms of biosynthesis were described as the following:
2
1
3
4
5
1- Acetyl Co-A reacts with 8 malonyl Co-A in the presence of fatty acid synthase which lead to
the formation of our 18 Carbons saturated fatty acid (without = bond) "Stearic Acid" and this is
called the primary metabolite.
2- The saturated fatty acid "Stearic acid" is converted to the unsaturated fatty acid "Oleic acid"
under the effect of delta 9 desaturase enzyme.
(Oleic acid is an unsaturated fatty acid contains one double bond at carbon number 9)
3-Under the effect of delta 12 deasturase enzyme, our oleic acid is converted to linoleic acid.
(Linoleic acid is an unsaturated fatty acid contains two double bonds at carbon number 9 and
carbon number 12).
4- Delta 12 acetylenase enzyme (the enzyme which responsible for the formation of triple bond
by removing the two Hs) converts the double bond which is located at carbon number 12 to
triple bond; which mean we can't form triple bond directly from the saturated compound, we
have first to form double bond by desaturase enzyme then form triple bond by the action of
acetylenase enzyme and this lead to the formation of Crepenynic Acid.
|Page2
Phytochemistry 1
5- Further desaturation of the crepenynic acid by using Delta 14 desaturase enzyme (form
double bond at position 14) leads to the formation of dehydrocrepenynic acid which has two
double bonds one at position 9 and the other at position 14, is only found in fungi.
6- Then delta 14 Acetylenase form triple point at position 14.
Nomenclature of our Acetylenic Compounds:
18:19c,12a, crepenynic acid
-
18: stands for the number of carbon in our acetylenic compound.
Here we have 18 carbons.
1: stands for the number of double bonds.
Here we have one double bond.
9: indicates the location of our double bonds.
Here it's located at carbon number 9.
C: stands for cis.
12: indicate the location of our Acetelynic bonds.
Here it's located at carbon number 12.
A: stands for acetylenes.
Two distinct proposals for the biogenesis of acetylenic bonds:
1- Desaturation of existing alkene (always we must have alkene {= bond}) functionality
through an iron-catalyzed dehydrogenation with molecular oxygen. Electrons are
provided by either NADH or NADPH.
2- The elimination of an activated enol carboxylate intermediate is thermodynamically
driven by CO2 formation, which may be coupled to the hydrolysis of pyrophosphate.
In most eukaryotics, the biosynthesis occurs in cytoplasm while in green plants, the
biosynthesis occur in the stroma of pastids.
* In Eukaryotes:
- Acetyl co-A is formed in the
mitochondria, which under the effect of
Polyketides synthase result in the
formation of polyketides.
- In the cytosol, there's a pool of Acetyl
co-A which under certain processes
lead to the formation of VLCFA "very
long chain fatty acid"
- Fatty acid modification occurs in the
endoplasmic reticulum "ER".
- So as we see the biosynthesis of acetylenic compound is way more complicated in
eukaryotes than in plants, because in the cytosol we have many sources to obtain
AcytelCoA but in plant it's obtain only from glucose.
- Whether it's in plant or in the cytosol always the triple bond will exist between C8-C18.
|Page3
Phytochemistry 1
-Flacarinol and Falcarindiol are secondary metabolites found in the root of American Ginseng
(Quinquefolium) and in the root of the carrots.
- The older our plant is, the higher its contents of falcarinol and falcarindiol.
** Echinacea:
The most common plant that contain Acetylenic compounds
- We take the rhizome and the upper part, the rhizome contains more active ingredient than the
upper parts.
- In Jordan it's classified as drug, mainly as the form of syrup for treatment of flu or cold.
-A native plant to the central plains of Eastern North America.
-There are three species: E. purpurea, E. angustifolia, and E. pallida.
-It grows on road banks, prairies, fields, and in dry, open woods.
History of Echinacea:
-It’s use originated by the Plains Indians.
-They used it to treat insect bites, snake bites, toothaches, sore throat, wounds, mumps,
smallpox, and measles.
-It became popular in Europe and America as a folk medicine.
Claims
•
That it improves the immune system to help prevent and fight infections
Common Uses
•
To treat and prevent colds, flu, or other infections
•
To stimulate the immune system in order to help fight infections
|Page4
Phytochemistry 1
* Chemistry:
-The activities of our compounds are not only due to the presence of polyacetylene, but also due
to the presence of the following components: Essential oil, Polysaccharides,
Polyacetylenes,Betain,Glycoside,Sesquiterpenes,CarypohyleneCopper,Iron,Tannins,Protein,fatty
acids, and Vitamins A, C, and E.
* Components of the Plant that are Thought to be Beneficial
-
Large polysaccharides (inulin)
May increase the production of T-cells and increase other natural killer cell activity.
-
Fat Soluable alkylamides and caffeic acid glycoside (echinacoside).
It's standardizes according to the presence of Caffeic acid.
-
Theoretical Basis:
Echinacea boosts the immune system by increasing the levels of interferon, which may
increase phagocytosis, cellular respiratory activity, and lymphocyte activation from the
release of tumor necrosis factor, interleukin-1, and interferon beta-2.
-
Warnings & Side Effects:
Should not be taken with auto-immune disorders such as: TB, leicosis, connective tissue
disorders, collagenosis, lupus, and AIDS.
Side effects are rare but include allergic reactions such as rashes and asthma.
They usually occur in people allergic to related plants in the daisy family.
-
Products and Forms:
The above ground parts and roots are made into teas, juices, extracts, or topical forms
Products include capsules, teas, and tinctures and the most common one is the syrup
form.
In Jordan this plant was registered as a drug, in other countries it was registered as
nutritional product Or OTC.
We collect the active ingredients from the lower parts of our plants due to its higher
concentration in those parts.
|Page5