lect11
... lactate, glycerol and the carbon skeletons of certain amino acids can all be used as substrates (propionyl-CoA can also be used) ...
... lactate, glycerol and the carbon skeletons of certain amino acids can all be used as substrates (propionyl-CoA can also be used) ...
CHAPTER 26: Lipid Metabolism - Richest energy source
... - we said acetyl CoA formed enters the Krebs cycle, or is used to form Ketone bodies - ketaone bodies are formed from the buildup of acetyl coA in the body with depletion of oxaloacetate = krebs cycle can’t start - caused by diabetes or diet low in carbohydrates (fatty acid oxidation increases to ...
... - we said acetyl CoA formed enters the Krebs cycle, or is used to form Ketone bodies - ketaone bodies are formed from the buildup of acetyl coA in the body with depletion of oxaloacetate = krebs cycle can’t start - caused by diabetes or diet low in carbohydrates (fatty acid oxidation increases to ...
STATE UNIVERSITY OF NEW YORK COLLEGE OF TECHNOLOGY CANTON, NEW YORK
... enzymes; relate structure to function of proteins; and explain enzyme catalysis and regulation; and apply thermodynamic and kinetic theories to enzyme reactions 3. Describe the physical and chemical properties of lipids, their synthesis and function in membranes and metabolism 4. Describe the centra ...
... enzymes; relate structure to function of proteins; and explain enzyme catalysis and regulation; and apply thermodynamic and kinetic theories to enzyme reactions 3. Describe the physical and chemical properties of lipids, their synthesis and function in membranes and metabolism 4. Describe the centra ...
Chemistry of Lipids
... Contain more than one double bond bond. Eg: Linoleic acid, linolenic acid and arachidonic acid. acid These are not synthesised in human body due to lack of the desaturase enzyme enzyme, which introduces double bonds beyond 9th and 10th carbon atoms. Glycerol It is a trihydric alcohol [three hy ...
... Contain more than one double bond bond. Eg: Linoleic acid, linolenic acid and arachidonic acid. acid These are not synthesised in human body due to lack of the desaturase enzyme enzyme, which introduces double bonds beyond 9th and 10th carbon atoms. Glycerol It is a trihydric alcohol [three hy ...
Lecture: Biochemistry I. Inorganic Compounds A. Water (H2O)
... a. 20 different amino acids (same in all life) i. amino end (NH2) ii. acid group (COOH) iii. R-group unique for each amino acid b. dehydration synthesis joins amino acids i. called a peptide bond ii. dipeptide - 2 amino acids iii. tripeptide - 3 amino acids iv. polypeptide - many amino acids 2. Leve ...
... a. 20 different amino acids (same in all life) i. amino end (NH2) ii. acid group (COOH) iii. R-group unique for each amino acid b. dehydration synthesis joins amino acids i. called a peptide bond ii. dipeptide - 2 amino acids iii. tripeptide - 3 amino acids iv. polypeptide - many amino acids 2. Leve ...
Chapter 3 Review Questions
... 1. Which statement correctly describes how carbon’s ability to form four bonds makes it uniquely suited to form macromolecules? A. It forms short, simple carbon chains. B. It forms large, complex, diverse molecules. C. It forms covalent bonds with other carbon atoms. D. It forms covalent bonds that ...
... 1. Which statement correctly describes how carbon’s ability to form four bonds makes it uniquely suited to form macromolecules? A. It forms short, simple carbon chains. B. It forms large, complex, diverse molecules. C. It forms covalent bonds with other carbon atoms. D. It forms covalent bonds that ...
Biomolecules I. Introduction. - biochemistry: study of chemical
... C. Polysaccharides: long chains of simple sugars linked together by dehydration synthesis. - due to size, they are water insoluble. - great storage products; also have structural roles. - polysaccharides of importance to body: starch & glycogen, both glucose polymers. 1. starch: storage CH2 O formed ...
... C. Polysaccharides: long chains of simple sugars linked together by dehydration synthesis. - due to size, they are water insoluble. - great storage products; also have structural roles. - polysaccharides of importance to body: starch & glycogen, both glucose polymers. 1. starch: storage CH2 O formed ...
Amino acids - Workforce3One
... the shape of a protein. - caused by changes in the protein’s environment -pH -temperature -salt concentration - causing loss of function. - may involve complete unfolding - Renaturation is refolding into natural shape ...
... the shape of a protein. - caused by changes in the protein’s environment -pH -temperature -salt concentration - causing loss of function. - may involve complete unfolding - Renaturation is refolding into natural shape ...
Role of Liver In Triglyceride Homeostasis
... Common Fatty Acids • C14:0 - myristic acid • C16:0 - palmitic acid • C18:0 - stearic acid • C18:1 9 - oleic acid • C18:2 6 - linoleic acid* • C18:3 3 - -linolenic acid*; 6 - -linolenic acid ...
... Common Fatty Acids • C14:0 - myristic acid • C16:0 - palmitic acid • C18:0 - stearic acid • C18:1 9 - oleic acid • C18:2 6 - linoleic acid* • C18:3 3 - -linolenic acid*; 6 - -linolenic acid ...
NHC Allowed Processes 020910v01
... Amination of Alcohols and Fatty Acids Reagents: Ammonia, Alkyl Amine Catalysts: Nickel, Palladium, various known other reducing agents Agricultural Inputs: Alcohols, Acids, Aldehydes, Ketones Description: The process of introducing an amine into an alcohol or fatty acid. Distillation of Essent ...
... Amination of Alcohols and Fatty Acids Reagents: Ammonia, Alkyl Amine Catalysts: Nickel, Palladium, various known other reducing agents Agricultural Inputs: Alcohols, Acids, Aldehydes, Ketones Description: The process of introducing an amine into an alcohol or fatty acid. Distillation of Essent ...
Macromolecule Notes Powerpoint
... • Cellulose and chitin are used in plants and animals for constructing cell walls and exoskeletons. We don’t have the enzymes that recognize how the glucose molecules are hooked together in this form so we don’t ...
... • Cellulose and chitin are used in plants and animals for constructing cell walls and exoskeletons. We don’t have the enzymes that recognize how the glucose molecules are hooked together in this form so we don’t ...
Macromolecule Notes - Ms. Dooley`s Science Class
... • Cellulose and chitin are used in plants and animals for constructing cell walls and exoskeletons. We don’t have the enzymes that recognize how the glucose molecules are hooked together in this form so we don’t ...
... • Cellulose and chitin are used in plants and animals for constructing cell walls and exoskeletons. We don’t have the enzymes that recognize how the glucose molecules are hooked together in this form so we don’t ...
Biology I SB1c Macromolecules and the Scientific Method Test
... Wax, fats, oils, and cholesterol 3. What are the monomers of nucleic acids? Nucleotides 4. What are lipids made of? Fatty acids 5. Which macromolecule stores genetic information? Nucleic acids such as DNA 6. What are some examples of carbohydrates? Polysaccharides and glucose 7. What are the subunit ...
... Wax, fats, oils, and cholesterol 3. What are the monomers of nucleic acids? Nucleotides 4. What are lipids made of? Fatty acids 5. Which macromolecule stores genetic information? Nucleic acids such as DNA 6. What are some examples of carbohydrates? Polysaccharides and glucose 7. What are the subunit ...
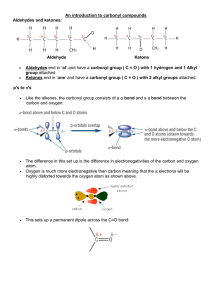
An introduction to carbonyl compounds Aldehydes and ketones
... Triglycerides are naturally occurring fats. They are triesters of propan - 1,2,3 - triol, glycerol and fatty acids. Glycerol has 3 alcohol groups which can react with a carboxylic acid (stearic acid) to form an ester. If all 3 join we make a triglyceride (an ester). The carboxylic acids occu ...
... Triglycerides are naturally occurring fats. They are triesters of propan - 1,2,3 - triol, glycerol and fatty acids. Glycerol has 3 alcohol groups which can react with a carboxylic acid (stearic acid) to form an ester. If all 3 join we make a triglyceride (an ester). The carboxylic acids occu ...
2. Organic Compounds and the Four Biomolec
... • In cells, compounds are built up and broken down in small steps by enzymes, which are proteins which cause specific chemical reactions to occur. Each enzyme causes one step in a metabolic pathway to occur. • An example: condensing 2 sugars together by removing a water (H2O) from two alcohol (-OH) ...
... • In cells, compounds are built up and broken down in small steps by enzymes, which are proteins which cause specific chemical reactions to occur. Each enzyme causes one step in a metabolic pathway to occur. • An example: condensing 2 sugars together by removing a water (H2O) from two alcohol (-OH) ...
Unit 1 Test Biology Chapter 2.3
... - They work together to make proteins. - DNA stores the information for putting amino acids together to make proteins, and RNA helps to build proteins. ...
... - They work together to make proteins. - DNA stores the information for putting amino acids together to make proteins, and RNA helps to build proteins. ...
Chapter 3: The Chemistry of Organic Molecules
... fatty acids, and one phosphate group. • Phosphate group is the “polar head” of molecule. • Fatty acid chains are “nonpolar tails” of molecule. • Plasma membrane in eukaryotic cells is a phospholipid bilayer. ...
... fatty acids, and one phosphate group. • Phosphate group is the “polar head” of molecule. • Fatty acid chains are “nonpolar tails” of molecule. • Plasma membrane in eukaryotic cells is a phospholipid bilayer. ...
Fatty Acid Metabolism
... lipid or de novo synthesis from acetyl-CoA derived from carbohydrate or amino acids. ...
... lipid or de novo synthesis from acetyl-CoA derived from carbohydrate or amino acids. ...
Final Review
... Oxidoreductases in the citric acid cycle include: isocitrate dehydrogenase, α-ketoglutarate dehydrogenase complex, succinate dehydrogenase, and malate dehydrogenase. 13. Which step(s) of the Kreb’s cycle is/are catalyzed by an isomerase? STEP 2 ...
... Oxidoreductases in the citric acid cycle include: isocitrate dehydrogenase, α-ketoglutarate dehydrogenase complex, succinate dehydrogenase, and malate dehydrogenase. 13. Which step(s) of the Kreb’s cycle is/are catalyzed by an isomerase? STEP 2 ...
Chem 2B
... 63. Explain how energy metabolism is regulated when a cell has a high level of NAD +. NAD+ is an co-enzyme that picked up H+ and e- to form NADH during the breaking down of carbohydrates, proteins and fats. ...
... 63. Explain how energy metabolism is regulated when a cell has a high level of NAD +. NAD+ is an co-enzyme that picked up H+ and e- to form NADH during the breaking down of carbohydrates, proteins and fats. ...
Final Review - Department of Chemistry ::: CALTECH
... The citric acid cycle - where electron carriers, NADH and FADH2, are made in the mitochondria Oxidative phosphorylation - this process occurs in the mitochondria, and uses the electron transport chain to produce ATP, the bulk of usable energy for the cell What happens in glycolysis? Over the course ...
... The citric acid cycle - where electron carriers, NADH and FADH2, are made in the mitochondria Oxidative phosphorylation - this process occurs in the mitochondria, and uses the electron transport chain to produce ATP, the bulk of usable energy for the cell What happens in glycolysis? Over the course ...
Macromolecules - Lisle CUSD 202
... monomers are linked together to form polymers dehydration synthesis (condensation) broken apart via hydrolysis ...
... monomers are linked together to form polymers dehydration synthesis (condensation) broken apart via hydrolysis ...
LOYOLA COLLEGE (AUTONOMOUS), CHENNAI – 600 034
... Answer any two of the following, each within 1500 words; Draw diagrams wherever necessary: (2x20= 40 marks) 26. Elaborate on pH scale and pH meter. Add a note on Henderson Hasselbalch equation. 27. Write in detail about the steps involved in synthesis and degradation of fatty acids. 28. Analyze biom ...
... Answer any two of the following, each within 1500 words; Draw diagrams wherever necessary: (2x20= 40 marks) 26. Elaborate on pH scale and pH meter. Add a note on Henderson Hasselbalch equation. 27. Write in detail about the steps involved in synthesis and degradation of fatty acids. 28. Analyze biom ...
Fatty acid synthesis

Fatty acid synthesis is the creation of fatty acids from acetyl-CoA and malonyl-CoA precursors through action of enzymes called fatty acid synthases. It is an important part of the lipogenesis process, which – together with glycolysis – functions to create fats from blood sugar in living organisms.