Oxidation and Synthesis of Fatty Acids in Soluble Enzyme Systems
... some member of the citric acid cycle is undergoing oxidation simultaneously fatty acid oxidation does not start (Table 2). Members of the citric acid cycle or substances which give rise to members of the cycle are referred to as sparkers since their oxidation sparks the oxidatioi of fatty acids. The ...
... some member of the citric acid cycle is undergoing oxidation simultaneously fatty acid oxidation does not start (Table 2). Members of the citric acid cycle or substances which give rise to members of the cycle are referred to as sparkers since their oxidation sparks the oxidatioi of fatty acids. The ...
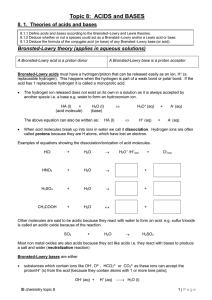
Topic 8: ACIDS and BASES
... positive ions like the H+ which never exists on its own and either reacts with water to form H3O+ or with a another base to form water. Other examples include CH3+ and Br+ (Hal+) which you will study in organic chemistry. molecules containing positive centres (mostly organic molecules) as a res ...
... positive ions like the H+ which never exists on its own and either reacts with water to form H3O+ or with a another base to form water. Other examples include CH3+ and Br+ (Hal+) which you will study in organic chemistry. molecules containing positive centres (mostly organic molecules) as a res ...
Citric Acid Cycle
... 1. Oxidation of 2o alcohol at C2 to a ketone to form oxalosuccinate (betaketo acid), and reduction of NAD+ to NADH 2. Next undergoes b-decarboxylation of carboxylate (beta) to ketone at C2 3. Mn2+ stabilizes enolate O-, which protonates to enol then tautomerizes to more stable ketone forming a-ketog ...
... 1. Oxidation of 2o alcohol at C2 to a ketone to form oxalosuccinate (betaketo acid), and reduction of NAD+ to NADH 2. Next undergoes b-decarboxylation of carboxylate (beta) to ketone at C2 3. Mn2+ stabilizes enolate O-, which protonates to enol then tautomerizes to more stable ketone forming a-ketog ...
Effect of salinity on growth of green alga Botryococcus braunii and
... the precursor of the non-isoprenoid hydrocarbons produced by the race A. Laureillard et al. (1988) reported that oleic acid was involved in the formation of very long chain fatty acid derivatives through chain elongation. It is also a precursor of PRB A and PRB B resistant biopolymer present in the ...
... the precursor of the non-isoprenoid hydrocarbons produced by the race A. Laureillard et al. (1988) reported that oleic acid was involved in the formation of very long chain fatty acid derivatives through chain elongation. It is also a precursor of PRB A and PRB B resistant biopolymer present in the ...
The investigation of enzymes structure, physical
... Thousands of proteins present in the human body perform functions too numerous to list. These include serving as carriers of vitamins, oxygen, and carbon dioxide plus structural, kinetic, catalytic, and signaling roles. It thus is not surprising that dire consequences can arise from mutations either ...
... Thousands of proteins present in the human body perform functions too numerous to list. These include serving as carriers of vitamins, oxygen, and carbon dioxide plus structural, kinetic, catalytic, and signaling roles. It thus is not surprising that dire consequences can arise from mutations either ...
Glycolysis and gluconeogenesis
... All three isozymes of pyruvate kinase are allosterically inhibited by ATP, acetyl-CoA and long chain fatty acids (all signs of an abundant energy supply). The liver isoenzyme (L form), but not the muscle isoenzyme (M form) is further regulated by phosphorylation. When the glucose level in blood decr ...
... All three isozymes of pyruvate kinase are allosterically inhibited by ATP, acetyl-CoA and long chain fatty acids (all signs of an abundant energy supply). The liver isoenzyme (L form), but not the muscle isoenzyme (M form) is further regulated by phosphorylation. When the glucose level in blood decr ...
BIO 101 Worksheet Metabolism and Cellular Respiration
... 7. _______ Water is produced in oxidative phosphorylation 8. _______ ATP is broken down to 34 ADP + 34 P in oxidative phosphorylation 9. _______ATP is synthesized by a ATP synthase 10. _______ ATP synthase requires H+ ions to operate 11. _______ The total amount of ATP produced by all cellular respi ...
... 7. _______ Water is produced in oxidative phosphorylation 8. _______ ATP is broken down to 34 ADP + 34 P in oxidative phosphorylation 9. _______ATP is synthesized by a ATP synthase 10. _______ ATP synthase requires H+ ions to operate 11. _______ The total amount of ATP produced by all cellular respi ...
CELLULAR RESPIRATION
... Electron acceptors in the chain accept NADH/FADH2 electrons. As electrons pass down a series of molecules to O2 – the O2 combines with H atoms to form H2O and ATP. YIELD: 10 NADH converts to 30 ATP, 2 FADH2 converts to 4 ATP Remember – FADH produces 2 ATP, NADH produces 3 ATP ...
... Electron acceptors in the chain accept NADH/FADH2 electrons. As electrons pass down a series of molecules to O2 – the O2 combines with H atoms to form H2O and ATP. YIELD: 10 NADH converts to 30 ATP, 2 FADH2 converts to 4 ATP Remember – FADH produces 2 ATP, NADH produces 3 ATP ...
NME2.31 - Energy Production
... The TCA cycle takes place inside the mitochondria of most cells o Involves a sequence of 8 reactions o Aerobic but does not directly require (gaseous) oxygen; uses water molecules Acetyl-CoA is fully oxidised to form CO2 and various energy-rich carrier molecules (e.g. NADH, FADH2) o Each cycle produ ...
... The TCA cycle takes place inside the mitochondria of most cells o Involves a sequence of 8 reactions o Aerobic but does not directly require (gaseous) oxygen; uses water molecules Acetyl-CoA is fully oxidised to form CO2 and various energy-rich carrier molecules (e.g. NADH, FADH2) o Each cycle produ ...
HL Construct your own polypeptide
... Today you have been given a challenging task. Can you construct a polypeptide and fold it into a quaternary structure? You will be given a fictional ‘protein’ to construct that is 10 amino acids in length You will need to show all 4 stages of folding (primary, secondary both beta sheet and alpha hel ...
... Today you have been given a challenging task. Can you construct a polypeptide and fold it into a quaternary structure? You will be given a fictional ‘protein’ to construct that is 10 amino acids in length You will need to show all 4 stages of folding (primary, secondary both beta sheet and alpha hel ...
Cell Respiration
... do this, pyruvate is combined a helper called “co-enzyme A” (CoA) to form a compound called Acetyl-CoA. We must release CO2 to do this and release some hydrogen so allow different NAD+ to pick them up as NADH. • This binding to co-enzyme A (CoA) accomplishes 2 important things, 1-it increases the pe ...
... do this, pyruvate is combined a helper called “co-enzyme A” (CoA) to form a compound called Acetyl-CoA. We must release CO2 to do this and release some hydrogen so allow different NAD+ to pick them up as NADH. • This binding to co-enzyme A (CoA) accomplishes 2 important things, 1-it increases the pe ...
Allessan® CAP - Corden Pharma
... Allessan®CAP as a water scavenger agent: Allessan®CAP is a pH neutral dehydration reagent, similar in strenghth to the highly reactive and hazardous phosphorous pentoxid and polyphosphoric acid, alternative to molecular sieves for water removal from organic solvents and providing Lewis acid catalys ...
... Allessan®CAP as a water scavenger agent: Allessan®CAP is a pH neutral dehydration reagent, similar in strenghth to the highly reactive and hazardous phosphorous pentoxid and polyphosphoric acid, alternative to molecular sieves for water removal from organic solvents and providing Lewis acid catalys ...
Fundamentals of Biochemistry. Life at the Molecular Level. 3rd Edition Brochure
... A. Pyruvate Dehydrogenase Is a Multienzyme Complex B. The Pyruvate Dehydrogenase Complex Catalyzes Five Reactions 3. Enzymes of the Citric Acid Cycle A. Citrate Synthase Joins an Acetyl Group to Oxaloacetate B. Aconitase Interconverts Citrate and Isocitrate C. NAD+-Dependent Isocitrate Dehydrogenase ...
... A. Pyruvate Dehydrogenase Is a Multienzyme Complex B. The Pyruvate Dehydrogenase Complex Catalyzes Five Reactions 3. Enzymes of the Citric Acid Cycle A. Citrate Synthase Joins an Acetyl Group to Oxaloacetate B. Aconitase Interconverts Citrate and Isocitrate C. NAD+-Dependent Isocitrate Dehydrogenase ...
File ch 14 ppt1
... Conjugate Acids and Bases, continued Strength of Conjugate Acids and Bases • The stronger an acid is, the weaker its conjugate base • The stronger a base is, the weaker its conjugate acid HCl(g ) + H2O(l ) H3O (aq ) + Cl– (aq ) strong acid ...
... Conjugate Acids and Bases, continued Strength of Conjugate Acids and Bases • The stronger an acid is, the weaker its conjugate base • The stronger a base is, the weaker its conjugate acid HCl(g ) + H2O(l ) H3O (aq ) + Cl– (aq ) strong acid ...
amino-terminal
... • A multimer with just a few subunits is often called an oligomer. • The repeating structural unit in such a multimeric protein, whether it is a single subunit or a group of subunits, is called a protomer. • The first oligomeric protein for which the three dimensional structure was determined was he ...
... • A multimer with just a few subunits is often called an oligomer. • The repeating structural unit in such a multimeric protein, whether it is a single subunit or a group of subunits, is called a protomer. • The first oligomeric protein for which the three dimensional structure was determined was he ...
13synthesis
... Biosynthesis and degradation of TG are regulated reciprocally. Depending on the metabolic recourses and requirements ...
... Biosynthesis and degradation of TG are regulated reciprocally. Depending on the metabolic recourses and requirements ...
Document
... phosphodiester bond? What is meant by the 5' and 3' ends of DNA and RNA? 4. Memorize the structure of the nucleotide ATP. This is a very important molecule and we will discuss it in great detail throughout the semester. 5. Know the purines and pyrimidines. Know the number of rings in each. What is t ...
... phosphodiester bond? What is meant by the 5' and 3' ends of DNA and RNA? 4. Memorize the structure of the nucleotide ATP. This is a very important molecule and we will discuss it in great detail throughout the semester. 5. Know the purines and pyrimidines. Know the number of rings in each. What is t ...
Lecture 1 - Columbus Labs
... dynamics of membrane proteins involved in bacterial pathogenesis using NMR, EPR, and Xray crystallographic techniques. ...
... dynamics of membrane proteins involved in bacterial pathogenesis using NMR, EPR, and Xray crystallographic techniques. ...
milliliters per liter. After 5-day-old cultures wvere
... greatest N15 enrichment. The amino group of glutamine and glutamic acid had the next highest N15 content while that of alanine was lower. These re- ...
... greatest N15 enrichment. The amino group of glutamine and glutamic acid had the next highest N15 content while that of alanine was lower. These re- ...
Document
... • Maple syrup urine disease (branched-chain ketonuria) – α-keto acid decarboxylase complex – Plasma and urinary levels of leucine, isoleucine, valine, α-keto acids, and α-hydroxy acids (reduced α-keto acids) are elevated ...
... • Maple syrup urine disease (branched-chain ketonuria) – α-keto acid decarboxylase complex – Plasma and urinary levels of leucine, isoleucine, valine, α-keto acids, and α-hydroxy acids (reduced α-keto acids) are elevated ...
PDF - Biochemical Journal
... and distillationi. By means of this isotope-dilution but PMA (0.5 m-mole/g. of protein) inhibits below method, the true chloride contents of biological pH 7-9 and accelerates above. Both raise the samples were measured with a coefficient of optimal pH. At pH 8-5 ADP and PMA in the variation of ± 0.6 ...
... and distillationi. By means of this isotope-dilution but PMA (0.5 m-mole/g. of protein) inhibits below method, the true chloride contents of biological pH 7-9 and accelerates above. Both raise the samples were measured with a coefficient of optimal pH. At pH 8-5 ADP and PMA in the variation of ± 0.6 ...
Notes - The University of Sydney
... average of these 2 pKas: (2.2 + 9.6)/2 = 5.9. The same process can be applied to the other uncharged amino acids; they will all have similar pIs. The pI alters dramatically when the amino acid has a charged side chain ie aspartate, glutamate, histidine, arginine and lysine. In the case of the acidic ...
... average of these 2 pKas: (2.2 + 9.6)/2 = 5.9. The same process can be applied to the other uncharged amino acids; they will all have similar pIs. The pI alters dramatically when the amino acid has a charged side chain ie aspartate, glutamate, histidine, arginine and lysine. In the case of the acidic ...
Determination and changes of free amino acids in royal
... 3.2. Gas chromatography (GC) and mass fragmentation of the derivatized free amino acids Although performing ion exchange chromatography, the eluate was rich in short chain free fatty acids, which represented 80% of the lipid fraction of RJ. The efficiency of ion exchange chromatography was evaluated ...
... 3.2. Gas chromatography (GC) and mass fragmentation of the derivatized free amino acids Although performing ion exchange chromatography, the eluate was rich in short chain free fatty acids, which represented 80% of the lipid fraction of RJ. The efficiency of ion exchange chromatography was evaluated ...
Biochemistry of Nervous System
... Regeneration of oxalacetate is necessary for oxidation of acetyl CoA & this is performed by two major anaplerotic pathways: 1- Degradation of isoleucine & valine amino acids to butyric succinyl CoA, which yields oxalacetate. This reaction requires vitamin B12 (coenzyme for methylmalonyl CoA mutase) ...
... Regeneration of oxalacetate is necessary for oxidation of acetyl CoA & this is performed by two major anaplerotic pathways: 1- Degradation of isoleucine & valine amino acids to butyric succinyl CoA, which yields oxalacetate. This reaction requires vitamin B12 (coenzyme for methylmalonyl CoA mutase) ...
2.3 Carbon-Based Molecules TEKS 9A
... • Carbohydrates can be broken down to provide energy for cells. • Some carbohydrates are part of cell structure. Polymer (starch) Starch is a polymer of glucose monomers that often has a branched structure. ...
... • Carbohydrates can be broken down to provide energy for cells. • Some carbohydrates are part of cell structure. Polymer (starch) Starch is a polymer of glucose monomers that often has a branched structure. ...
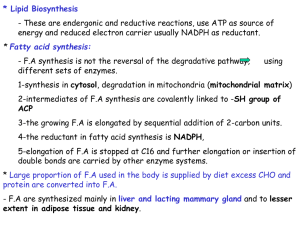
Fatty acid synthesis

Fatty acid synthesis is the creation of fatty acids from acetyl-CoA and malonyl-CoA precursors through action of enzymes called fatty acid synthases. It is an important part of the lipogenesis process, which – together with glycolysis – functions to create fats from blood sugar in living organisms.