
Chapter 14 Review Question Answers
... Valproate is a potent inhibitor of epoxide hydrolase and UDP-glucuronyl transferase (the enzymes needed for the glucuronidation of many drug molecules). Inhibition of epoxide hydrolase by valproate prolongs the biological half-life of the arene oxide intermediate and thus increases phenytoin-induced ...
... Valproate is a potent inhibitor of epoxide hydrolase and UDP-glucuronyl transferase (the enzymes needed for the glucuronidation of many drug molecules). Inhibition of epoxide hydrolase by valproate prolongs the biological half-life of the arene oxide intermediate and thus increases phenytoin-induced ...
REVIEW: Bio 139 Lab Practical #1 All labs from beginning of the
... pH indicator: yellow = acid; red/brick red = alkaline. Carbohydrate fermentation produces acids; aerobic respiration raises the pH. Results expressed as slant/butt A = acid; K = alkaline. A/A = ferments glucose, AND either sucrose or lactose or both. K/A = ferments glucose only. K/K = no fermentatio ...
... pH indicator: yellow = acid; red/brick red = alkaline. Carbohydrate fermentation produces acids; aerobic respiration raises the pH. Results expressed as slant/butt A = acid; K = alkaline. A/A = ferments glucose, AND either sucrose or lactose or both. K/A = ferments glucose only. K/K = no fermentatio ...
File
... • If you add a polar substance to a polar liquid, they will mix. • If you add a non-polar substance to a polar liquid, they will not mix. – Ex. Water and oil ...
... • If you add a polar substance to a polar liquid, they will mix. • If you add a non-polar substance to a polar liquid, they will not mix. – Ex. Water and oil ...
2012 jf lecture 2.pptx
... • PAH converts the essential amino acid phenylalanine to other essential amino acids eg tyrosine. • Lack of PAH causes phenylalanine accumulation, lack of tyrosine – normal at birth with gradual loss of mental function, severe learning disabilities and seizures • Treatment: intake of phenylalanin ...
... • PAH converts the essential amino acid phenylalanine to other essential amino acids eg tyrosine. • Lack of PAH causes phenylalanine accumulation, lack of tyrosine – normal at birth with gradual loss of mental function, severe learning disabilities and seizures • Treatment: intake of phenylalanin ...
Nucleotides, Vitamins, Cosubstrates, and Coenzymes
... the cell (ATP). All Nucleotides are composed of / release upon hydrolysis: • A Heterocyclic amine. The nitrogens of the molecule can have basic properties. • An aldopentose sugar - Ribose or 2-Deoxyribose. • One or more phosphate(s). The heterocyclic base is linked to C-1 of the ribose or deoxyribos ...
... the cell (ATP). All Nucleotides are composed of / release upon hydrolysis: • A Heterocyclic amine. The nitrogens of the molecule can have basic properties. • An aldopentose sugar - Ribose or 2-Deoxyribose. • One or more phosphate(s). The heterocyclic base is linked to C-1 of the ribose or deoxyribos ...
Modern applications of amino acids and dipeptides
... be added separately as an additional reactor feed. This stability problem also prevents sterilization by heat treatment and requires l-glutamine to be sterile filtered into an autoclaved medium. One solution to these problems is to use simple dipeptides instead of the component amino acids. The dipe ...
... be added separately as an additional reactor feed. This stability problem also prevents sterilization by heat treatment and requires l-glutamine to be sterile filtered into an autoclaved medium. One solution to these problems is to use simple dipeptides instead of the component amino acids. The dipe ...
What are proteins?
... Proteins are organic compounds. Proteins contain the following elements: carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen, as well as nitrogen. Proteins are made of many units called amino acids. Amino acids are compounds with an amino group (NH2) on one end and a carboxyl group (-COOH) on the other end. There are 20 ...
... Proteins are organic compounds. Proteins contain the following elements: carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen, as well as nitrogen. Proteins are made of many units called amino acids. Amino acids are compounds with an amino group (NH2) on one end and a carboxyl group (-COOH) on the other end. There are 20 ...
Bioelectrochemical Determination of Citric Acid in Real Samples
... better mixing with the sample solution. In the absence of TPP no response was observed while for concentrations higher than 0.8 mm TPP the response became constant; subsequent work used 1mM TPP. Several cations were examined as activators of POD. In addition to sensitivity, the criterion for the fin ...
... better mixing with the sample solution. In the absence of TPP no response was observed while for concentrations higher than 0.8 mm TPP the response became constant; subsequent work used 1mM TPP. Several cations were examined as activators of POD. In addition to sensitivity, the criterion for the fin ...
Regulation of Elovl and fatty acid metabolism
... Fatty acids taken up from the diet as well as a significant amount of the fatty acids produced by FAS, undergo further elongation into long chain fatty acids (LCFA > C18) and very long chain fatty acids (VLCFA > C20). As early as in the nineteen sixties, Nugteren made significant advances in the rat ...
... Fatty acids taken up from the diet as well as a significant amount of the fatty acids produced by FAS, undergo further elongation into long chain fatty acids (LCFA > C18) and very long chain fatty acids (VLCFA > C20). As early as in the nineteen sixties, Nugteren made significant advances in the rat ...
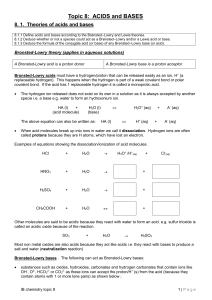
Topic 8: ACIDS and BASES
... positive ions like the H+ which never exists on its own and either reacts with water to form H3O+ or with a another base to form water. Other examples include CH3+ and Br+ (Hal+) which you will study in organic chemistry. molecules containing positive centres (mostly organic molecules) as a res ...
... positive ions like the H+ which never exists on its own and either reacts with water to form H3O+ or with a another base to form water. Other examples include CH3+ and Br+ (Hal+) which you will study in organic chemistry. molecules containing positive centres (mostly organic molecules) as a res ...
Modeling with Toobers
... Protein Modeling Using Toobers (or Pipe Cleaners) Draw two amino acids forming the peptide bond in the space below. You can denote the side chains of these amino acids as R1 and R2. ...
... Protein Modeling Using Toobers (or Pipe Cleaners) Draw two amino acids forming the peptide bond in the space below. You can denote the side chains of these amino acids as R1 and R2. ...
File - Wk 1-2
... opposite direction to increase blood glucose concentration to normal. Insulin:glucagon ratio is low and when <0.5 (due to ↑glucagon and ↓insulin) ↑ glycogenolysis ↑ aa metabolism ↑ gluconeogenesis ↑ lipolysis Under most normal conditions, the insulin feedback mechanism is much more importa ...
... opposite direction to increase blood glucose concentration to normal. Insulin:glucagon ratio is low and when <0.5 (due to ↑glucagon and ↓insulin) ↑ glycogenolysis ↑ aa metabolism ↑ gluconeogenesis ↑ lipolysis Under most normal conditions, the insulin feedback mechanism is much more importa ...
Document
... synthesis by inhibiting an early step (usually the first “committed” step (unique to the pathway) ...
... synthesis by inhibiting an early step (usually the first “committed” step (unique to the pathway) ...
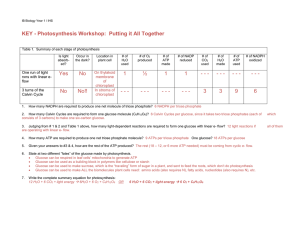
KEY - Photosynthesis Workshop: Putting it All Together
... 2. How many Calvin Cycles are required to form one glucose molecule (C6H12O6)? 6 Calvin Cycles per glucose, since it takes two triose phosphates (each of consists of 3 carbons) to make one six-carbon glucose. ...
... 2. How many Calvin Cycles are required to form one glucose molecule (C6H12O6)? 6 Calvin Cycles per glucose, since it takes two triose phosphates (each of consists of 3 carbons) to make one six-carbon glucose. ...
Document
... Glucose (C6H12O6) + 2 ADP + 2 Pi + 2 NAD+ (cytoplasm) + 8 NAD+ + 2 FAD + 2 GDP + 2Pi + 2 H2O (mitochondria) ...
... Glucose (C6H12O6) + 2 ADP + 2 Pi + 2 NAD+ (cytoplasm) + 8 NAD+ + 2 FAD + 2 GDP + 2Pi + 2 H2O (mitochondria) ...
Preparation of pyruvate for the citric acid cycle Recap 1. We have
... Aerobic conditions 1. Converts to acetyl CoA (by pyruvate dehydrogenase) for use in the TCA cycle and oxidative phosphorylation (leads to more ATP production) 2. Converts to oxaloacetate , which can then shuttle into the synthesize glucose (can also be done from lactate) Anaerobic conditions 3. It i ...
... Aerobic conditions 1. Converts to acetyl CoA (by pyruvate dehydrogenase) for use in the TCA cycle and oxidative phosphorylation (leads to more ATP production) 2. Converts to oxaloacetate , which can then shuttle into the synthesize glucose (can also be done from lactate) Anaerobic conditions 3. It i ...
Purine and pyrimidi..
... AMP or GMP is metabolized to give hypoxanthine which is then converted into xanthine and finally into uric acid as in the next slide. Most of uric acid is excreted by the kidney. The remaining uric acid travels through the intestines, where bacteria help break it down. Normally these actions keep th ...
... AMP or GMP is metabolized to give hypoxanthine which is then converted into xanthine and finally into uric acid as in the next slide. Most of uric acid is excreted by the kidney. The remaining uric acid travels through the intestines, where bacteria help break it down. Normally these actions keep th ...
Chapter 21
... oxygen in blood (four molecules of O2). • CO is poisonous because it binds 200 times more strongly to the Fe2+ than does O2 (Cells can die from lack of O2). ...
... oxygen in blood (four molecules of O2). • CO is poisonous because it binds 200 times more strongly to the Fe2+ than does O2 (Cells can die from lack of O2). ...
The Citric Acid Cycle
... Stage I All the fuel molecules are oxidized to generate a common two-carbon unit, acetyl-CoA. Stage II The acetyl-CoA is completely oxidized into CO2, with electrons collected by NAD+ and FAD via a cyclic pathway (the citric acid cycle, Krebs cycle, or tricarboxylic acid cycle). Stage III Electr ...
... Stage I All the fuel molecules are oxidized to generate a common two-carbon unit, acetyl-CoA. Stage II The acetyl-CoA is completely oxidized into CO2, with electrons collected by NAD+ and FAD via a cyclic pathway (the citric acid cycle, Krebs cycle, or tricarboxylic acid cycle). Stage III Electr ...
Transcriptome analysis reveals unique C4
... green microalga species of Trebouxiophyceae [9], has recently been reported to accumulate an unprecedentedly high amount of ArA-rich triacylglycerols (TAG) in cytoplasmic lipid bodies [10]. When M. incisa was cultured under nitrogen starvation for 27 d, its ArA content increased from 1.9% to 7.0% of ...
... green microalga species of Trebouxiophyceae [9], has recently been reported to accumulate an unprecedentedly high amount of ArA-rich triacylglycerols (TAG) in cytoplasmic lipid bodies [10]. When M. incisa was cultured under nitrogen starvation for 27 d, its ArA content increased from 1.9% to 7.0% of ...
Amino acids [qualitative tests]
... 1.Ninhydrin (triketohydrindene hydrate) degrades amino acids into aldehydes (on pH range 4-8), ammonia and CO2 though a series of reactions. 2.Ninhydrin then condenses with ammonia and hydrindantin to produce an intensely blue or purple pigment, sometimes called ruhemann's purple ...
... 1.Ninhydrin (triketohydrindene hydrate) degrades amino acids into aldehydes (on pH range 4-8), ammonia and CO2 though a series of reactions. 2.Ninhydrin then condenses with ammonia and hydrindantin to produce an intensely blue or purple pigment, sometimes called ruhemann's purple ...
College Accounting: A Practical Approach, Cdn
... Chapter 5: Introduction to Proteins: The Primary Level of Protein Structure ...
... Chapter 5: Introduction to Proteins: The Primary Level of Protein Structure ...
Final Exam Revision Answers 2009
... species (A – E) below. Choose the correct answer from “A – E” (questions #26-28). Note: “EtOH – E” may be used more than once. ...
... species (A – E) below. Choose the correct answer from “A – E” (questions #26-28). Note: “EtOH – E” may be used more than once. ...
X-ray Crystallographic Structure of Ibuprofen Bound to Human
... adipocytes. The role of serum albumin in the uptake of long- chain fatty acids has been assumed to be the solubilization of fatty acid in the aqueous environment. Serum albumin provides a reservoir of bound fatty acid to replenish uncomplexed fatty acid, degraded by cellular uptake. he experiment wa ...
... adipocytes. The role of serum albumin in the uptake of long- chain fatty acids has been assumed to be the solubilization of fatty acid in the aqueous environment. Serum albumin provides a reservoir of bound fatty acid to replenish uncomplexed fatty acid, degraded by cellular uptake. he experiment wa ...
Fatty acid synthesis

Fatty acid synthesis is the creation of fatty acids from acetyl-CoA and malonyl-CoA precursors through action of enzymes called fatty acid synthases. It is an important part of the lipogenesis process, which – together with glycolysis – functions to create fats from blood sugar in living organisms.


















![Amino acids [qualitative tests]](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/008282328_1-c8bb4ef27caebe478c13494a7af59cc2-300x300.png)


