5 carbohydrates and the Krebs Cycle
... o Embden-Meyerhof pathway produces 4 mol of ATP per mol of glucose, and uses up 1 mol. The end product is phosphoglyceraldehyde o This is an ANAEROBIC process o Thus, there is a net gain of 3 mol of ATP o However, when the glucose enters the cell, phosphorylating it takes 1 mol of ATP o Thus, for ...
... o Embden-Meyerhof pathway produces 4 mol of ATP per mol of glucose, and uses up 1 mol. The end product is phosphoglyceraldehyde o This is an ANAEROBIC process o Thus, there is a net gain of 3 mol of ATP o However, when the glucose enters the cell, phosphorylating it takes 1 mol of ATP o Thus, for ...
Test 1
... exported out of cell smooth ER - membrane sac distal from rough Er, proteins inside Er have now been synthesized and are now being processed, lipid synthesis. Golgi apparatus - used in final processing of secretory proteins Peroxisome - membrane bound organelle used to isolate chemical reaction invo ...
... exported out of cell smooth ER - membrane sac distal from rough Er, proteins inside Er have now been synthesized and are now being processed, lipid synthesis. Golgi apparatus - used in final processing of secretory proteins Peroxisome - membrane bound organelle used to isolate chemical reaction invo ...
History of Fermentation Processes and Their Fundamental
... Energy of organic molecules is not useable to living organisms—requires conversion into the “currency” of the cell, ATP, adenosine triphosphate ...
... Energy of organic molecules is not useable to living organisms—requires conversion into the “currency” of the cell, ATP, adenosine triphosphate ...
Protein Folding and The Impact of Mutations
... Cysteines are one of the 20 amino acids Cysteines are like the obnoxious couples that are always together – they can’t stand to be apart Two cysteines will always move closer to each other When they move close, they will form what is called a “disulfide bond” or “disulfide bridge” ...
... Cysteines are one of the 20 amino acids Cysteines are like the obnoxious couples that are always together – they can’t stand to be apart Two cysteines will always move closer to each other When they move close, they will form what is called a “disulfide bond” or “disulfide bridge” ...
HEALTHCARE PROFESSIONAL - Council for Bile Acid Deficiency
... indentified. Patients may present with neonatal cholestasis, neurologic disease or fat and fat-soluble vitamin malabsorption. If untreated, progressive liver disease may develop or reduced intestinal bile acid concentrations may lead to serious morbidity or mortality (Heubi et al., 2007). Disorders ...
... indentified. Patients may present with neonatal cholestasis, neurologic disease or fat and fat-soluble vitamin malabsorption. If untreated, progressive liver disease may develop or reduced intestinal bile acid concentrations may lead to serious morbidity or mortality (Heubi et al., 2007). Disorders ...
Lecture Notes
... – An amino acid that contains a __________ carboxyl group in its side chain – R = –CH2COOH, or -COOH ...
... – An amino acid that contains a __________ carboxyl group in its side chain – R = –CH2COOH, or -COOH ...
Amino acid a
... • The name and abbreviation of amino acids – All the AAs were given a trivial (common) name. • Glutamate from wheat gluten. • Tyrosine from cheese (“tyros” in Greek). – Each AA is given a 3 letter abbreviation and 1 ...
... • The name and abbreviation of amino acids – All the AAs were given a trivial (common) name. • Glutamate from wheat gluten. • Tyrosine from cheese (“tyros” in Greek). – Each AA is given a 3 letter abbreviation and 1 ...
Fuel Metabolism PART 1: Structure and Function of Protein
... that transfers the acetyl group to coenzyme A, and a dihydrolipoyl dehydrogenase that reoxidizes lipoic acid. Thiamine pyrophosphate, lipoic acid, coenzyme A, NAD+, and FAD serve as cofactors for these reactions. In addition, a kinase is present that phosphorylates and inactivates the decarboxylase ...
... that transfers the acetyl group to coenzyme A, and a dihydrolipoyl dehydrogenase that reoxidizes lipoic acid. Thiamine pyrophosphate, lipoic acid, coenzyme A, NAD+, and FAD serve as cofactors for these reactions. In addition, a kinase is present that phosphorylates and inactivates the decarboxylase ...
Effect of Systemic Fungicide on Nucleic Acid, Amino Acid and
... control. Amino acids such as glycine, asparagines, alanine, methionine, phenyl.alanine were found in both control and treated plants. While cystein, proline, tryptophane and valine were observed in appreciable amount in treated samples as compare to control after first and second spray. Reduction in ...
... control. Amino acids such as glycine, asparagines, alanine, methionine, phenyl.alanine were found in both control and treated plants. While cystein, proline, tryptophane and valine were observed in appreciable amount in treated samples as compare to control after first and second spray. Reduction in ...
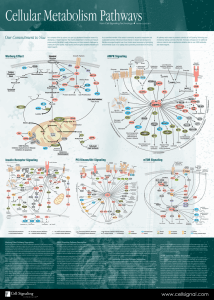
Cellular Metabolism Pathways
... Cancer cells frequently use glutamine as a secondary fuel source, which enters the mitochondria and can be used to replenish Krebs Cycle intermediates or can be used to produce more pyruvate through the action of malic enzyme. Highly proliferative cells need to produce excess lipid, nucleotide, and ...
... Cancer cells frequently use glutamine as a secondary fuel source, which enters the mitochondria and can be used to replenish Krebs Cycle intermediates or can be used to produce more pyruvate through the action of malic enzyme. Highly proliferative cells need to produce excess lipid, nucleotide, and ...
Chemical Nature of the Amino Acids
... relevant to the make-up of mammalian proteins (see below). Several other amino acids are found in the body free or in combined states (i.e. not associated with peptides or proteins). These non-protein associated amino acids perform specialized functions. Several of the amino acids found in proteins ...
... relevant to the make-up of mammalian proteins (see below). Several other amino acids are found in the body free or in combined states (i.e. not associated with peptides or proteins). These non-protein associated amino acids perform specialized functions. Several of the amino acids found in proteins ...
Chapter 1
... Hepatic Catabolism & Uses of Sulfur (S)-Containing Amino Acids • Cysteine – Used for protein & glutathione synthesis – Converted to cysteine sulfinate, used to produce taurine – Taurine important in retina, functions as bile salt & inhibitory neurotransmitter – Cysteine degradation yields pyruvate ...
... Hepatic Catabolism & Uses of Sulfur (S)-Containing Amino Acids • Cysteine – Used for protein & glutathione synthesis – Converted to cysteine sulfinate, used to produce taurine – Taurine important in retina, functions as bile salt & inhibitory neurotransmitter – Cysteine degradation yields pyruvate ...
Lesson on Proteins
... They are made from repeating sub-units that are linked together. Why do peptide chains fold? They want to achieve their most relaxed state Explain how humans can have fewer genes for proteins than some insects and yet still be more complex? We have several quaternary proteins. By combing 2 or more p ...
... They are made from repeating sub-units that are linked together. Why do peptide chains fold? They want to achieve their most relaxed state Explain how humans can have fewer genes for proteins than some insects and yet still be more complex? We have several quaternary proteins. By combing 2 or more p ...
Glycolysis
... What do we need to accomplish the oxidation of pyruvate? • NAD+ and FAD+; each can carry 2 e• oxygen; needs 2 e- to fill outer valence shell of electrons ...
... What do we need to accomplish the oxidation of pyruvate? • NAD+ and FAD+; each can carry 2 e• oxygen; needs 2 e- to fill outer valence shell of electrons ...
www.studyguide.pk
... (c) Alanine reacts with both acids and bases. Write an equation for the reaction between alanine and sodium hydroxide, drawing the displayed formula of the organic product. ...
... (c) Alanine reacts with both acids and bases. Write an equation for the reaction between alanine and sodium hydroxide, drawing the displayed formula of the organic product. ...
Amino Acids
... Disruption of the disulfide bonds may change the three-dimensional structure of the proteins so that they lose their bioactivity (such as trypsin inhibition activity or potential ...
... Disruption of the disulfide bonds may change the three-dimensional structure of the proteins so that they lose their bioactivity (such as trypsin inhibition activity or potential ...
Multiple Choice Review- Photosynthesis and Cellular Respiration
... b. NADH donates electrons to the electron transport chain c. Starts with glucose d. Carried out by yeast 11. In which stage of aerobic cellular respiration is glucose broken down into two molecules of pyruvate? a. Oxidative Phosphorylation b. Citric Acid Cycle c. Pyruvate Dehydrogenase Complex d. Gl ...
... b. NADH donates electrons to the electron transport chain c. Starts with glucose d. Carried out by yeast 11. In which stage of aerobic cellular respiration is glucose broken down into two molecules of pyruvate? a. Oxidative Phosphorylation b. Citric Acid Cycle c. Pyruvate Dehydrogenase Complex d. Gl ...
Translation Notes
... – Organisms use 20 different amino acids to build proteins – Your body makes 12, others come from food you eat ...
... – Organisms use 20 different amino acids to build proteins – Your body makes 12, others come from food you eat ...
Plant Lipoxygenases. Physiological and Molecular Features
... most common substrates for LOX (Siedow, 1991). Oxygen can be added to either end of the pentadiene system (regiospecificity). In the case of linoleic or linolenic acids, this leads to two possible products, the 9- and 13-hydroperoxy fatty acids (Siedow, 1991). In vitro, most LOXs prefer free fatty a ...
... most common substrates for LOX (Siedow, 1991). Oxygen can be added to either end of the pentadiene system (regiospecificity). In the case of linoleic or linolenic acids, this leads to two possible products, the 9- and 13-hydroperoxy fatty acids (Siedow, 1991). In vitro, most LOXs prefer free fatty a ...
Biochemistry
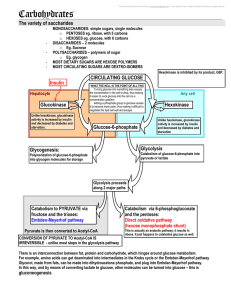
... oligosaccharides, polysaccharides, glycoconjugates (3) Physiologic significance of carbohydrates: major source of energy, provide materials for synthesis of other substance, serve as the structural components. (4) Digestion and absorption of carbohydrates (5) Main metabolic pathways of carbohydrate ...
... oligosaccharides, polysaccharides, glycoconjugates (3) Physiologic significance of carbohydrates: major source of energy, provide materials for synthesis of other substance, serve as the structural components. (4) Digestion and absorption of carbohydrates (5) Main metabolic pathways of carbohydrate ...
Cell Respiration - Glycolysis PPT
... Oxidation of Pyruvate to Acetyl CoA • Before the citric acid cycle can begin, pyruvate must be converted to acetyl Coenzyme A (acetyl CoA), which links glycolysis to the citric acid cycle • This step is carried out by a multienzyme complex that catalyzes three reactions ...
... Oxidation of Pyruvate to Acetyl CoA • Before the citric acid cycle can begin, pyruvate must be converted to acetyl Coenzyme A (acetyl CoA), which links glycolysis to the citric acid cycle • This step is carried out by a multienzyme complex that catalyzes three reactions ...
Cloning and sequence analysis of putative type II fatty
... KR) is the first reductive step. Two isozymes, FabA and FabZ (β-hydroxyacyl-ACP dehydratases, HD), catalyse the dehydration of β-hydroxyacyl-ACP to trans-2-acyl-ACP. FabA is a bifunctional enzyme involved in the introduction of a cis-double bond into the growing acyl chain (Heath and Rock 1996). The ...
... KR) is the first reductive step. Two isozymes, FabA and FabZ (β-hydroxyacyl-ACP dehydratases, HD), catalyse the dehydration of β-hydroxyacyl-ACP to trans-2-acyl-ACP. FabA is a bifunctional enzyme involved in the introduction of a cis-double bond into the growing acyl chain (Heath and Rock 1996). The ...
B2 - Enzymes
... to describe how enzymes are used everyday Starter: Which of these uses enzymes? ...
... to describe how enzymes are used everyday Starter: Which of these uses enzymes? ...
Fatty acid synthesis

Fatty acid synthesis is the creation of fatty acids from acetyl-CoA and malonyl-CoA precursors through action of enzymes called fatty acid synthases. It is an important part of the lipogenesis process, which – together with glycolysis – functions to create fats from blood sugar in living organisms.