Metabolism
... During the process 2 molecules of NAD+ are reduced to form 2 NADH and 2H+ (NAD+ is the oxidized form – less energy and NADH is the reduced form – more energy) Copyright © 2006 Pearson Education, Inc., publishing as Benjamin Cummings ...
... During the process 2 molecules of NAD+ are reduced to form 2 NADH and 2H+ (NAD+ is the oxidized form – less energy and NADH is the reduced form – more energy) Copyright © 2006 Pearson Education, Inc., publishing as Benjamin Cummings ...
The Structure and Function of Large Biological Molecules
... • Hydrogenating vegetable oils also creates unsaturated fats with trans double bonds • These trans fats may contribute more than saturated fats to cardiovascular disease ...
... • Hydrogenating vegetable oils also creates unsaturated fats with trans double bonds • These trans fats may contribute more than saturated fats to cardiovascular disease ...
B2 - Enzymes
... to describe how enzymes are used everyday Starter: Which of these uses enzymes? ...
... to describe how enzymes are used everyday Starter: Which of these uses enzymes? ...
Primary structure: the sequence of amino acids in a polypeptide chain
... Catalysts: virtually all reactions in living systems are catalyzed by proteins called enzymes Movement: muscles are made up of proteins called myosin and actin Transport: hemoglobin transports oxygen from the lungs to cells; other proteins transport molecules across cell membranes Hormones: many hor ...
... Catalysts: virtually all reactions in living systems are catalyzed by proteins called enzymes Movement: muscles are made up of proteins called myosin and actin Transport: hemoglobin transports oxygen from the lungs to cells; other proteins transport molecules across cell membranes Hormones: many hor ...
Chapter Nine - The Krebs Cycle
... • Hans Kreb discovered its cyclic nature • Goes by three names – Citric acid cycle – Tricarboxylic cycle – Krebs cycle ...
... • Hans Kreb discovered its cyclic nature • Goes by three names – Citric acid cycle – Tricarboxylic cycle – Krebs cycle ...
Introduction to: Cellular Respiration
... Like a bank, you put money in to earn interest. Net ATP gained per glucose molecule=2 ...
... Like a bank, you put money in to earn interest. Net ATP gained per glucose molecule=2 ...
3-3.1 Indole Alkaloids
... It causes vigorous contraction of the uterus. It is mainly used as an oxytocic in order to aid delivery or to prevent postpartum hemorrhage. ...
... It causes vigorous contraction of the uterus. It is mainly used as an oxytocic in order to aid delivery or to prevent postpartum hemorrhage. ...
bio II ch 8 brookings guided pp
... 2 NADH (glycolysis) → 6ATP 2 NADH (acetyl CoA) →6ATP 6 NADH (Kreb’s) → 18 ATP 2 FADH2 (Kreb’s) → 4 ATP 38 TOTAL ATP from 1 molecule of glucose (-2 ATP to transport 2 pyruvate into mitochondria) NET of 36 ATP ...
... 2 NADH (glycolysis) → 6ATP 2 NADH (acetyl CoA) →6ATP 6 NADH (Kreb’s) → 18 ATP 2 FADH2 (Kreb’s) → 4 ATP 38 TOTAL ATP from 1 molecule of glucose (-2 ATP to transport 2 pyruvate into mitochondria) NET of 36 ATP ...
2.3 Carbon-Based Molecules
... – All amino acids have similar structures. – Each amino acid monomer has a carbon that is bonded to four other parts. Three of these parts are the same in ALL amino acids: - A hydrogen atom - An amino group (NH2- a part that contains nitrogen (N)) - And a carboxyl group (COOH) ...
... – All amino acids have similar structures. – Each amino acid monomer has a carbon that is bonded to four other parts. Three of these parts are the same in ALL amino acids: - A hydrogen atom - An amino group (NH2- a part that contains nitrogen (N)) - And a carboxyl group (COOH) ...
detailed lecture outline
... reduction sequence, enough energy is released to support the synthesis of ATP from ADP. o The coenzyme FAD accepts two hydrogen atoms from the TCA cycle and in doing so gains two electrons. o The oxidized form of the coenzyme NAD has a positive charge o This coenzyme also gains two electrons as two ...
... reduction sequence, enough energy is released to support the synthesis of ATP from ADP. o The coenzyme FAD accepts two hydrogen atoms from the TCA cycle and in doing so gains two electrons. o The oxidized form of the coenzyme NAD has a positive charge o This coenzyme also gains two electrons as two ...
bioengineering 938 pantothenic acid – applications, synthesis and
... alanine, is over expressed (15). Over expression of FMS1 caused excess pantothenic acid to be excreted into the medium, whereas deletion mutants required βalanine or pantothenic acid for growth. White et al. concluded that yeast is naturally capable of pantothenic acid biosynthesis, and that β-alani ...
... alanine, is over expressed (15). Over expression of FMS1 caused excess pantothenic acid to be excreted into the medium, whereas deletion mutants required βalanine or pantothenic acid for growth. White et al. concluded that yeast is naturally capable of pantothenic acid biosynthesis, and that β-alani ...
5. TCA Cycle
... Central metabolic hub of cell TCA/Krebs Cycle is the final common pathway for the oxidation of fuel molecules (proteins, fatty acids, carbs) Important source of precursors ...
... Central metabolic hub of cell TCA/Krebs Cycle is the final common pathway for the oxidation of fuel molecules (proteins, fatty acids, carbs) Important source of precursors ...
Systems-level metabolic flux profiling identifies fatty acid synthesis as a target for anti-viral therapy.
... extent (Figs. 2e,f). This suggested that some of the carbon passing from glucose to citrate was redirected from the TCA cycle. Citrate, in addition to being a TCA cycle intermediate, also shuttles two carbon units from the mitochondrion to the cytosol, where they are used for fatty acid and choleste ...
... extent (Figs. 2e,f). This suggested that some of the carbon passing from glucose to citrate was redirected from the TCA cycle. Citrate, in addition to being a TCA cycle intermediate, also shuttles two carbon units from the mitochondrion to the cytosol, where they are used for fatty acid and choleste ...
Clostridia
... some of the carboxylic acid groups are esterified with methanol. During fermentation, the ester groups are hydrolyzed, and methanol is released ...
... some of the carboxylic acid groups are esterified with methanol. During fermentation, the ester groups are hydrolyzed, and methanol is released ...
Amino Acid Metabolism
... One carbon unit metabolism • Folic acid / folate is an essential vitamin, and as such it cannot be synthesized within the human body • Folate itself is not an active cofactor; its doubly-reduced form, is tetrahydrofolate (THF) • Tetrahydrofolate (THF) : the carrier of one carbon accepts one carbon ...
... One carbon unit metabolism • Folic acid / folate is an essential vitamin, and as such it cannot be synthesized within the human body • Folate itself is not an active cofactor; its doubly-reduced form, is tetrahydrofolate (THF) • Tetrahydrofolate (THF) : the carrier of one carbon accepts one carbon ...
Fe-S
... 12e- from the oxidation of glucose are not transferred directly to O2, go to NAD+ and FAD to form 10NADH and 2FADH2 These are reoxidized, passing their electrons to the electrontransport chain to reduce O2 to H2O causing the mitochondrion to create a proton gradient. This pH gradient is used to driv ...
... 12e- from the oxidation of glucose are not transferred directly to O2, go to NAD+ and FAD to form 10NADH and 2FADH2 These are reoxidized, passing their electrons to the electrontransport chain to reduce O2 to H2O causing the mitochondrion to create a proton gradient. This pH gradient is used to driv ...
Biochemistry Study Guide NITROGEN METABOLISM
... 2 ATP are required. Basically these are used to "charge" or "activate" ammonia with a highenergy phosphate bond, before we subsequently start urea synthesis. N-Acetylglutamate is absolutely required as a cofactor. This compound also serves a regulatory role in urea synthesis. The rate of carba ...
... 2 ATP are required. Basically these are used to "charge" or "activate" ammonia with a highenergy phosphate bond, before we subsequently start urea synthesis. N-Acetylglutamate is absolutely required as a cofactor. This compound also serves a regulatory role in urea synthesis. The rate of carba ...
Cellular Respiration Part II: Glycolysis
... • Before the citric acid cycle can begin, pyruvate must be converted to acetyl Coenzyme A (acetyl CoA), which links glycolysis to the citric acid cycle • This step is carried out by a multienzyme complex that catalyzes three reactions ...
... • Before the citric acid cycle can begin, pyruvate must be converted to acetyl Coenzyme A (acetyl CoA), which links glycolysis to the citric acid cycle • This step is carried out by a multienzyme complex that catalyzes three reactions ...
ch3b_SP13x
... – Yield raw materials (amino acids, etc) and chemical energy (NADH, ATP) – Convergent: diverse starting materials broken down to conserved set of ...
... – Yield raw materials (amino acids, etc) and chemical energy (NADH, ATP) – Convergent: diverse starting materials broken down to conserved set of ...
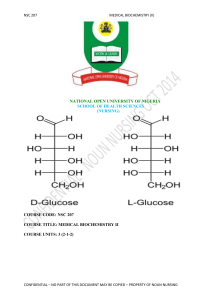
NSC 207 - National Open University of Nigeria
... The glycolytic pathway has a dual role (i) It degrades glucose to generate ATP and (ii) It provides building blocks for synthetic reactions. The rate of conversion of glucose into pyruvate is regulated to meet these 2 major cellular needs. Enzymes catalyzing essentially irreversible reactions are po ...
... The glycolytic pathway has a dual role (i) It degrades glucose to generate ATP and (ii) It provides building blocks for synthetic reactions. The rate of conversion of glucose into pyruvate is regulated to meet these 2 major cellular needs. Enzymes catalyzing essentially irreversible reactions are po ...
Lecture 27
... activated by N-acetylglutamate. N-acetylglutamate is synthesized from glutamate and acetylCoA by N-acetylglutamate synthase, it is hydrolyzed by a specific hydrolase. Rate of urea production is dependent on [N-acetylglutamate]. When aa breakdown rates increase, excess nitrogen must be excreted. This ...
... activated by N-acetylglutamate. N-acetylglutamate is synthesized from glutamate and acetylCoA by N-acetylglutamate synthase, it is hydrolyzed by a specific hydrolase. Rate of urea production is dependent on [N-acetylglutamate]. When aa breakdown rates increase, excess nitrogen must be excreted. This ...
Proteins
... lungs to cells; other proteins transport molecules across cell membranes. • 5. Hormones: Many hormones are proteins, among them insulin, oxytocin, and human growth hormone. ...
... lungs to cells; other proteins transport molecules across cell membranes. • 5. Hormones: Many hormones are proteins, among them insulin, oxytocin, and human growth hormone. ...
Antioxidants B-Vitamins Minerals
... gasoline is stored. Inhalation of MTBE may cause nose and throat irritation, as well as headaches, nausea, dizziness and mental confusion. Animal studies suggest that drinking MTBE may cause gastrointestinal irritation, liver and kidney damage and nervous system effects. Styrene is classified by the ...
... gasoline is stored. Inhalation of MTBE may cause nose and throat irritation, as well as headaches, nausea, dizziness and mental confusion. Animal studies suggest that drinking MTBE may cause gastrointestinal irritation, liver and kidney damage and nervous system effects. Styrene is classified by the ...
Fatty acid synthesis

Fatty acid synthesis is the creation of fatty acids from acetyl-CoA and malonyl-CoA precursors through action of enzymes called fatty acid synthases. It is an important part of the lipogenesis process, which – together with glycolysis – functions to create fats from blood sugar in living organisms.