Biochemistry and the Cell - Tanque Verde Unified District
... (1996) The unique properties (characteristics) of water make life possible on Earth. Select three properties of water and: a) for each property, identify and define the property and explain it in terms of the physical/chemical nature of water. b) for each property, describe one example of how the pr ...
... (1996) The unique properties (characteristics) of water make life possible on Earth. Select three properties of water and: a) for each property, identify and define the property and explain it in terms of the physical/chemical nature of water. b) for each property, describe one example of how the pr ...
Protein primary structure: Amino acids
... associated with the formation of hydration shell (out of water molecules) around protein backbone. The maximum in Fig. 3 is due to the formation of HB between water oxygens and protein amide hydrogens. For the D and A pair of atoms the maximum in g(r) function is reached at about 2.9 Å. The protein- ...
... associated with the formation of hydration shell (out of water molecules) around protein backbone. The maximum in Fig. 3 is due to the formation of HB between water oxygens and protein amide hydrogens. For the D and A pair of atoms the maximum in g(r) function is reached at about 2.9 Å. The protein- ...
Protein_hierarchy
... acids are linked by hydrogen bonds in an alpha helix or beta pleated sheet. • The tertiary structure describes the folding of a polypeptide chain that result from the molecular interactions among the R groups of the different amino acids( H, disulphide, ionic bonds) • The arrangement of two or more ...
... acids are linked by hydrogen bonds in an alpha helix or beta pleated sheet. • The tertiary structure describes the folding of a polypeptide chain that result from the molecular interactions among the R groups of the different amino acids( H, disulphide, ionic bonds) • The arrangement of two or more ...
Chapter 8
... It is an analogue of H and inhibits xanthine oxidase which catalyzes the oxidation of H and X. ...
... It is an analogue of H and inhibits xanthine oxidase which catalyzes the oxidation of H and X. ...
19 Dr. Nafez Abu Tarboosh Qusai Al Sharef
... by oxygen atoms. --Why are those so important? Because they help the coenzyme to bind with Mg which preserve the structure (when Mg is bound it will stabilize the whole structure). Referring to the previous point: 1-The part responsible for binding is the pyrophosphate. 2-The part responsible for ca ...
... by oxygen atoms. --Why are those so important? Because they help the coenzyme to bind with Mg which preserve the structure (when Mg is bound it will stabilize the whole structure). Referring to the previous point: 1-The part responsible for binding is the pyrophosphate. 2-The part responsible for ca ...
Glycolysis, Krebs cycle and Cytochrome chain
... Occurs in and involves the enzymes in the matrix of the mitochondria. Acetyl Co A then enters the Krebs citric acid cycle (stage 2) ( tri-carboxylic acid cycle, TCA), where a series of compounds beginning with citric acid (C6) undergoes oxidative decarboxylation to produce C5 and C4 compounds. The p ...
... Occurs in and involves the enzymes in the matrix of the mitochondria. Acetyl Co A then enters the Krebs citric acid cycle (stage 2) ( tri-carboxylic acid cycle, TCA), where a series of compounds beginning with citric acid (C6) undergoes oxidative decarboxylation to produce C5 and C4 compounds. The p ...
Biosc_48_Chapter_5_lecture
... acid fermentation (Similar to how yeast ferments glucose into alcohol) Still yields a net gain of 2 ATP a. Muscle cells can survive for awhile without oxygen by using lactic acid fermentation. b. RBCs can only use lactic acid fermentation because they lack mitochondria. ...
... acid fermentation (Similar to how yeast ferments glucose into alcohol) Still yields a net gain of 2 ATP a. Muscle cells can survive for awhile without oxygen by using lactic acid fermentation. b. RBCs can only use lactic acid fermentation because they lack mitochondria. ...
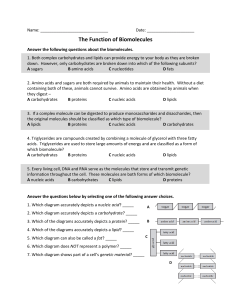
Function of Biomolecules Worksheet
... Use the information in the diagrams to determine which biomolecules are being compared 12. Which set of biomolecules is being compared in the diagram to the right? A carbohydrates and proteins B n ...
... Use the information in the diagrams to determine which biomolecules are being compared 12. Which set of biomolecules is being compared in the diagram to the right? A carbohydrates and proteins B n ...
Slide ()
... Pathways, enzymes, and coenzymes involved in the homocystinurias. Methionine transfers a methyl group during its conversion to homocysteine. Defects in methyl transfer or in the subsequent metabolism of homocysteine by the pyridoxal phosphate (vitamin B6)-dependent cystathionine β-synthase increase ...
... Pathways, enzymes, and coenzymes involved in the homocystinurias. Methionine transfers a methyl group during its conversion to homocysteine. Defects in methyl transfer or in the subsequent metabolism of homocysteine by the pyridoxal phosphate (vitamin B6)-dependent cystathionine β-synthase increase ...
Exam 1 with Key
... 6. (12 pts) The mass of a protein was determined by gel filtration chromatography to be 60 kd. Chromatography in the presence of 6 M urea yields a 30 kd species. When the chromatography is repeated in the presence of 6 M urea and 10 mM β-mercaptoethanol, a single molecular species of 15 kd results. ...
... 6. (12 pts) The mass of a protein was determined by gel filtration chromatography to be 60 kd. Chromatography in the presence of 6 M urea yields a 30 kd species. When the chromatography is repeated in the presence of 6 M urea and 10 mM β-mercaptoethanol, a single molecular species of 15 kd results. ...
Slide ()
... Pathways, enzymes, and coenzymes involved in the homocystinurias. Methionine transfers a methyl group during its conversion to homocysteine. Defects in methyl transfer or in the subsequent metabolism of homocysteine by the pyridoxal phosphate (vitamin B6)-dependent cystathionine β-synthase increase ...
... Pathways, enzymes, and coenzymes involved in the homocystinurias. Methionine transfers a methyl group during its conversion to homocysteine. Defects in methyl transfer or in the subsequent metabolism of homocysteine by the pyridoxal phosphate (vitamin B6)-dependent cystathionine β-synthase increase ...
Sol. RUBISC - askIITians
... substrate complex occurs. At a state when the substrate is bound to an enzyme active site, a new structure of substrate is formed. In the graph, if ‘P’ is at lower level than ‘S’ reaction is exothermic i-e energy is supplied to make product ‘P’. The ‘S’ has to go through much higher energy state kno ...
... substrate complex occurs. At a state when the substrate is bound to an enzyme active site, a new structure of substrate is formed. In the graph, if ‘P’ is at lower level than ‘S’ reaction is exothermic i-e energy is supplied to make product ‘P’. The ‘S’ has to go through much higher energy state kno ...
CH_18_8_Degradation_Amino_Acids
... Match each the intermediate with the amino acid that provides its carbon skeleton: pyruvate, fumarate, or ketoglutarate. A. B. C. D. ...
... Match each the intermediate with the amino acid that provides its carbon skeleton: pyruvate, fumarate, or ketoglutarate. A. B. C. D. ...
Appendix B HISS Codes for Metabolic Investigations
... Suitable samples for more wide ranging investigations MUST be collected in the acute phase, if the diagnostic window is not to be missed. When further samples, e.g. hypoglycaemia investigations, are collected during the acute presentation, it is essential that any necessary acute pre-analytical hand ...
... Suitable samples for more wide ranging investigations MUST be collected in the acute phase, if the diagnostic window is not to be missed. When further samples, e.g. hypoglycaemia investigations, are collected during the acute presentation, it is essential that any necessary acute pre-analytical hand ...
BOC-ON - Sigma
... This reagent offers a distinct advantage over t-BOC azide which can require reaction temperatures of 50-60°C (t-BOC azide is thermally unstable and decomposes with apparent detonation at temperatures above 80°C).1 The oxime by-product can be easily and completely removed from the reaction mixture by ...
... This reagent offers a distinct advantage over t-BOC azide which can require reaction temperatures of 50-60°C (t-BOC azide is thermally unstable and decomposes with apparent detonation at temperatures above 80°C).1 The oxime by-product can be easily and completely removed from the reaction mixture by ...
Chemical Properties of Amino Acids
... low pH – maybe 0 or 1) and calculate its net charge 4. Slowly move up in pH to the first ionizable group’s pKa and deprotonate it (reduce charge by 1) 5. Do this until each group is deprotonated. Now you have identified all charged forms and at which pH each transition occurs. 6. Identify the fo ...
... low pH – maybe 0 or 1) and calculate its net charge 4. Slowly move up in pH to the first ionizable group’s pKa and deprotonate it (reduce charge by 1) 5. Do this until each group is deprotonated. Now you have identified all charged forms and at which pH each transition occurs. 6. Identify the fo ...
short chain polypeptide test
... permeability (leaky gut syndrome) or inadequate digestion (enzymes and acid). Amino acids are the basic building blocks of very large molecules called proteins. When two or more amino acids are joined together they are called peptides. So called ‘short-chain polypeptides’ are up to around 30 amino a ...
... permeability (leaky gut syndrome) or inadequate digestion (enzymes and acid). Amino acids are the basic building blocks of very large molecules called proteins. When two or more amino acids are joined together they are called peptides. So called ‘short-chain polypeptides’ are up to around 30 amino a ...
Full Text
... H7-roseobacticide B (Figure S3). These results establish the role of Phe as the source of both the tropone moiety and the aromatic side chain in roseobacticide B as well as those of Tyr and Trp in generating the other roseobacticide analogs. Given that amino acids serve as roseobacticide precursors, ...
... H7-roseobacticide B (Figure S3). These results establish the role of Phe as the source of both the tropone moiety and the aromatic side chain in roseobacticide B as well as those of Tyr and Trp in generating the other roseobacticide analogs. Given that amino acids serve as roseobacticide precursors, ...
PROTEIN TURNOVER AND NITROGEN ECONOMY - U
... Nitrogen removal from nonhepatic tissues - glutamate dehydrogenase; one direction reaction involves addition of nitrogen to alphaketoglutarate as ammonia (non-hepatic tissues, remove harmful ammonia from these tissues) - glutamate non transported across plasma membrane, but glutamine easily leaves ...
... Nitrogen removal from nonhepatic tissues - glutamate dehydrogenase; one direction reaction involves addition of nitrogen to alphaketoglutarate as ammonia (non-hepatic tissues, remove harmful ammonia from these tissues) - glutamate non transported across plasma membrane, but glutamine easily leaves ...
Fructose-1,6 - LSU School of Medicine
... High Glucagon -> High cAMP -> activation of PKA -> phosphorylation of bifunctional enzyme -> inhibition of PFK2, activation of FBPase2 -> decrease in fructose 2,6-bisphosphate -> no stimulation of glycolysis, no inhibition of gluconeogenesis -> Gluconeogenesis prevails! ...
... High Glucagon -> High cAMP -> activation of PKA -> phosphorylation of bifunctional enzyme -> inhibition of PFK2, activation of FBPase2 -> decrease in fructose 2,6-bisphosphate -> no stimulation of glycolysis, no inhibition of gluconeogenesis -> Gluconeogenesis prevails! ...
KEY Biochemistry Macromolecules – POGIL
... 2. Figure 8 depicts a RNA nucleotide. Study the structure and state what makes it different from the DNA nuclotide. HINT: Look at the sugar!!! IN RNA, THE SUGAR HAS ONE EXTRA OXYGEN 3. Both the DNA and RNA nucleotide contain 5 elements; name them. CARBON, NITROGEN, OXYGEN, HYDROGEN, PHOSPHORUS 4. Fi ...
... 2. Figure 8 depicts a RNA nucleotide. Study the structure and state what makes it different from the DNA nuclotide. HINT: Look at the sugar!!! IN RNA, THE SUGAR HAS ONE EXTRA OXYGEN 3. Both the DNA and RNA nucleotide contain 5 elements; name them. CARBON, NITROGEN, OXYGEN, HYDROGEN, PHOSPHORUS 4. Fi ...
Supplementary Notes
... Figure 6a, lanes 5–23). One exception was Gly, which was not incorporated into GFP at all (lanes 4 and 24). Because it was confirmed that Gly was attached to the 3'-end of tRNA like the other amino acids, the complete lack of incorporation was unanticipated. We thus suspected that unknown mechanisms ...
... Figure 6a, lanes 5–23). One exception was Gly, which was not incorporated into GFP at all (lanes 4 and 24). Because it was confirmed that Gly was attached to the 3'-end of tRNA like the other amino acids, the complete lack of incorporation was unanticipated. We thus suspected that unknown mechanisms ...
ATP citrate lyase – biology and implication in human
... of the enzyme and a possible regulatory role of its phosphorylation have been variable. A possible reason for this is the fact that ACLY was isolated from mammalian tissues or eukaryote systems that were able to phosphorylate the enzyme prior to extraction and purification. Thus, variable phosphoryl ...
... of the enzyme and a possible regulatory role of its phosphorylation have been variable. A possible reason for this is the fact that ACLY was isolated from mammalian tissues or eukaryote systems that were able to phosphorylate the enzyme prior to extraction and purification. Thus, variable phosphoryl ...
Fatty acid synthesis

Fatty acid synthesis is the creation of fatty acids from acetyl-CoA and malonyl-CoA precursors through action of enzymes called fatty acid synthases. It is an important part of the lipogenesis process, which – together with glycolysis – functions to create fats from blood sugar in living organisms.