Supplementary Notes
... Figure 6a, lanes 5–23). One exception was Gly, which was not incorporated into GFP at all (lanes 4 and 24). Because it was confirmed that Gly was attached to the 3'-end of tRNA like the other amino acids, the complete lack of incorporation was unanticipated. We thus suspected that unknown mechanisms ...
... Figure 6a, lanes 5–23). One exception was Gly, which was not incorporated into GFP at all (lanes 4 and 24). Because it was confirmed that Gly was attached to the 3'-end of tRNA like the other amino acids, the complete lack of incorporation was unanticipated. We thus suspected that unknown mechanisms ...
Acid K a
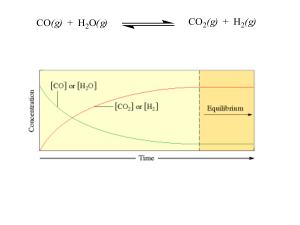
... 2.0 moles of NH3 gas are introduced into a previously evacuated 1.0 L container. At a certain temperature the NH3 partially dissociates by the following equation. 2 NH3(g) ...
... 2.0 moles of NH3 gas are introduced into a previously evacuated 1.0 L container. At a certain temperature the NH3 partially dissociates by the following equation. 2 NH3(g) ...
Function of prostaglandins
... linolenic acid (eicosapentaenoate precursor) are essential fatty acids, so they must be taken in the diet otherwise the body can not synthesize the eicosanoids. Minor ...
... linolenic acid (eicosapentaenoate precursor) are essential fatty acids, so they must be taken in the diet otherwise the body can not synthesize the eicosanoids. Minor ...
Worked solutions to textbook questions 1 Chapter 12 Pathways to
... A fatty acid molecule consists of a hydrocarbon chain with a carboxy (–COOH) group at one end. A fat, or triglyceride, is the product of a condensation reaction between three fatty acid molecules and a glycerol molecule. The fatty acid groups that make up a saturated fat contain only single carbon– ...
... A fatty acid molecule consists of a hydrocarbon chain with a carboxy (–COOH) group at one end. A fat, or triglyceride, is the product of a condensation reaction between three fatty acid molecules and a glycerol molecule. The fatty acid groups that make up a saturated fat contain only single carbon– ...
Year 12 ATAR Chemistry Course Outline 2017
... secondary alcohols produce ketones; these reactions have characteristic observations and can be represented with equations alcohols can react with carboxylic acids in a condensation reaction to produce esters and can be represented with equations functional groups within organic compounds display ch ...
... secondary alcohols produce ketones; these reactions have characteristic observations and can be represented with equations alcohols can react with carboxylic acids in a condensation reaction to produce esters and can be represented with equations functional groups within organic compounds display ch ...
Titration curve of amino acids
... pKa for particular Ionizable group is equal the pH at which the Ionizable group is at its best buffering capacity. Considering applying the Henderson-Hasselbalch equation to the titration of glycine with acid and base, glycine has two Ionizable groups: a carboxyl group and an amino group, with pKa v ...
... pKa for particular Ionizable group is equal the pH at which the Ionizable group is at its best buffering capacity. Considering applying the Henderson-Hasselbalch equation to the titration of glycine with acid and base, glycine has two Ionizable groups: a carboxyl group and an amino group, with pKa v ...
Primary Structure
... sequence in Figure 2 of the appendix, identifying each section of the sequence that is also found here. The protein is a modified single chain A Fv antibody fragment scFv6H4 that binds to methamphetamine and one of its derivates. The matches in Blastp 2.2.24 (appendix 2) are these two best ones for ...
... sequence in Figure 2 of the appendix, identifying each section of the sequence that is also found here. The protein is a modified single chain A Fv antibody fragment scFv6H4 that binds to methamphetamine and one of its derivates. The matches in Blastp 2.2.24 (appendix 2) are these two best ones for ...
L- Amino Acid Assay Kit (Colorimetric)
... groups, as well as a side-chain (R group) which confers uniqueness to each amino acid. The main elements of an amino acid are carbon, hydrogen, oxygen, and nitrogen, although other elements can be found in some amino acids. About 500 amino acids are known, but only 20 are coded in the human genome. ...
... groups, as well as a side-chain (R group) which confers uniqueness to each amino acid. The main elements of an amino acid are carbon, hydrogen, oxygen, and nitrogen, although other elements can be found in some amino acids. About 500 amino acids are known, but only 20 are coded in the human genome. ...
Questions for Respiration and Photoshyntesis
... 1. What are oxidation/reduction reactions? Chem. rxns that involve a partial or complete transfer of e- from one reactant to another 2. The ETC involves a series of redox reactions in which electrons pass from carrier to carrier down to oxygen the final electron acceptor. 3. What are the three main ...
... 1. What are oxidation/reduction reactions? Chem. rxns that involve a partial or complete transfer of e- from one reactant to another 2. The ETC involves a series of redox reactions in which electrons pass from carrier to carrier down to oxygen the final electron acceptor. 3. What are the three main ...
AMINO ACIDS IN THE ASTEROIDAL WATER - USRA
... chondrites suggests that amino acids may be formed through Fischer-Tropsch type (FTT) gas-grain reactions after the meteorite parent body cooled to lower temperatures. β-alanine, which is a n-ω-amino acid [9], is also one of the most abundant amino acids in Zag, and its presence is consistent with i ...
... chondrites suggests that amino acids may be formed through Fischer-Tropsch type (FTT) gas-grain reactions after the meteorite parent body cooled to lower temperatures. β-alanine, which is a n-ω-amino acid [9], is also one of the most abundant amino acids in Zag, and its presence is consistent with i ...
Antioxidant activity of anacardic acids Food Chemistry
... the same concentration. The negative result of anacardic acid (C15:3) can explain a structural feature in which the electron donating alkenyl group is located at the meta-position to the hydroxyl group so that it does not stabilize the phenoxy radicals (Cuvelier, Richard, & Berset, 1992). In connect ...
... the same concentration. The negative result of anacardic acid (C15:3) can explain a structural feature in which the electron donating alkenyl group is located at the meta-position to the hydroxyl group so that it does not stabilize the phenoxy radicals (Cuvelier, Richard, & Berset, 1992). In connect ...
Cell Respiration PP
... Glycolysis (in cytoplasm) • All respiration begins with glycolysis in the cytoplasm • Glucose (6C) is cleaved into 2 molecules of pyruvate (3C) • This requires 2 ATP. It produces 4 • 2NAD+ are reduced to 2 NADPH ...
... Glycolysis (in cytoplasm) • All respiration begins with glycolysis in the cytoplasm • Glucose (6C) is cleaved into 2 molecules of pyruvate (3C) • This requires 2 ATP. It produces 4 • 2NAD+ are reduced to 2 NADPH ...
Hormones of the Gut
... bladder to contract--cholecystokinin. 2. 1940s: Extract of duodenal mucosa stimulates pancreas to secrete enzymes--pancreozymin. 3. 1964-8: Purification of a single substance that stimulated both contraction of the gall bladder and pancreatic enzyme secretion--settled on one name: cholecystokinin (C ...
... bladder to contract--cholecystokinin. 2. 1940s: Extract of duodenal mucosa stimulates pancreas to secrete enzymes--pancreozymin. 3. 1964-8: Purification of a single substance that stimulated both contraction of the gall bladder and pancreatic enzyme secretion--settled on one name: cholecystokinin (C ...
Protein Folding and The Impact of Mutations
... Cysteines are one of the 20 amino acids Cysteines are like the obnoxious couples that are always together – they can’t stand to be apart Two cysteines will always move closer to each other When they move close, they will form what is called a “disulfide bond” or “disulfide bridge” ...
... Cysteines are one of the 20 amino acids Cysteines are like the obnoxious couples that are always together – they can’t stand to be apart Two cysteines will always move closer to each other When they move close, they will form what is called a “disulfide bond” or “disulfide bridge” ...
Stearoyl-CoA desaturase 1 deficiency increases fatty acid oxidation
... diet-induced weight gain relative to wild-type mice. The resistance to diet-induced obesity is due to increased energy expenditure (4). SCD1⫺兾⫺ mice also have increased fasting levels of plasma ketone bodies but reduced levels of plasma insulin and leptin. Moreover, mice with mutations in the SCD1 g ...
... diet-induced weight gain relative to wild-type mice. The resistance to diet-induced obesity is due to increased energy expenditure (4). SCD1⫺兾⫺ mice also have increased fasting levels of plasma ketone bodies but reduced levels of plasma insulin and leptin. Moreover, mice with mutations in the SCD1 g ...
Document
... result. Nonfermenting bacteria that metabolize glucose via oxidative metabolism give an oxidative result. e.g. Pseudomonas aeruginosa • Non saccharolytic (Negative OF result): Nonsacchrolytic bacteria give a negative OF result. The negative result is indicated by no color change in the oil-covered t ...
... result. Nonfermenting bacteria that metabolize glucose via oxidative metabolism give an oxidative result. e.g. Pseudomonas aeruginosa • Non saccharolytic (Negative OF result): Nonsacchrolytic bacteria give a negative OF result. The negative result is indicated by no color change in the oil-covered t ...
9 essential amino acids your body can`t live without
... transporting essential oxygen around the body, accounts for 16%. Protein also has an essential function in every cell including in membranes, transporters, enzymes, components of the immune system, and is also a precursor to hormones. ...
... transporting essential oxygen around the body, accounts for 16%. Protein also has an essential function in every cell including in membranes, transporters, enzymes, components of the immune system, and is also a precursor to hormones. ...
RESEARCH NOTES
... or in the presence of very Iw levels of leucine. In many cows a combination of L-iroleucine and L-leucine (each of 1 pmolq’ml) gave growth several times higher than on 2 pmole/ml. (b) Arginine, lysine, histidine ond methionine inhibit the rote of growth on leucine but it is not known whether the omo ...
... or in the presence of very Iw levels of leucine. In many cows a combination of L-iroleucine and L-leucine (each of 1 pmolq’ml) gave growth several times higher than on 2 pmole/ml. (b) Arginine, lysine, histidine ond methionine inhibit the rote of growth on leucine but it is not known whether the omo ...
1. An inner engine keeps us alive
... Figure 1.3. Overnight fast, i.e., GB does not eat for more than about eight to 12 hours. Glucose is still circulating in the blood, but this glucose does not come from ingested glucose. Instead, muscle proteins are broken down, and the liver makes glucose from them. This glucose goes into circulatio ...
... Figure 1.3. Overnight fast, i.e., GB does not eat for more than about eight to 12 hours. Glucose is still circulating in the blood, but this glucose does not come from ingested glucose. Instead, muscle proteins are broken down, and the liver makes glucose from them. This glucose goes into circulatio ...
Proteins
... Another major compound of living things is protein. Proteins make up the bulk of all solid material within your body and other living organisms. Proteins are the most structurally sophisticated molecules known. They vary extensively in structure with each type of protein having a unique three-dimens ...
... Another major compound of living things is protein. Proteins make up the bulk of all solid material within your body and other living organisms. Proteins are the most structurally sophisticated molecules known. They vary extensively in structure with each type of protein having a unique three-dimens ...
Document
... The nitrogen cycle. Organic nitrogenous compounds are formed by the incorporation of NH4+ into carbon skeletons. Ammonium can be formed from oxidized inorganic percursors by reductive reactions: nitrogen fixation reduces N2 to NH4+; nitrate assimilation reduces NO3- to NH4+. Nitrifying bacteria can ...
... The nitrogen cycle. Organic nitrogenous compounds are formed by the incorporation of NH4+ into carbon skeletons. Ammonium can be formed from oxidized inorganic percursors by reductive reactions: nitrogen fixation reduces N2 to NH4+; nitrate assimilation reduces NO3- to NH4+. Nitrifying bacteria can ...
The Building Blocks Teacher Key
... acids to complete necessary functions, including maintaining organs and bones, and promoting muscle growth and repair. Animal foods are the only source of complete proteins. ...
... acids to complete necessary functions, including maintaining organs and bones, and promoting muscle growth and repair. Animal foods are the only source of complete proteins. ...
Fatty acid synthesis

Fatty acid synthesis is the creation of fatty acids from acetyl-CoA and malonyl-CoA precursors through action of enzymes called fatty acid synthases. It is an important part of the lipogenesis process, which – together with glycolysis – functions to create fats from blood sugar in living organisms.