* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Slide ()
Fatty acid synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Genetic code wikipedia , lookup
Metalloprotein wikipedia , lookup
Biochemical cascade wikipedia , lookup
Gaseous signaling molecules wikipedia , lookup
Evolution of metal ions in biological systems wikipedia , lookup
Lipid signaling wikipedia , lookup
Proteolysis wikipedia , lookup
Biochemistry wikipedia , lookup
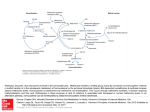
Pathways, enzymes, and coenzymes involved in the homocystinurias. Methionine transfers a methyl group during its conversion to homocysteine. Defects in methyl transfer or in the subsequent metabolism of homocysteine by the pyridoxal phosphate (vitamin B6)-dependent cystathionine β-synthase increase plasma methionine levels. Homocysteine is transformed into methionine via remethylation. This occurs through methionine synthase, a reaction requiring methylcobalamin and folic acid. Deficiencies in these enzymes or lack of cofactors is associated with decreased or normal methionine levels. In an alternative pathway, homocysteine can be remethylated by betaine:homocysteine methyl transferase. Source: Chapter 364. Inherited Disorders of Amino Acid Metabolism in Adults, Harrison's Principles of Internal Medicine, 18e Citation: Longo DL, Fauci AS, Kasper DL, Hauser SL, Jameson J, Loscalzo J. Harrison's Principles of Internal Medicine, 18e; 2012 Available at: http://mhmedical.com/ Accessed: May 12, 2017 Copyright © 2017 McGraw-Hill Education. All rights reserved