Nonracemic Allylic Boronates through Enantiotopic-Group
... replaced with neopentylglycol or 2,4-dimethylpentane-2,4-diol ligands. With these alternate boron ligands, lower reactivity and lower selectivity were observed in the cross-coupling with 1bromo-2-methylpropene (18% 1H NMR yield, 85:15 er for the former; 13% 1H NMR yield, 89:11 er for the latter). Th ...
... replaced with neopentylglycol or 2,4-dimethylpentane-2,4-diol ligands. With these alternate boron ligands, lower reactivity and lower selectivity were observed in the cross-coupling with 1bromo-2-methylpropene (18% 1H NMR yield, 85:15 er for the former; 13% 1H NMR yield, 89:11 er for the latter). Th ...
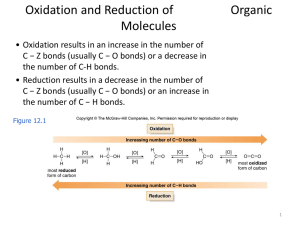
Oxidation and Reduction of Organic Molecules
... • When hydrogenation of two alkenes gives the same alkane, the more stable alkene has the smaller heat of hydrogenation. ...
... • When hydrogenation of two alkenes gives the same alkane, the more stable alkene has the smaller heat of hydrogenation. ...
Chapter 23 - Simpson County Schools
... Extremely important to carbohydrate chemistry due to nearly all carbohydrates are found as ringed molecules because they form intramolecular hemiacetals or hemiketals. The acetal/ketal reaction provides the means by which carbohydrates link together to form the wellknown carbohydrate polymers such a ...
... Extremely important to carbohydrate chemistry due to nearly all carbohydrates are found as ringed molecules because they form intramolecular hemiacetals or hemiketals. The acetal/ketal reaction provides the means by which carbohydrates link together to form the wellknown carbohydrate polymers such a ...
Microwave-Assisted Sulfamide Synthesis
... was recently reported has several limitations, especially with ortho-isomers [1]. Even though other available methods report high yields, they either require reagents that are not readily accessible or they focus on specific structures rather than a general procedure [6]. Winum and co-workers report ...
... was recently reported has several limitations, especially with ortho-isomers [1]. Even though other available methods report high yields, they either require reagents that are not readily accessible or they focus on specific structures rather than a general procedure [6]. Winum and co-workers report ...
15_12_13rw
... Francis A. Carey, Organic Chemistry, Fourth Edition. Copyright © 2000 The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved. ...
... Francis A. Carey, Organic Chemistry, Fourth Edition. Copyright © 2000 The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved. ...
OR Practice Problem - HCC Southeast Commons
... C5H6NCrO3Cl) in dichloromethane – carboxylic acids via other reagents (CrO3, …) ...
... C5H6NCrO3Cl) in dichloromethane – carboxylic acids via other reagents (CrO3, …) ...
NaBH4 Reduction of Vanillin
... Experiment 1: NaBH4 Reduction of Vanillin The borate, –BH3‐OEt, formed from the Lewis acid‐base reaction of –OEt and BH3, has three remaining B—H bonds, each of which, in turn, reduces another molecule of the starting ketone, as shown below. ...
... Experiment 1: NaBH4 Reduction of Vanillin The borate, –BH3‐OEt, formed from the Lewis acid‐base reaction of –OEt and BH3, has three remaining B—H bonds, each of which, in turn, reduces another molecule of the starting ketone, as shown below. ...
ppt
... In general, the C-O bonds of ethers have low reactivity. 16.3: Physical Properties of Ethers the O-H group of alcohols act as both an H-bond donor (Lewis acid) and H-bond acceptor (Lewis base). Ethers are only H-bond acceptors (Lewis base) 16.4: Crown Ethers (Please read) ...
... In general, the C-O bonds of ethers have low reactivity. 16.3: Physical Properties of Ethers the O-H group of alcohols act as both an H-bond donor (Lewis acid) and H-bond acceptor (Lewis base). Ethers are only H-bond acceptors (Lewis base) 16.4: Crown Ethers (Please read) ...
EXPERIMENT 4 (Organic Chemistry II) Pahlavan/Cherif
... Part IV. Jones Reagent ( Chromic acid test) In a small test tube, place about 1 mL acetone, 1 mL alcohol , and 2 –3 drops of the Jones reagent. Observer the color change, clear, orange ( formation of Cr +6 as CrO3 ), or blue-green (formation of Cr 3+ ). Try this test with 1-butanol, 2-butanol, 2-met ...
... Part IV. Jones Reagent ( Chromic acid test) In a small test tube, place about 1 mL acetone, 1 mL alcohol , and 2 –3 drops of the Jones reagent. Observer the color change, clear, orange ( formation of Cr +6 as CrO3 ), or blue-green (formation of Cr 3+ ). Try this test with 1-butanol, 2-butanol, 2-met ...
Isolating High Value Aromatics from Lignin Stockpiles
... carbenes, a procedure developed by Tamm et. al. was repeated to form the previously reported 2-iminoimidazoles of IPr and SIPr .11 This procedure was adopted in use with the BIm carbene to successfully produce the previously unreported 2-imino-1,3diisopropylbenzimidazoline; this new compound was als ...
... carbenes, a procedure developed by Tamm et. al. was repeated to form the previously reported 2-iminoimidazoles of IPr and SIPr .11 This procedure was adopted in use with the BIm carbene to successfully produce the previously unreported 2-imino-1,3diisopropylbenzimidazoline; this new compound was als ...
Selectivity of sodium borohydride
... range of functional groups including aldehydes, ketones, esters, carboxylic acids, amides, nitriles and epoxides. In contrast, sodium borohydride is less reactive and can be used in water or alcohol solvents and is more selective in its reactivity and reduces fewer functional groups. However, both r ...
... range of functional groups including aldehydes, ketones, esters, carboxylic acids, amides, nitriles and epoxides. In contrast, sodium borohydride is less reactive and can be used in water or alcohol solvents and is more selective in its reactivity and reduces fewer functional groups. However, both r ...
unit 6 alcohols
... with one mole of the Grignard, a ketone forms. The ketone can be attacked by a second mole of the Grignard reagent. Esters: Now the LG is RO-, not usually considered “good,” but the reaction takes place by nucleophilic acyl substitution, not by SN2. In this mechanism, RO- leaving is exothermic and ...
... with one mole of the Grignard, a ketone forms. The ketone can be attacked by a second mole of the Grignard reagent. Esters: Now the LG is RO-, not usually considered “good,” but the reaction takes place by nucleophilic acyl substitution, not by SN2. In this mechanism, RO- leaving is exothermic and ...
Rhenium(VII) Catalysis of Prins Cyclization Reactions
... more complex aldehyde 17, prepared by a metathesis reaction between crotonaldehyde and the corresponding terminal alkene, was noticeably slower than the others. All of the products showed very good selectivity for the equatorial alcohol THP products. Unsaturated aldehydes will be useful for forming ...
... more complex aldehyde 17, prepared by a metathesis reaction between crotonaldehyde and the corresponding terminal alkene, was noticeably slower than the others. All of the products showed very good selectivity for the equatorial alcohol THP products. Unsaturated aldehydes will be useful for forming ...
File
... (formation of ester) Nuffield Chemistry experiment 2.3 (forming cyclohexene from cyclohexanol) ...
... (formation of ester) Nuffield Chemistry experiment 2.3 (forming cyclohexene from cyclohexanol) ...
ASYMMETRIC CATALYSIS
... transformations into catalytic reactions and developing highly active catalysts that feature broad substrate scopes that can function under mild and simple reaction conditions remain key problems. It is especially important to identify reactions that are based on readily available starting materials ...
... transformations into catalytic reactions and developing highly active catalysts that feature broad substrate scopes that can function under mild and simple reaction conditions remain key problems. It is especially important to identify reactions that are based on readily available starting materials ...
Presentation8_108
... soluble in organic solvents such as alcohol and ether. •Boiling points of alcohols Boiling point of alcohols are much higher than those of alkenes, halo alkenes or ethers of comparable molecular masses. This is because in alcohols intermolecular hydrogen bonding exists due to which a large amount of ...
... soluble in organic solvents such as alcohol and ether. •Boiling points of alcohols Boiling point of alcohols are much higher than those of alkenes, halo alkenes or ethers of comparable molecular masses. This is because in alcohols intermolecular hydrogen bonding exists due to which a large amount of ...
File
... (formation of ester) Nuffield Chemistry experiment 2.3 (forming cyclohexene from cyclohexanol) ...
... (formation of ester) Nuffield Chemistry experiment 2.3 (forming cyclohexene from cyclohexanol) ...
Reactions of Alcohols - John Carroll University
... synthesis, however, dehydrogenation is not practical, and cost is not as large a factor as it would be in industry. Most labs would have chromium trioxide or sodium dichromate available, and the chromic acid oxidation would be simple. PCC and the Swern oxidation would also work, although these reage ...
... synthesis, however, dehydrogenation is not practical, and cost is not as large a factor as it would be in industry. Most labs would have chromium trioxide or sodium dichromate available, and the chromic acid oxidation would be simple. PCC and the Swern oxidation would also work, although these reage ...
Document
... hydrocarbon chain*** Carboxylic acid naming is done the same as a normal hydrocarbon EXCEPT at the end of the hydrocarbon name you add “–oic acid” ...
... hydrocarbon chain*** Carboxylic acid naming is done the same as a normal hydrocarbon EXCEPT at the end of the hydrocarbon name you add “–oic acid” ...
Level 3: Organics Part I
... Note: Tertiary alcohols cannot be oxidised at all. The –OH can’t form double bonds with the carbon that it is attached to because that carbon is already bonded to three other carbons CH3 H3C ...
... Note: Tertiary alcohols cannot be oxidised at all. The –OH can’t form double bonds with the carbon that it is attached to because that carbon is already bonded to three other carbons CH3 H3C ...
effective: september 2003
... given the formulas of the substrates and reagents be able to predict the major product of the reaction including competition between elimination and substitution, oxidations of alcohols and aldehydes, catalytic hydrogenation, hydration of alkenes, ring opening of epoxides, radical halogenation of al ...
... given the formulas of the substrates and reagents be able to predict the major product of the reaction including competition between elimination and substitution, oxidations of alcohols and aldehydes, catalytic hydrogenation, hydration of alkenes, ring opening of epoxides, radical halogenation of al ...
EXPERIMENT 4 (Organic Chemistry II) Pahlavan/Cherif
... Figure 1- Hydrogen bonding between (a) alcohol molecules, and (b) alcohol and water molecules Also, considering their molecular masses as compared to alkanes, alcohols have relatively high boiling points. Individual alcohol molecules are attracted to each other by hydrogen bonds. A higher temperatur ...
... Figure 1- Hydrogen bonding between (a) alcohol molecules, and (b) alcohol and water molecules Also, considering their molecular masses as compared to alkanes, alcohols have relatively high boiling points. Individual alcohol molecules are attracted to each other by hydrogen bonds. A higher temperatur ...
Unit 11 – Alcohols, Phenols and Ethers
... A. Esterfication is a reversible process. To prevent the backward reaction, water is removed a soon as it is formed by conc. H2SO4 which is a dehydrating agent. 14. Production of ester from RCOCl is carried out in the presence of a base (pyridine). A. The base neutralizes the acid, HCL formed and sh ...
... A. Esterfication is a reversible process. To prevent the backward reaction, water is removed a soon as it is formed by conc. H2SO4 which is a dehydrating agent. 14. Production of ester from RCOCl is carried out in the presence of a base (pyridine). A. The base neutralizes the acid, HCL formed and sh ...
nucleophilic addition
... Formaldehyde is the most easily oxidized aldehyde. When mixed with another aldehyde that doesn’t have any alphahydrogens and conc. NaOH, all of the formaldehyde is oxidized and all of the other aldehyde is reduced. Crossed Cannizzaro: CH=O ...
... Formaldehyde is the most easily oxidized aldehyde. When mixed with another aldehyde that doesn’t have any alphahydrogens and conc. NaOH, all of the formaldehyde is oxidized and all of the other aldehyde is reduced. Crossed Cannizzaro: CH=O ...
101. Alcohols as alkylating agents in heteroarene C H functionalization
... and our recent work on the development of a photoredox-catalysed Minisci reaction18, we questioned whether it would be possible to generate alkyl radicals from alcohols and use them as alkylating agents in a heteroaromatic C–H functionalization reaction (Fig. 1c). While there are a few early reports ...
... and our recent work on the development of a photoredox-catalysed Minisci reaction18, we questioned whether it would be possible to generate alkyl radicals from alcohols and use them as alkylating agents in a heteroaromatic C–H functionalization reaction (Fig. 1c). While there are a few early reports ...
Kinetic resolution

In organic chemistry, kinetic resolution is a means of differentiating two enantiomers in a racemic mixture. In kinetic resolution, two enantiomers react with different reaction rates in a chemical reaction with a chiral catalyst or reagent, resulting in an enantioenriched sample of the less reactive enantiomer. As opposed to chiral resolution, kinetic resolution does not rely on different physical properties of diastereomeric products, but rather on the different chemical properties of the racemic starting materials. This enantiomeric excess (ee) of the unreacted starting material continually rises as more product is formed, reaching 100% just before full completion of the reaction. Kinetic resolution relies upon differences in reactivity between enantiomers or enantiomeric complexes. Kinetic resolution is a concept in organic chemistry and can be used for the preparation of chiral molecules in organic synthesis. Kinetic resolution reactions utilizing purely synthetic reagents and catalysts are much less common than the use of enzymatic kinetic resolution in application towards organic synthesis, although a number of useful synthetic techniques have been developed in the past 30 years.