Chemistry
... 2. Explain the difference between 10, 20 and 30 alkyl halides, with suitable examples. 3. Allyl halides are more reactive than alkyl halides. Why? 4. What are the reagents required prepare alkyl halide from the following (i) alcohol (ii) alkene (iv) alkanes 5. Explain the reactions used to convert b ...
... 2. Explain the difference between 10, 20 and 30 alkyl halides, with suitable examples. 3. Allyl halides are more reactive than alkyl halides. Why? 4. What are the reagents required prepare alkyl halide from the following (i) alcohol (ii) alkene (iv) alkanes 5. Explain the reactions used to convert b ...
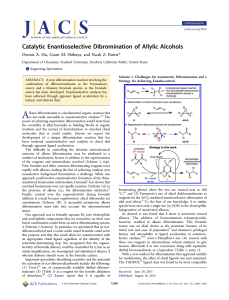
Catalytic Enantioselective Dibromination of Allylic Alcohols
... and product utility. Indeed, cinnamyl alcohol (6) was converted to dibromide (−)-7 with 43% ee using (R,R)-TADDOL 8 (entry 3). Allylic ethers, amides, and sulfonamides were all less reactive, and the products were racemic. Optimization12 of the backbone and aryl groups on the diol led to the identifi ...
... and product utility. Indeed, cinnamyl alcohol (6) was converted to dibromide (−)-7 with 43% ee using (R,R)-TADDOL 8 (entry 3). Allylic ethers, amides, and sulfonamides were all less reactive, and the products were racemic. Optimization12 of the backbone and aryl groups on the diol led to the identifi ...
View Article - Asian Journal of Chemistry
... sodium hydroxide solution. Liquid bromine ( 4.2 mL, 80 mmol) was added dropwise in 2 h when the mixture maintained at 100 - 130 ºC heated by oil bath, excess time was prolonged for reaction until the colour of the reaction mixture turned to light yellow, after that the oil bath was removed and ethyl ...
... sodium hydroxide solution. Liquid bromine ( 4.2 mL, 80 mmol) was added dropwise in 2 h when the mixture maintained at 100 - 130 ºC heated by oil bath, excess time was prolonged for reaction until the colour of the reaction mixture turned to light yellow, after that the oil bath was removed and ethyl ...
Chapter 14 Selenium reagents
... Allylic selenides are convertible into allyl-lithium reagents for further reactio with electrophiles. Hydrogenolysis of carbon-selenium bonds is achievable using catalytic methods, dissolving metals, triaryltin hydrides and ‘nickel boride’. 1,2,3-Selenadiazole undergo elimination, giving alky ...
... Allylic selenides are convertible into allyl-lithium reagents for further reactio with electrophiles. Hydrogenolysis of carbon-selenium bonds is achievable using catalytic methods, dissolving metals, triaryltin hydrides and ‘nickel boride’. 1,2,3-Selenadiazole undergo elimination, giving alky ...
Direct ester condensation catalyzed by bulky diarylammonium
... condensation reaction of carboxylic acids with alcohols is catalyzed by Brønsted acids such as HCl, H2SO4, p-toluenesulfonic acid and so on for acid-resistance substrates. For acid-sensitive substrates, weak Brønsted acids such as pyridinium p-toluenesulfonate should be used. However, these have low ...
... condensation reaction of carboxylic acids with alcohols is catalyzed by Brønsted acids such as HCl, H2SO4, p-toluenesulfonic acid and so on for acid-resistance substrates. For acid-sensitive substrates, weak Brønsted acids such as pyridinium p-toluenesulfonate should be used. However, these have low ...
1.1 10 Oxidation of alcohols and aldehydes
... After a bottle of wine has been opened, ethanal can form within as little as two hours. White wines and older reds are particularly susceptible to oxidation. Figure 5 Wine tasting ...
... After a bottle of wine has been opened, ethanal can form within as little as two hours. White wines and older reds are particularly susceptible to oxidation. Figure 5 Wine tasting ...
Chapter 9
... Naming Alcohols Attached to Rings • When an OH group is bonded to a ring, the ring is numbered beginning with the OH group. • Because the functional group is at C1, the 1 is usually omitted from the name. • The ring is then numbered in a clockwise or counterclockwise fashion to give the next substi ...
... Naming Alcohols Attached to Rings • When an OH group is bonded to a ring, the ring is numbered beginning with the OH group. • Because the functional group is at C1, the 1 is usually omitted from the name. • The ring is then numbered in a clockwise or counterclockwise fashion to give the next substi ...
Alcohols and Thiols
... a significant energy involved with this type of bonding, which causes the individual molecules to want to “stick” together. The most noticeable result is in the surprisingly high boiling points of small alcohols. Water, having two hydrogens on oxygen, is one of the simplest hydrogenbonding molecule ...
... a significant energy involved with this type of bonding, which causes the individual molecules to want to “stick” together. The most noticeable result is in the surprisingly high boiling points of small alcohols. Water, having two hydrogens on oxygen, is one of the simplest hydrogenbonding molecule ...
Document
... • Methanol (CH3OH) • Often Called Wood Alcohol (Distilled From Wood) • Prepared Now via Catalytic Hydrogenation Reactions • Ethanol (CH3CH2OH) • Made Through Fermentation of Sugars, in Alcoholic Drinks • Common Solvent in Organic Labs (Absolute Ethanol) • Ethylene Glycol (HOCH2CH2OH) ...
... • Methanol (CH3OH) • Often Called Wood Alcohol (Distilled From Wood) • Prepared Now via Catalytic Hydrogenation Reactions • Ethanol (CH3CH2OH) • Made Through Fermentation of Sugars, in Alcoholic Drinks • Common Solvent in Organic Labs (Absolute Ethanol) • Ethylene Glycol (HOCH2CH2OH) ...
Reactions of Alcohols
... • Oxidation: loss of H2, gain of O, O2, or X2 • Reduction: gain of H2 or H-, loss of O, O2, or X2 • Neither: gain or loss of H+, H2O, HX ...
... • Oxidation: loss of H2, gain of O, O2, or X2 • Reduction: gain of H2 or H-, loss of O, O2, or X2 • Neither: gain or loss of H+, H2O, HX ...
Regents Unit 15b: Halides, Alcohols, & Ethers
... • One or more H’s in a hydrocarbon can be replaced by an atom or group of atoms. • An atom or group of atoms in an organic molecule that always behaves in the same way is called a functional group. • Adding a functional group changes the chemical & physical properties in specific ways, depending on ...
... • One or more H’s in a hydrocarbon can be replaced by an atom or group of atoms. • An atom or group of atoms in an organic molecule that always behaves in the same way is called a functional group. • Adding a functional group changes the chemical & physical properties in specific ways, depending on ...
Dehydration of alcohols
... It is another object of this invention to dehydrate an 45 standard conditions) per kilogram of alcohol is useful in the practice of this invention. alcohol to produce an ole?n. It is a further object of this This invention is especially well suited for continuous invention to produce ole?ns from an ...
... It is another object of this invention to dehydrate an 45 standard conditions) per kilogram of alcohol is useful in the practice of this invention. alcohol to produce an ole?n. It is a further object of this This invention is especially well suited for continuous invention to produce ole?ns from an ...
Chapter 22 HEIN
... 3. Combine the two names from Steps 1 and 2, giving the alkoxy name and its position on the longest carbon chain first, to form the ...
... 3. Combine the two names from Steps 1 and 2, giving the alkoxy name and its position on the longest carbon chain first, to form the ...
Chapter 1
... Predict the Product of Dehydration • What are the major and minor products when 3methyl-2-butanol is dehydrated? • Zaitsev’s rule states that in an elimination reaction the alkene with the greatest number of alkyl groups on the double bonded carbon is the major product of the reaction ...
... Predict the Product of Dehydration • What are the major and minor products when 3methyl-2-butanol is dehydrated? • Zaitsev’s rule states that in an elimination reaction the alkene with the greatest number of alkyl groups on the double bonded carbon is the major product of the reaction ...
Chapter 1 - chemistry
... The number of carbon atoms attached to the alkyl group determines whether the carbon is primary, secondary, or tertiary. Halocarbons in which a halogen is attached to a carbon of an arene (aromatic hydrocarbon) ring are called aryl halides. The attractions between halocarbon molecules are primarily ...
... The number of carbon atoms attached to the alkyl group determines whether the carbon is primary, secondary, or tertiary. Halocarbons in which a halogen is attached to a carbon of an arene (aromatic hydrocarbon) ring are called aryl halides. The attractions between halocarbon molecules are primarily ...
6-organic - fixurscore
... Reaction: primary alcoholcarboxylic acid Reagent: potassium dichromate(VI) solution and dilute sulphuric acid Conditions: use an excess of dichromate, and heat under reflux: (distill off product after the reaction ...
... Reaction: primary alcoholcarboxylic acid Reagent: potassium dichromate(VI) solution and dilute sulphuric acid Conditions: use an excess of dichromate, and heat under reflux: (distill off product after the reaction ...
Organometallic Chemistry
... • Because of the double bond geometry, coordination of the (E)crotylboronic ester places the Me preferentially equatorial, whereas coordination of the (Z)-crotylboronic ester places the Me axial, as illustrated in the cyclohexane chair-form transition state conformations A and B, respectively. In bo ...
... • Because of the double bond geometry, coordination of the (E)crotylboronic ester places the Me preferentially equatorial, whereas coordination of the (Z)-crotylboronic ester places the Me axial, as illustrated in the cyclohexane chair-form transition state conformations A and B, respectively. In bo ...
Alcohols, Penols, and Thiols
... • Substitution rxn gives alkyl halide • Rate and mechanism depend on classifcation • 3° react the fastest • t-butyl alcohol reacts with HCl at RT to make t-butyl ...
... • Substitution rxn gives alkyl halide • Rate and mechanism depend on classifcation • 3° react the fastest • t-butyl alcohol reacts with HCl at RT to make t-butyl ...
Lex 4.1 Alcohols Thiols Ethers
... • Many side effects • Not in use anymore history of ether anesthesia ...
... • Many side effects • Not in use anymore history of ether anesthesia ...
Ethers, Sulfides, Epoxides
... shown next. This cation can now react with an alcohol to yield an acetal. The alcohol becomes part of an acetal and is protected. ...
... shown next. This cation can now react with an alcohol to yield an acetal. The alcohol becomes part of an acetal and is protected. ...
DCC-promoted peptide coupling
... N,N'-Dicyclohexylcarbodiimide is an organic compound with the chemical formula C13H22N2 whose primary use is to couple amino acids during artificial peptide synthesis. Under standard conditions, it exists in the form of white crystals with a heavy, sweet odor. The low melting point of this material ...
... N,N'-Dicyclohexylcarbodiimide is an organic compound with the chemical formula C13H22N2 whose primary use is to couple amino acids during artificial peptide synthesis. Under standard conditions, it exists in the form of white crystals with a heavy, sweet odor. The low melting point of this material ...
Acidity of Alcohols
... The acidity increases as the negative charge at the OH decreases (delocalized): a) phenols are more acidic than Alcohols due to resonance effect (delocalization of the negative charge) ...
... The acidity increases as the negative charge at the OH decreases (delocalized): a) phenols are more acidic than Alcohols due to resonance effect (delocalization of the negative charge) ...
Background Information
... When condensation products (β-hydroxycarbonyl compounds) undergo E2 elimination, the resulting product is referred to as an α,β-unsaturated carbonyl. In the case of the dibenzalacetone reaction, the product is referred to as an α,β-unsaturated ketone. These products are very stable (due to resonance ...
... When condensation products (β-hydroxycarbonyl compounds) undergo E2 elimination, the resulting product is referred to as an α,β-unsaturated carbonyl. In the case of the dibenzalacetone reaction, the product is referred to as an α,β-unsaturated ketone. These products are very stable (due to resonance ...
Nuggets of Knowledge for Chapter 12 – Alcohols
... o step 1: nucleophilic attack of one of the H’s attached to the B or Al with its electrons to the carbon of the C=O, pushing one pair of electrons onto the oxygen and forming an alkoxide. (This could be called attack-push up.) o step 2: the alkoxide takes a hydrogen, forming the alcohol. In the case ...
... o step 1: nucleophilic attack of one of the H’s attached to the B or Al with its electrons to the carbon of the C=O, pushing one pair of electrons onto the oxygen and forming an alkoxide. (This could be called attack-push up.) o step 2: the alkoxide takes a hydrogen, forming the alcohol. In the case ...
Kinetic resolution

In organic chemistry, kinetic resolution is a means of differentiating two enantiomers in a racemic mixture. In kinetic resolution, two enantiomers react with different reaction rates in a chemical reaction with a chiral catalyst or reagent, resulting in an enantioenriched sample of the less reactive enantiomer. As opposed to chiral resolution, kinetic resolution does not rely on different physical properties of diastereomeric products, but rather on the different chemical properties of the racemic starting materials. This enantiomeric excess (ee) of the unreacted starting material continually rises as more product is formed, reaching 100% just before full completion of the reaction. Kinetic resolution relies upon differences in reactivity between enantiomers or enantiomeric complexes. Kinetic resolution is a concept in organic chemistry and can be used for the preparation of chiral molecules in organic synthesis. Kinetic resolution reactions utilizing purely synthetic reagents and catalysts are much less common than the use of enzymatic kinetic resolution in application towards organic synthesis, although a number of useful synthetic techniques have been developed in the past 30 years.