(1) and New York University (2)
... We intend to use these ligands to further develop circularly polarized fluorescence excitation (CPE), which is based on fluorescence-detected circular dichroism, which gives better contrast and eliminates many spectral interferences. ...
... We intend to use these ligands to further develop circularly polarized fluorescence excitation (CPE), which is based on fluorescence-detected circular dichroism, which gives better contrast and eliminates many spectral interferences. ...
101. Alcohols as alkylating agents in heteroarene C H functionalization
... and our recent work on the development of a photoredox-catalysed Minisci reaction18, we questioned whether it would be possible to generate alkyl radicals from alcohols and use them as alkylating agents in a heteroaromatic C–H functionalization reaction (Fig. 1c). While there are a few early reports ...
... and our recent work on the development of a photoredox-catalysed Minisci reaction18, we questioned whether it would be possible to generate alkyl radicals from alcohols and use them as alkylating agents in a heteroaromatic C–H functionalization reaction (Fig. 1c). While there are a few early reports ...
Stereochemistry - Kantipur Engineering College
... For example, if we want to separate the enantiomers of 2-hydroxylpropionic acid, we add an enantiomerically pure (R)-2-phenyl-ethylamine as a resolving agent. The two enantiomers interact with (R)-2-phenyl-ethylamine to form two distinct salt species that are diastereomers of each other. The diaster ...
... For example, if we want to separate the enantiomers of 2-hydroxylpropionic acid, we add an enantiomerically pure (R)-2-phenyl-ethylamine as a resolving agent. The two enantiomers interact with (R)-2-phenyl-ethylamine to form two distinct salt species that are diastereomers of each other. The diaster ...
alcohols ws 1 - Chesterhouse School
... (d) Lactic acid is chiral. Draw displayed formulae of the two optical isomers of lactic acid clearly showing their three-dimensional structures. Indicate with an asterisk (*) the chiral carbon atom in each. ...
... (d) Lactic acid is chiral. Draw displayed formulae of the two optical isomers of lactic acid clearly showing their three-dimensional structures. Indicate with an asterisk (*) the chiral carbon atom in each. ...
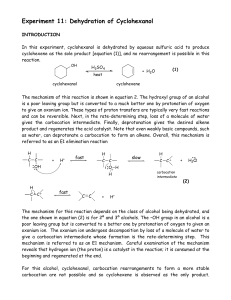
Dehydration of Cyclohexanol
... and treated with calcium chloride, CaCl2, to remove traces of moisture that are ...
... and treated with calcium chloride, CaCl2, to remove traces of moisture that are ...
Oxidation Reactions
... Directed epoxidation reactions, as their name implies are reactions in which the reagent containing the oxygen that is to be transferred to the substrate is tethered to the reacting substrate through a non-covalent interaction (e.g. H-bond or metal-ligand interaction). Typical substrates are allylic ...
... Directed epoxidation reactions, as their name implies are reactions in which the reagent containing the oxygen that is to be transferred to the substrate is tethered to the reacting substrate through a non-covalent interaction (e.g. H-bond or metal-ligand interaction). Typical substrates are allylic ...
Alcohols, Ethers, Aldehydes, and Ketones
... –OH and an –OR bound to the same carbon. NOTE: An oxygen in a ring structure is considered part of an –OR group. ...
... –OH and an –OR bound to the same carbon. NOTE: An oxygen in a ring structure is considered part of an –OR group. ...
Organic Chemistry II
... Nomenclature of Alkenes Number the C chain from the end that brings you to the double bond sooner, then use the alkane naming rules and -ene. ...
... Nomenclature of Alkenes Number the C chain from the end that brings you to the double bond sooner, then use the alkane naming rules and -ene. ...
16.2: Structure and Bonding in Ethers and Epoxides
... The sulfur atom of sulfides is much more nucleophilic than the oxygen atom of ethers, and will react with alkyl halides to give stable sulfonium salts. ...
... The sulfur atom of sulfides is much more nucleophilic than the oxygen atom of ethers, and will react with alkyl halides to give stable sulfonium salts. ...
8.1 Alcohols, Phenols, and Ethers
... Ethers contain an oxygen atom bound to two alkyl groups, each of which may be aliphatic or aromatic. Ethers are distinguished from other organic compounds because they lack a continuous chain of carbons. This is the first time we have encountered an organic compound containing a heteroatom (non-carb ...
... Ethers contain an oxygen atom bound to two alkyl groups, each of which may be aliphatic or aromatic. Ethers are distinguished from other organic compounds because they lack a continuous chain of carbons. This is the first time we have encountered an organic compound containing a heteroatom (non-carb ...
Esters are reduced by hydride reagents to give alcohols or aldehydes.
... Esters form enolates that can be alkylated. Treatment of esters with a strong base at low temperatures produces ester enolates (acidic -hydrogens). These enolates react like ketone enolates, undergoing alkylations. ...
... Esters form enolates that can be alkylated. Treatment of esters with a strong base at low temperatures produces ester enolates (acidic -hydrogens). These enolates react like ketone enolates, undergoing alkylations. ...
- Iranian Journal of Science and Technology (Sciences)
... in N-(diphenylphosphino) triethylammonium ptoluenesulfonate (IL-6) to afford the desired products. The optimized stoichiometric ratio of NBS/RCO2H/ArOH for the conversion of phenol to phenyl benzoate was found to be 1.0/1.2/1.0. We thereafter used the optimized conditions for the synthesis of phenol ...
... in N-(diphenylphosphino) triethylammonium ptoluenesulfonate (IL-6) to afford the desired products. The optimized stoichiometric ratio of NBS/RCO2H/ArOH for the conversion of phenol to phenyl benzoate was found to be 1.0/1.2/1.0. We thereafter used the optimized conditions for the synthesis of phenol ...
Microsoft Word
... Thesis entitled "Asymmetric Dihydroxylation and Wittig-Horner approach to the Synthesis of Bioactive Molecules and Heterogeneous Catalysis for Organic Transformations" is divided into five chapters. Chapter 1: describes a brief introduction to the Sharpless Asymmetric dihydroxylation (SAD) and its a ...
... Thesis entitled "Asymmetric Dihydroxylation and Wittig-Horner approach to the Synthesis of Bioactive Molecules and Heterogeneous Catalysis for Organic Transformations" is divided into five chapters. Chapter 1: describes a brief introduction to the Sharpless Asymmetric dihydroxylation (SAD) and its a ...
INTRODUCTION - Open Access Repository of Indian Theses
... 3. A Mild and Highly Efficient Synthesis of 3-Pyrrolyl-Indolinones and Pyrrolyl-Indeno[1,2-b]Quinoxalines using BiCl3 as a Catalyst An efficient synthesis of 3-pyrrolyl-indolinones and pyrrolyl-indeno[1,2-b] quinoxalines is described by the reaction of 4-hydroxyproline with isatin or indeno[1,2b]qui ...
... 3. A Mild and Highly Efficient Synthesis of 3-Pyrrolyl-Indolinones and Pyrrolyl-Indeno[1,2-b]Quinoxalines using BiCl3 as a Catalyst An efficient synthesis of 3-pyrrolyl-indolinones and pyrrolyl-indeno[1,2-b] quinoxalines is described by the reaction of 4-hydroxyproline with isatin or indeno[1,2b]qui ...
Chapter 16: Ethers, Epoxides, and Sulfides
... In general, the C-O bonds of ethers have low reactivity. 16.3: Physical Properties of Ethers the O-H group of alcohols act as both an H-bond donor (Lewis acid) and H-bond acceptor (Lewis base). Ethers are only H-bond acceptors (Lewis base) 16.4: Crown Ethers (Please read) ...
... In general, the C-O bonds of ethers have low reactivity. 16.3: Physical Properties of Ethers the O-H group of alcohols act as both an H-bond donor (Lewis acid) and H-bond acceptor (Lewis base). Ethers are only H-bond acceptors (Lewis base) 16.4: Crown Ethers (Please read) ...
Alcohol and Ether
... Alcohols are organic compounds. They are mostly used as sweeteners and in making perfumes. Alcohols are valuable in the synthesis of other compounds. They are the most used to produce organic chemicals in industry. The two best-known of alcohols are ethanol and methanol (or methyl alcohol). ...
... Alcohols are organic compounds. They are mostly used as sweeteners and in making perfumes. Alcohols are valuable in the synthesis of other compounds. They are the most used to produce organic chemicals in industry. The two best-known of alcohols are ethanol and methanol (or methyl alcohol). ...
Mon Feb 15 lecture
... — this pathway avoids the intermediacy of a high-E 1° cation. (This is frequently observed in carbocation chemistry; we've already seen a similar concerted rearrangement and leaving group (water) departure in the reaction of some 1° alcohols with strong acid.) ...
... — this pathway avoids the intermediacy of a high-E 1° cation. (This is frequently observed in carbocation chemistry; we've already seen a similar concerted rearrangement and leaving group (water) departure in the reaction of some 1° alcohols with strong acid.) ...
Reactions of Alcohols
... The ZnCl2 coordinates to the hydroxyl oxygen, and this generates a far superior leaving group. Primary alcohols react in a similar fashion except the free cation is not generated, and the substitution is of S N2 ...
... The ZnCl2 coordinates to the hydroxyl oxygen, and this generates a far superior leaving group. Primary alcohols react in a similar fashion except the free cation is not generated, and the substitution is of S N2 ...
Chapter 11 Lecture Notes: Alcohols, Ethers, Aldehydes, and Ketones
... group and an -OH group that are bonded to the same carbon. Carbons that are bonded to both an -OR group and an -OH group are called hemiacetal carbons. Carbon number 1 in the ring structure shown meets this criterion. The OH that is bonded to carbon number 1 is obvious, but the OR may not be immedia ...
... group and an -OH group that are bonded to the same carbon. Carbons that are bonded to both an -OR group and an -OH group are called hemiacetal carbons. Carbon number 1 in the ring structure shown meets this criterion. The OH that is bonded to carbon number 1 is obvious, but the OR may not be immedia ...
Alcohols, Phenols, and Ethers
... Lower molecular weight alcohols are soluble in water. This is due to hydrogen bonding between hydroxy group and water. ...
... Lower molecular weight alcohols are soluble in water. This is due to hydrogen bonding between hydroxy group and water. ...
C6 Alcohols
... The table above shows the molecular and displayed formula of alcohols with one to five hydrocarbons (there are MANY more) – REMEMBER these! Only ethanol is made using fermentation, using very specific conditions: 1) If the temperature is too low, the enzymes in the yeast are inactive 2) If the tempe ...
... The table above shows the molecular and displayed formula of alcohols with one to five hydrocarbons (there are MANY more) – REMEMBER these! Only ethanol is made using fermentation, using very specific conditions: 1) If the temperature is too low, the enzymes in the yeast are inactive 2) If the tempe ...
Kinetic resolution

In organic chemistry, kinetic resolution is a means of differentiating two enantiomers in a racemic mixture. In kinetic resolution, two enantiomers react with different reaction rates in a chemical reaction with a chiral catalyst or reagent, resulting in an enantioenriched sample of the less reactive enantiomer. As opposed to chiral resolution, kinetic resolution does not rely on different physical properties of diastereomeric products, but rather on the different chemical properties of the racemic starting materials. This enantiomeric excess (ee) of the unreacted starting material continually rises as more product is formed, reaching 100% just before full completion of the reaction. Kinetic resolution relies upon differences in reactivity between enantiomers or enantiomeric complexes. Kinetic resolution is a concept in organic chemistry and can be used for the preparation of chiral molecules in organic synthesis. Kinetic resolution reactions utilizing purely synthetic reagents and catalysts are much less common than the use of enzymatic kinetic resolution in application towards organic synthesis, although a number of useful synthetic techniques have been developed in the past 30 years.