Genes & Chromosomes
... The chromosome theory of heredity states: That genes are located on the chromosome and each gene occupies a specific place on that chromosome. Each chromosome contains just one allele for each of its genes. ...
... The chromosome theory of heredity states: That genes are located on the chromosome and each gene occupies a specific place on that chromosome. Each chromosome contains just one allele for each of its genes. ...
mutations - bYTEBoss
... Changes in number and structure of entire chromosomes When DNA or Chromosomes are changed, the proteins they make may alter the cells and their functions ...
... Changes in number and structure of entire chromosomes When DNA or Chromosomes are changed, the proteins they make may alter the cells and their functions ...
Changes in DNA can produce Variation
... Not smoking can prevent emphysema and many types of cancer ...
... Not smoking can prevent emphysema and many types of cancer ...
Ch. 7 Gene Expresion part 2
... Mutations are permanent changes in the nucleotide sequence of DNA, which may alter a gene product A mutation that changes a gene’s product may have harmful effects • Example: Mutations that affect the proteins in hemoglobin reduce blood’s ability to carry oxygen ...
... Mutations are permanent changes in the nucleotide sequence of DNA, which may alter a gene product A mutation that changes a gene’s product may have harmful effects • Example: Mutations that affect the proteins in hemoglobin reduce blood’s ability to carry oxygen ...
17 - Genetic Mutation
... chromosomes or parts of chromosomes can be lost, changed, or mixed up. Down syndrome and Turner syndrome are both examples of the effects of chromosome dysfunction. Single Gene Disorders Single gene disorders are caused by a single gene losing or altering part of its structure by mutation. An exampl ...
... chromosomes or parts of chromosomes can be lost, changed, or mixed up. Down syndrome and Turner syndrome are both examples of the effects of chromosome dysfunction. Single Gene Disorders Single gene disorders are caused by a single gene losing or altering part of its structure by mutation. An exampl ...
Chapter 1 Study Questions
... antiparallel, 5’ end, 3’ end, complementary, major groove, minor groove. 9. How do the following terms pertain to DNA replication: semi-conservative model, Okazaki fragments, leading strand, lagging strand? 10. What are the roles of the following proteins in DNA replication: Topoisomerase, helicase, ...
... antiparallel, 5’ end, 3’ end, complementary, major groove, minor groove. 9. How do the following terms pertain to DNA replication: semi-conservative model, Okazaki fragments, leading strand, lagging strand? 10. What are the roles of the following proteins in DNA replication: Topoisomerase, helicase, ...
Topic 4: Genetics - Peoria Public Schools
... differences in the DNA sequence. 4. Different alleles for the same gene all occupy the same locus on a chromosome. 5. Genome refers to the whole or complete genetic information of an organism. 6. When genes change in an organism, a mutation is said to have occurred. 7. A mutation involves a base cha ...
... differences in the DNA sequence. 4. Different alleles for the same gene all occupy the same locus on a chromosome. 5. Genome refers to the whole or complete genetic information of an organism. 6. When genes change in an organism, a mutation is said to have occurred. 7. A mutation involves a base cha ...
Complete DNA Function Vocab with definitions
... RNA, in which it forms base pairs with adenine. One of a class of RNA molecules that transport amino acids to ribosomes for incorporation into a polypeptide undergoing synthesis. The RNA that is a permanent structural part of a ribosome. ...
... RNA, in which it forms base pairs with adenine. One of a class of RNA molecules that transport amino acids to ribosomes for incorporation into a polypeptide undergoing synthesis. The RNA that is a permanent structural part of a ribosome. ...
Virtual DNA Lab
... 4. Examine the picture. Which type of bonds hold the DNA bases together? ____________________ 5. What molecule do genes create? ____________________________________________________ What is a Gene? 6. Why are genes called the instruction manual for our body? _______________________________ __________ ...
... 4. Examine the picture. Which type of bonds hold the DNA bases together? ____________________ 5. What molecule do genes create? ____________________________________________________ What is a Gene? 6. Why are genes called the instruction manual for our body? _______________________________ __________ ...
www.endogenet.org Molecular Genetics Service Profile GHRHR
... Expression of GHRHR is localised to the pituitary gland, hypothalamus, renal medulla, placenta and other tissues and is up-regulated by the PIT1 protein. GHRHR is involved in anterior pituitary cell development and differentiation, and may play a role in proliferation of the somatotroph cell lineage ...
... Expression of GHRHR is localised to the pituitary gland, hypothalamus, renal medulla, placenta and other tissues and is up-regulated by the PIT1 protein. GHRHR is involved in anterior pituitary cell development and differentiation, and may play a role in proliferation of the somatotroph cell lineage ...
Nuclear Genes
... Can arise through exposure to mutagenic agents, but the vast majority occur spontaneously through errors in DNA replication and repair. Somatic mutations & Germ line mutation It is estimated that each individual carries up to six lethal or semilethal recessive mutant alleles ...
... Can arise through exposure to mutagenic agents, but the vast majority occur spontaneously through errors in DNA replication and repair. Somatic mutations & Germ line mutation It is estimated that each individual carries up to six lethal or semilethal recessive mutant alleles ...
MULTIPLE CHOICE
... _____ The fluctuation test of Luria and Delbruck (studying resistance to bacteriophge T1 infection) established that A. T1 phage was a mutagen. B. Mutations could arise prior to the time they were selected C. The mutation rate varies greatly from experiment to experiment. D. In E. coli the number of ...
... _____ The fluctuation test of Luria and Delbruck (studying resistance to bacteriophge T1 infection) established that A. T1 phage was a mutagen. B. Mutations could arise prior to the time they were selected C. The mutation rate varies greatly from experiment to experiment. D. In E. coli the number of ...
Lecture 3: Mutations
... m=mutant, Df=gene deletion, Dp=gene duplication. Phenotypes are compared with: > phenotype is more severe than. Amorphic describes a mutation that causes complete loss of gene function. Amorph is sometimes used interchangeably with "genetic null". An amorphic mutation might cause complete loss of pr ...
... m=mutant, Df=gene deletion, Dp=gene duplication. Phenotypes are compared with: > phenotype is more severe than. Amorphic describes a mutation that causes complete loss of gene function. Amorph is sometimes used interchangeably with "genetic null". An amorphic mutation might cause complete loss of pr ...
Document
... • A Gene is the fundamental physical and functional unit of heredity. A gene is an ordered sequence of nucleotides located in a particular position on a particular chromosome that encodes a specific functional product (i.e., a protein or RNA molecule). • A Genome is all the genetic material (DNA) in ...
... • A Gene is the fundamental physical and functional unit of heredity. A gene is an ordered sequence of nucleotides located in a particular position on a particular chromosome that encodes a specific functional product (i.e., a protein or RNA molecule). • A Genome is all the genetic material (DNA) in ...
Lesson 12 Mutations
... In an insertion, one or more nitrogenous bases are inserted during the copying ...
... In an insertion, one or more nitrogenous bases are inserted during the copying ...
Genetics
... *Since chromosomes come in pairs (GENE PAIR), there exist two open slots for each gene. (One from each parent) *Sometimes there are two or more forms of the gene, called alleles, for a particular trait. Often there is a dominant and a recessive gene like the tall (TT or Tt) and short (tt) pea plants ...
... *Since chromosomes come in pairs (GENE PAIR), there exist two open slots for each gene. (One from each parent) *Sometimes there are two or more forms of the gene, called alleles, for a particular trait. Often there is a dominant and a recessive gene like the tall (TT or Tt) and short (tt) pea plants ...
Ch 17 Evolution of Populations
... Sometimes crossing-over involves an unequal swapping of DNA so that one chromosome in the pair gets extra DNA. ...
... Sometimes crossing-over involves an unequal swapping of DNA so that one chromosome in the pair gets extra DNA. ...
17.4_Molecular_Evolution
... Sometimes crossing-over involves an unequal swapping of DNA so that one chromosome in the pair gets extra DNA. ...
... Sometimes crossing-over involves an unequal swapping of DNA so that one chromosome in the pair gets extra DNA. ...
ppt3 - NMSU Astronomy
... They could easily travel from one plant to another in the solar system and possibly even persist between the stars (we do not know how long they can survive in space, but we think they can persist at least for several centuries). ...
... They could easily travel from one plant to another in the solar system and possibly even persist between the stars (we do not know how long they can survive in space, but we think they can persist at least for several centuries). ...
Genes Chromosomes and DNA
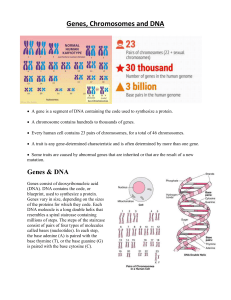
... A chromosome contains hundreds to thousands of genes. Every human cell contains 23 pairs of chromosomes, for a total of 46 chromosomes. A trait is any gene-determined characteristic and is often determined by more than one gene. Some traits are caused by abnormal genes that are inherited or ...
... A chromosome contains hundreds to thousands of genes. Every human cell contains 23 pairs of chromosomes, for a total of 46 chromosomes. A trait is any gene-determined characteristic and is often determined by more than one gene. Some traits are caused by abnormal genes that are inherited or ...
24. DNA testing
... Almost all mutations are single nt changes, 65% of mutations are deletions of 1 or although most common is a 3 nt deletion more exons 5% duplications 30% nonsense or splice site mutations New mutations are very rare New mutations are very frequent Mosaicism not a problem Mosaicism is common; especia ...
... Almost all mutations are single nt changes, 65% of mutations are deletions of 1 or although most common is a 3 nt deletion more exons 5% duplications 30% nonsense or splice site mutations New mutations are very rare New mutations are very frequent Mosaicism not a problem Mosaicism is common; especia ...
BIO 220 Chapter 8 lecture outline Vocabulary Central dogma of
... Mutations Types Silent Base substitution (point mutation) Missense Nonsense Frameshift Mugatens Nitrous acid Nucleoside analogs Aflatoxin Radiation Identification of mutants Positive and negative selection Ames test Horizonal gene transfer Transformation ...
... Mutations Types Silent Base substitution (point mutation) Missense Nonsense Frameshift Mugatens Nitrous acid Nucleoside analogs Aflatoxin Radiation Identification of mutants Positive and negative selection Ames test Horizonal gene transfer Transformation ...
Point mutation

A point mutation, or single base modification, is a type of mutation that causes a single nucleotide base change, insertion, or deletion of the genetic material, DNA or RNA. The term frameshift mutation indicates the addition or deletion of a base pair. A point mutant is an individual that is affected by a point mutation.Repeat induced point mutations are recurring point mutations, discussed below.