Genetic Engineering Short Notes
... 1. Genetic engineering- remaking genes for practical purposes 2. Recombinant DNA- DNA made from two or more different organisms 3. Restriction enzyme- enzymes that recognize short specific DNA sequences and that cut the DNA there 4. Plasmid- small, circular DNA molecules that can replicate independa ...
... 1. Genetic engineering- remaking genes for practical purposes 2. Recombinant DNA- DNA made from two or more different organisms 3. Restriction enzyme- enzymes that recognize short specific DNA sequences and that cut the DNA there 4. Plasmid- small, circular DNA molecules that can replicate independa ...
Assignment 1
... This is the only ORF that shows no in-frame stop codon in the sequence given. And these are three amino acids following the first Met amino acid for this ORF. Q10. If the third base (U) of the resulting mRNA is mutated to G, then what would be the effect of the mutation on the polypeptide being synt ...
... This is the only ORF that shows no in-frame stop codon in the sequence given. And these are three amino acids following the first Met amino acid for this ORF. Q10. If the third base (U) of the resulting mRNA is mutated to G, then what would be the effect of the mutation on the polypeptide being synt ...
Vocabulary to Know
... c. Does this person have a genetic disorder? If so, which one. 6. How are kayotypes used by genetic counselors? 7. Siblings are given up for adoption at birth and raised separately from one another for twenty-five years. When they meet for the first time, they realize that although they share the so ...
... c. Does this person have a genetic disorder? If so, which one. 6. How are kayotypes used by genetic counselors? 7. Siblings are given up for adoption at birth and raised separately from one another for twenty-five years. When they meet for the first time, they realize that although they share the so ...
CAUSE - Cloudfront.net
... with this disorder can’t stop bleeding when bleed to death from minor injured; can ________________ cuts or suffer internal bleeding from bruises or bumps. ...
... with this disorder can’t stop bleeding when bleed to death from minor injured; can ________________ cuts or suffer internal bleeding from bruises or bumps. ...
Lecture 11 Biol302 Spring 2012
... Transitions—purine for purine and pyrimidine for pyrimidine substitutions, Transversions—purine for pyrimidine and pyrimidine for purine substitutions, and Frameshift mutations—additions or deletions of one or two nucleotide pairs, which alter the reading frame of the gene distal to the site of the ...
... Transitions—purine for purine and pyrimidine for pyrimidine substitutions, Transversions—purine for pyrimidine and pyrimidine for purine substitutions, and Frameshift mutations—additions or deletions of one or two nucleotide pairs, which alter the reading frame of the gene distal to the site of the ...
Mutations
... “reading frame” of a codon depends on the starting point insertions or deletions may shift the reading frame which may cause the remaining sequence of nucleotides to be “read” as different codons ...
... “reading frame” of a codon depends on the starting point insertions or deletions may shift the reading frame which may cause the remaining sequence of nucleotides to be “read” as different codons ...
Lecture 4
... converted into a string of amino acids during protein synthesis, point mutations often manifest as functional changes in the final protein product. Thus, there exist functional groupings for point mutations. These groupings are divided into: Silent mutations result in a new codon (a triplet nucleoti ...
... converted into a string of amino acids during protein synthesis, point mutations often manifest as functional changes in the final protein product. Thus, there exist functional groupings for point mutations. These groupings are divided into: Silent mutations result in a new codon (a triplet nucleoti ...
Meiosis
... 1. Deletion – gene that codes for a trait is missing Ex. Lactose intolerance, sickle cell anemia ...
... 1. Deletion – gene that codes for a trait is missing Ex. Lactose intolerance, sickle cell anemia ...
Chromosomes and Mutations Chromosomes and
... What are the results of chromosomal mutations? • If it occurs in gametes (sex) cells: • Can cause birth defects, miscarriage, or no change • Few are passed on to next generation because zygote usually dies ...
... What are the results of chromosomal mutations? • If it occurs in gametes (sex) cells: • Can cause birth defects, miscarriage, or no change • Few are passed on to next generation because zygote usually dies ...
Proteins to Phenotype
... Mutations create "alleles" Alleles: Different forms of a gene at same location on chromosome. Polymorphism: Existence of many common variants (alleles) of a gene in a population. Morph = allele = variant Each organism normally has two alleles for each gene! High number of different alleles leads to ...
... Mutations create "alleles" Alleles: Different forms of a gene at same location on chromosome. Polymorphism: Existence of many common variants (alleles) of a gene in a population. Morph = allele = variant Each organism normally has two alleles for each gene! High number of different alleles leads to ...
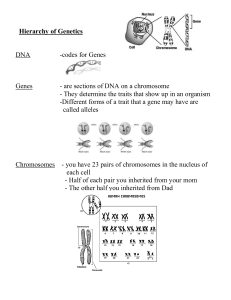
Unit 6: Genetics
... Describe the role of ribosomes, ER, Golgi apparatus, and the nucleus in the production of specific types of proteins. ◦ Ribosomes: A cellular structure composed of RNA and proteins that is the site of protein synthesis in eukaryotic and prokaryotic cells. ◦ Endoplasmic reticulum: An organelle, conta ...
... Describe the role of ribosomes, ER, Golgi apparatus, and the nucleus in the production of specific types of proteins. ◦ Ribosomes: A cellular structure composed of RNA and proteins that is the site of protein synthesis in eukaryotic and prokaryotic cells. ◦ Endoplasmic reticulum: An organelle, conta ...
Mutations, Karyotyping, Pedigrees
... Look at your codon chart or codon wheel. What would happen if the following Point Mutation Occurred: CCACCC GGAGGU UCUUCA Amino acid meaning was not altered Silent mutation ...
... Look at your codon chart or codon wheel. What would happen if the following Point Mutation Occurred: CCACCC GGAGGU UCUUCA Amino acid meaning was not altered Silent mutation ...
AP BIO Unit 6 Review Ch. 14,15,16,18,19 Westbrook Gene
... What must happen for transcription to be initiated? (many steps) Eukaryotes have regulatory proteins which have two distinct binding domains that allows for “control from a distance.” What are those binding domains called? What is the sequence of three tRNA nucleotides that is complementary to and b ...
... What must happen for transcription to be initiated? (many steps) Eukaryotes have regulatory proteins which have two distinct binding domains that allows for “control from a distance.” What are those binding domains called? What is the sequence of three tRNA nucleotides that is complementary to and b ...
3rd Quarter Biology Assessment
... a. The effects of mutations on genes vary widely. Some have little or no effect; and some produce beneficial variations. Some negatively disrupt gene function. b. Whether a mutation is negative or beneficial is not dependent on how its DNA changes relative to the organism’s situation. c. Mutations a ...
... a. The effects of mutations on genes vary widely. Some have little or no effect; and some produce beneficial variations. Some negatively disrupt gene function. b. Whether a mutation is negative or beneficial is not dependent on how its DNA changes relative to the organism’s situation. c. Mutations a ...
UTACCEL 2010
... By understanding the function of a gene in one organism, scientists can get an idea of what function that gene may perform in a more complex organism such as humans. The knowledge gained can then be applied to various fields such as medicine, biological engineering and forensics. ...
... By understanding the function of a gene in one organism, scientists can get an idea of what function that gene may perform in a more complex organism such as humans. The knowledge gained can then be applied to various fields such as medicine, biological engineering and forensics. ...
Evolution and Genetic Engineering Keystone Vocabulary
... population by a small number of indivuals from a larger population. 14. The addition (insertion mutation) or removal (deletion mutation) of one or more nucleotides that is not indivisible by three, therefore resulting in a completely different amino acid sequence than what would be normal. The earli ...
... population by a small number of indivuals from a larger population. 14. The addition (insertion mutation) or removal (deletion mutation) of one or more nucleotides that is not indivisible by three, therefore resulting in a completely different amino acid sequence than what would be normal. The earli ...
Genes and proteins in Health and Disease
... within genes in the non-coding regions (introns) just next to the coding regions (exons). Before mRNA leaves the nucleus, the introns are removed and the exons are joined together (splicing). A mutation that alters the specific sequence denoting the site at which the splicing of an intron takes plac ...
... within genes in the non-coding regions (introns) just next to the coding regions (exons). Before mRNA leaves the nucleus, the introns are removed and the exons are joined together (splicing). A mutation that alters the specific sequence denoting the site at which the splicing of an intron takes plac ...
This is Option 1
... Option 1 Question 1. (11 pts) Huntington disease (HD) is caused by a variable expressed but fully penetrant autosomal dominant mutation that causes late onset (post-reproductive) neurodegeneration. The mutations that cause HD involve an expansion of a triplet repeat located in the coding region of ...
... Option 1 Question 1. (11 pts) Huntington disease (HD) is caused by a variable expressed but fully penetrant autosomal dominant mutation that causes late onset (post-reproductive) neurodegeneration. The mutations that cause HD involve an expansion of a triplet repeat located in the coding region of ...
doc
... using pea plants, discovering that parents pass on specific traits to offspring by ways of “factors” as Mendel called them Heredity — the passing of traits from parents to offspring Heterozygous — an individual having two alleles for a trait that are different Hitchhiker’s Thumb — a recessive trait ...
... using pea plants, discovering that parents pass on specific traits to offspring by ways of “factors” as Mendel called them Heredity — the passing of traits from parents to offspring Heterozygous — an individual having two alleles for a trait that are different Hitchhiker’s Thumb — a recessive trait ...
Mutations - Northeast High School
... component. One small DNA alteration in a critical gene can lead to a severe inherited disease, predispose us to chronic diseases, even render us more vulnerable to an infectious disease, and sometimes result in beneficial new genes and functions. These small DNA alterations are known as mutations. M ...
... component. One small DNA alteration in a critical gene can lead to a severe inherited disease, predispose us to chronic diseases, even render us more vulnerable to an infectious disease, and sometimes result in beneficial new genes and functions. These small DNA alterations are known as mutations. M ...
Point mutation

A point mutation, or single base modification, is a type of mutation that causes a single nucleotide base change, insertion, or deletion of the genetic material, DNA or RNA. The term frameshift mutation indicates the addition or deletion of a base pair. A point mutant is an individual that is affected by a point mutation.Repeat induced point mutations are recurring point mutations, discussed below.